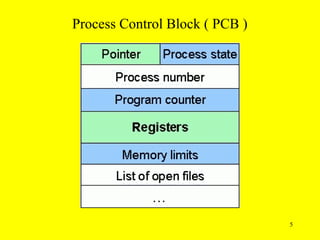
The document discusses process control blocks (PCBs) which represent processes in an operating system. A PCB contains various key information about a process including:
- Process state, number, and other scheduling information
- CPU register values
- Memory allocation details
- I/O device access permissions
- Accounting data on CPU and memory usage
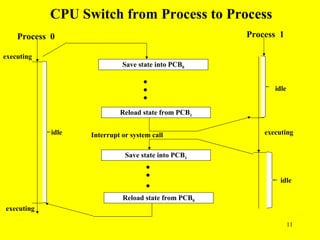
When the CPU switches from one process to another, it saves the current process's register values in its PCB and loads values from the next process's PCB. This allows processes to continue execution seamlessly across CPU time slices.