Embed presentation
Download to read offline




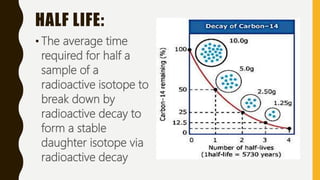



This document discusses absolute dating and radiometric dating. Absolute dating determines the numeric age of a geologic object by measuring the radioactive decay of isotopes with long half-lives. Radiometric dating compares the percentages of radioactive parent isotopes to stable daughter isotopes produced after half lives to calculate the age of a sample. Examples of practice problems show how to calculate the number of half lives needed for a sample amount to decay and determine half life from initial and final isotope amounts.







