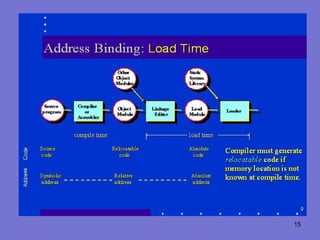
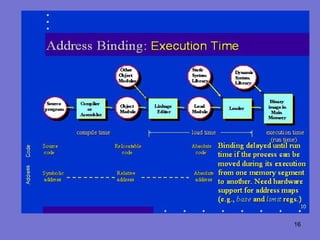
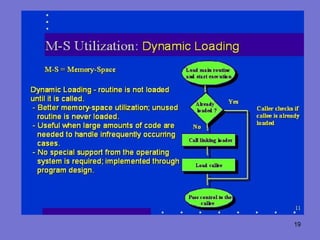
The document discusses storage management, address binding, and dynamic loading in operating systems. It explains that storage management involves allocating memory to multiple processes while preventing overlap. Address binding refers to mapping addresses between different spaces like symbolic, relocatable, and absolute as a program is compiled, loaded, and executed. Dynamic loading allows routines to be loaded only when called rather than all at once, improving memory utilization by loading unused routines only as needed.