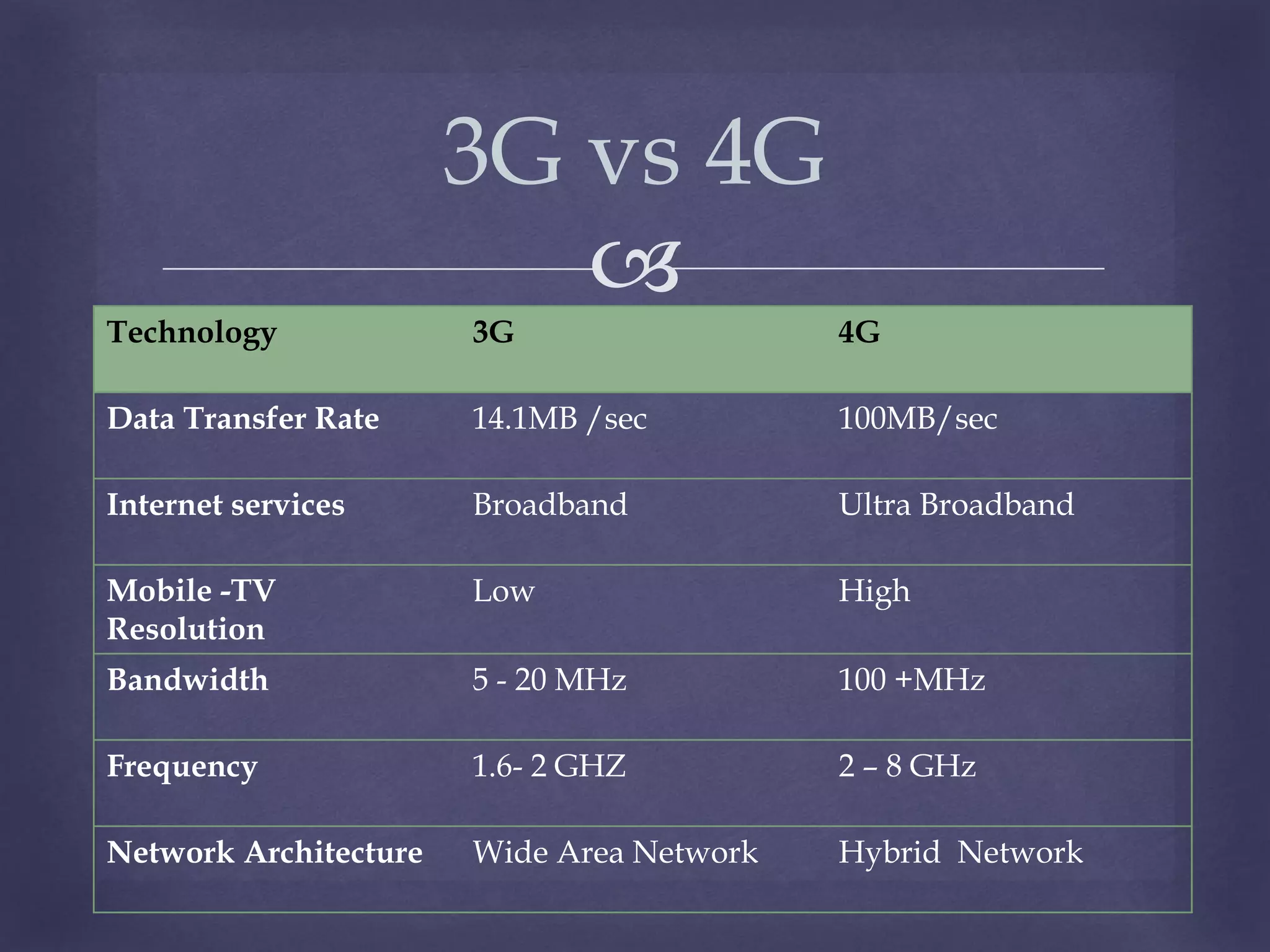
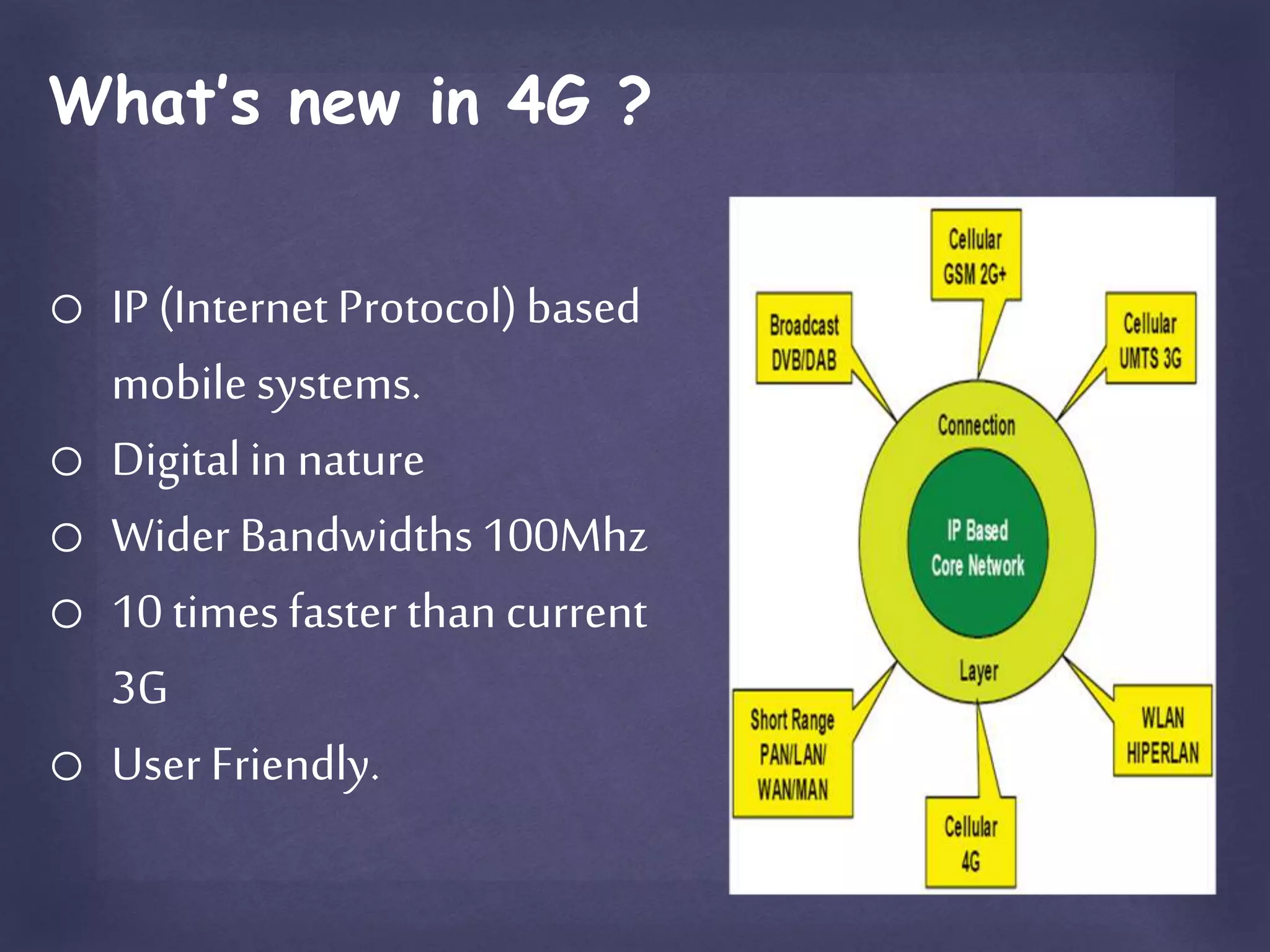
The document provides an overview of the evolution of mobile technology from 1G to 4G. It discusses the key differences between 3G and 4G such as data transfer rates and bandwidth. 4G provides ultra-broadband internet access at speeds up to 100 Mbps for high mobility using technologies like LTE. It allows for applications like video conferencing and location-based services through an IP-based mobile system with wider bandwidths and a digital, hybrid network architecture. In conclusion, 4G can be described as providing mobile multimedia access anytime, anywhere with global mobility support through an integrated, customized personal network.