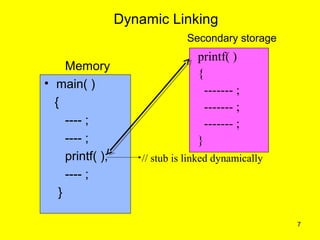
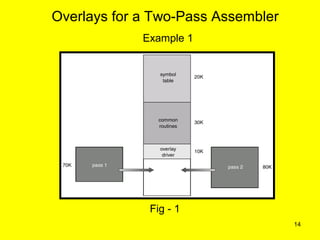
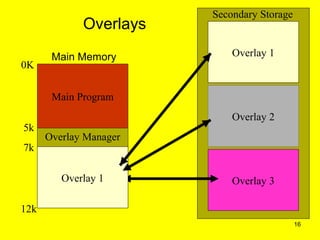
Dynamic linking and overlays are techniques for improving memory utilization in operating systems. Dynamic linking postpones linking of library routines until execution using stubs. This allows better memory usage and automatic use of new library versions. Overlays improve memory usage for large programs by loading only required parts into memory at a given time using an overlay manager. Both have advantages of improved memory usage but overlays require complex programming and are slower.