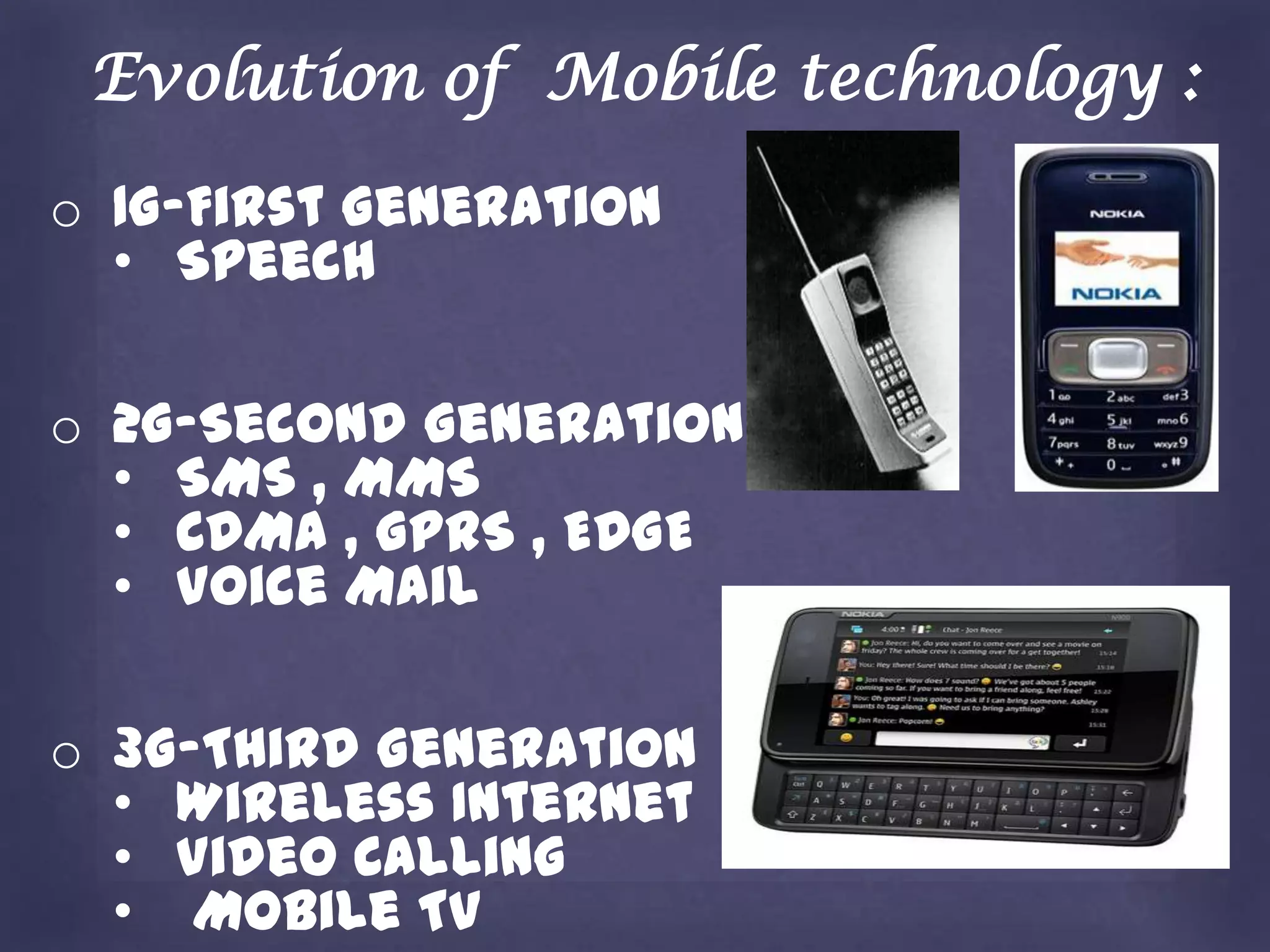
4G is the fourth generation of cellular communications that provides significantly faster data transfer speeds than 3G, up to 100 Mbps for high mobility and 1 Gbps for low mobility. It uses an all-IP packet switched network and utilizes technologies like LTE, WiMAX, OFDM, and software defined radios. 4G enables many new applications like virtual presence, navigation, telemedicine and provides advantages like high usability, support for multimedia, and higher bandwidth, but also has disadvantages like higher costs and more battery usage.