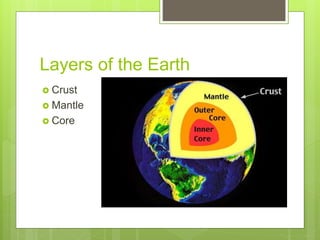
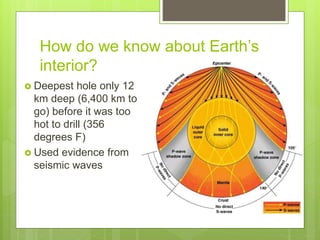
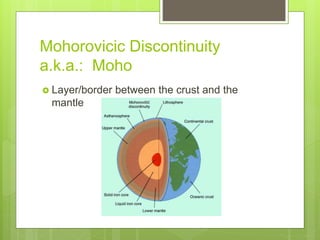
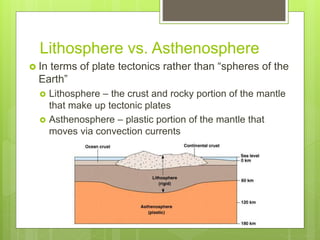
The document discusses the structure and composition of the Earth. It is made up of layers from the crust on the outside to the core at the center. The crust and upper mantle make up the lithosphere which rests on the asthenosphere. Below the mantle is the core, with an outer liquid layer and inner solid center. Seismic waves provide evidence about the interior layers since humans have only been able to drill down 12 km.