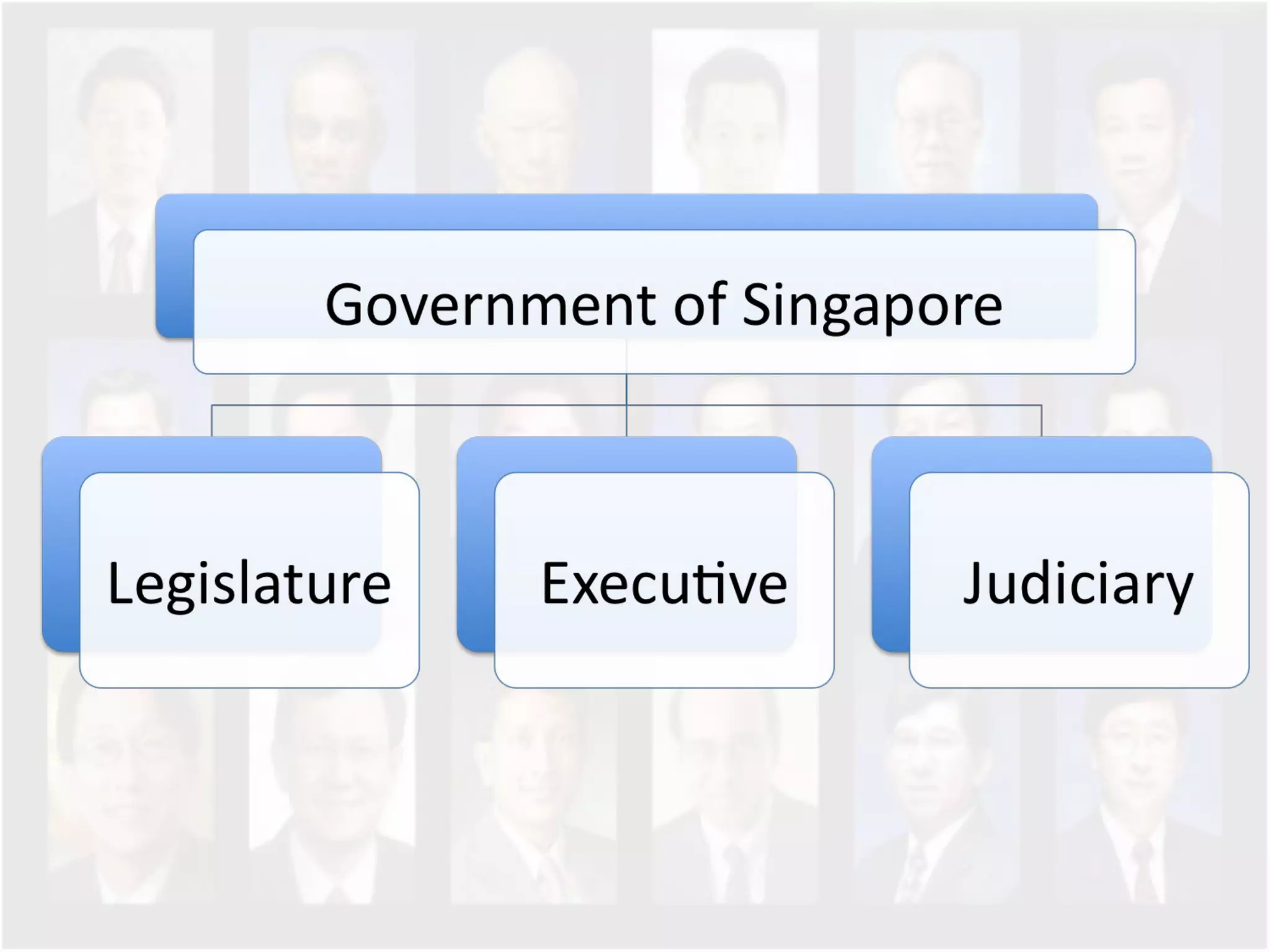
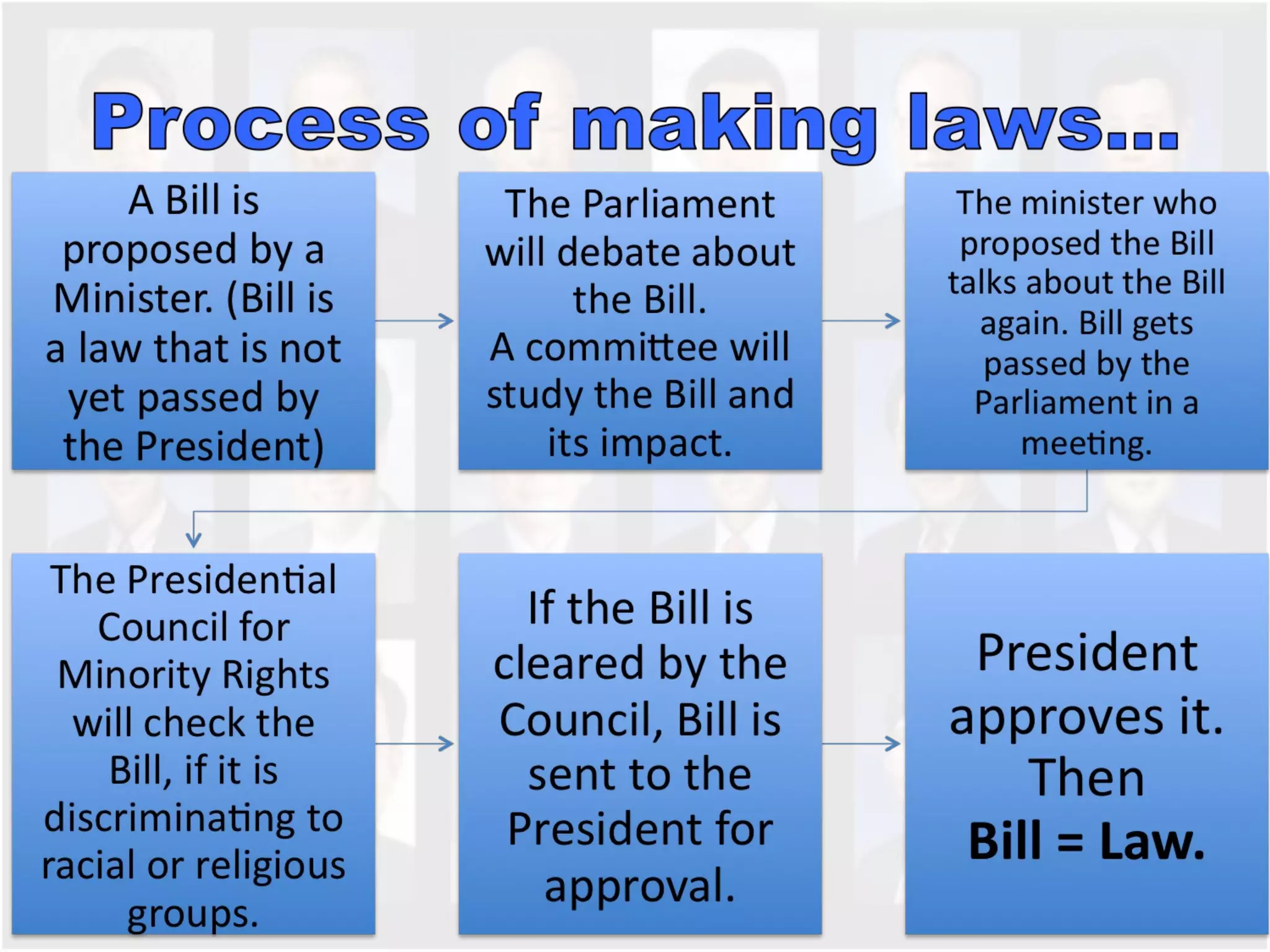
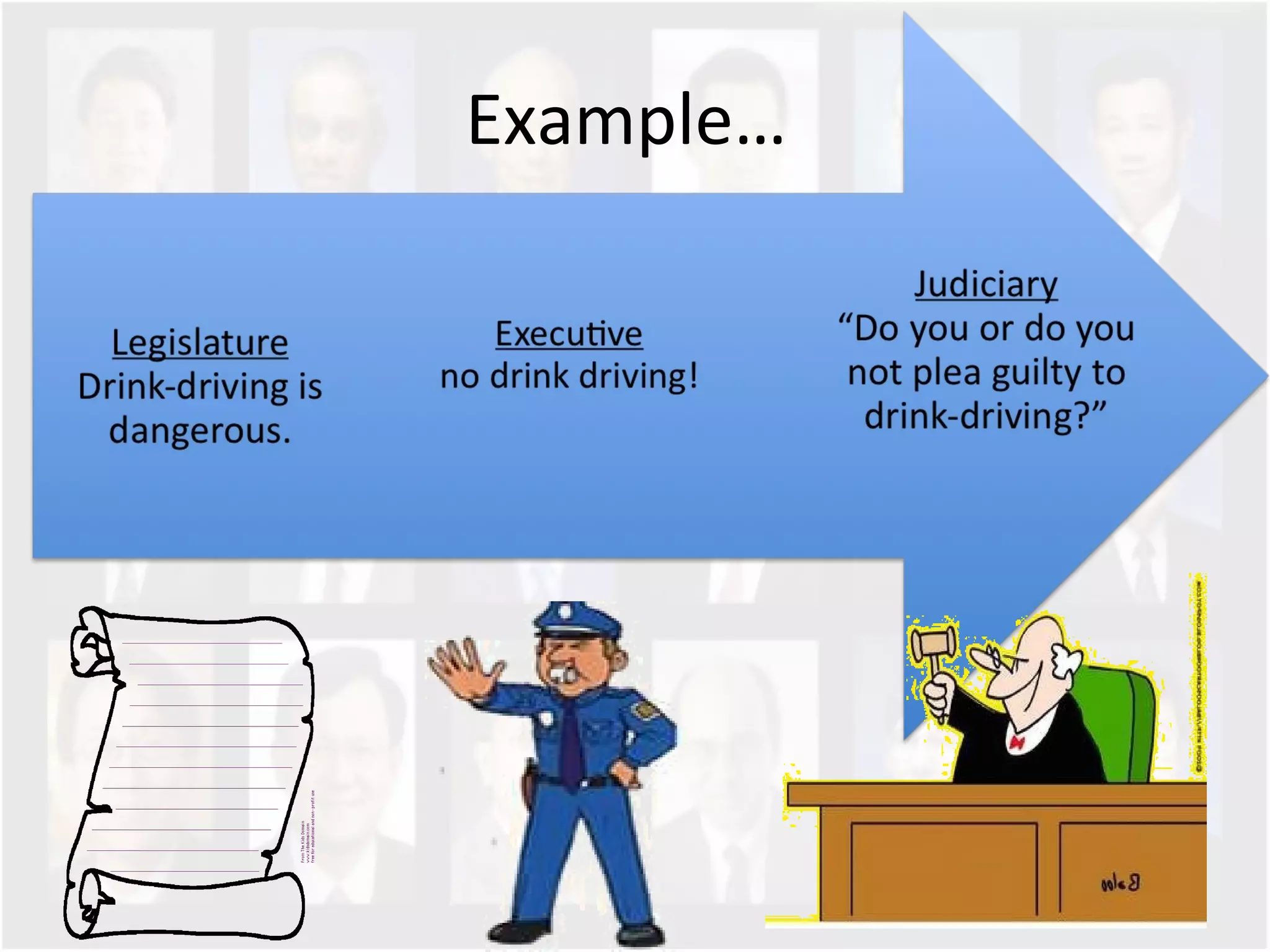
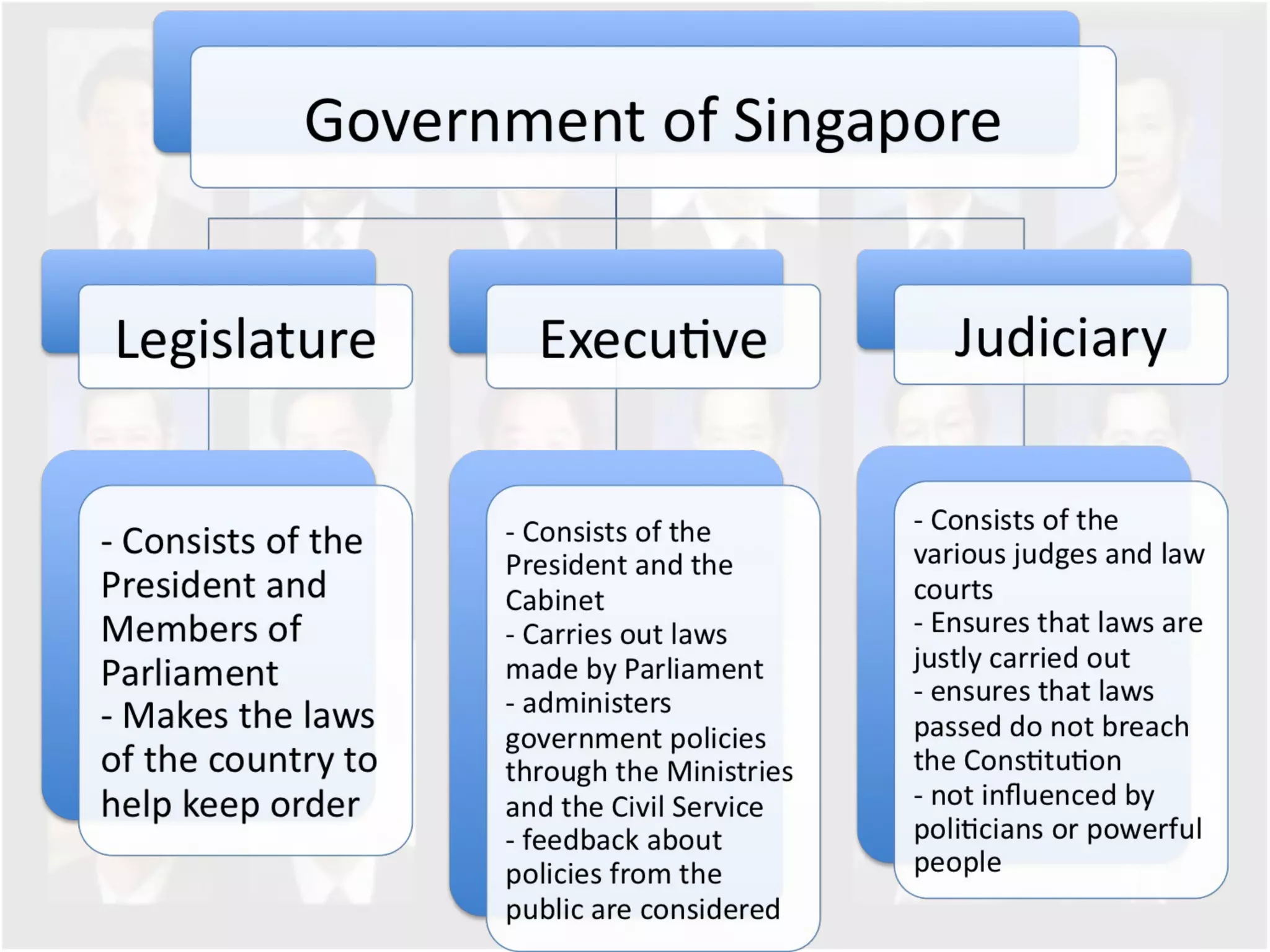
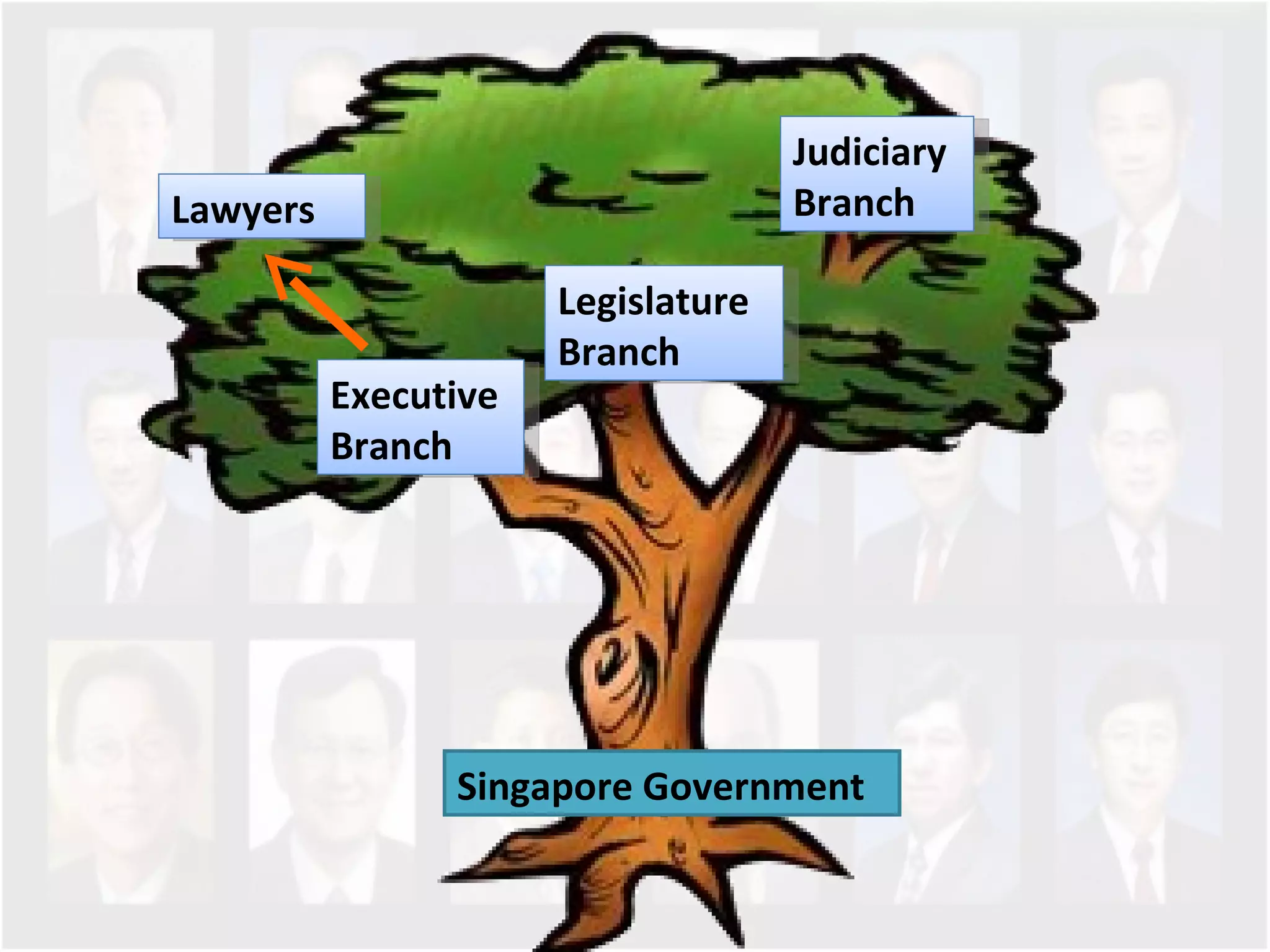
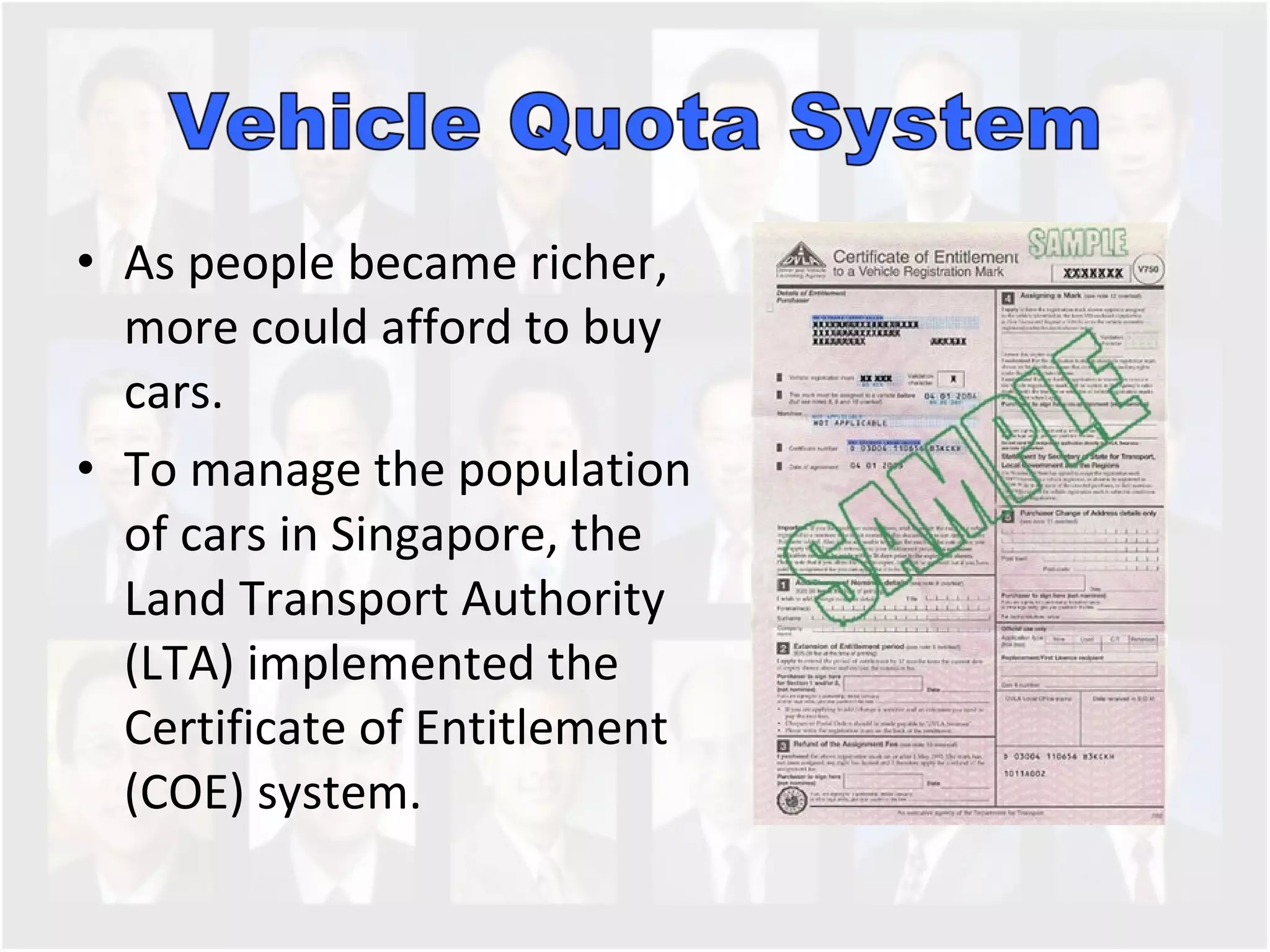
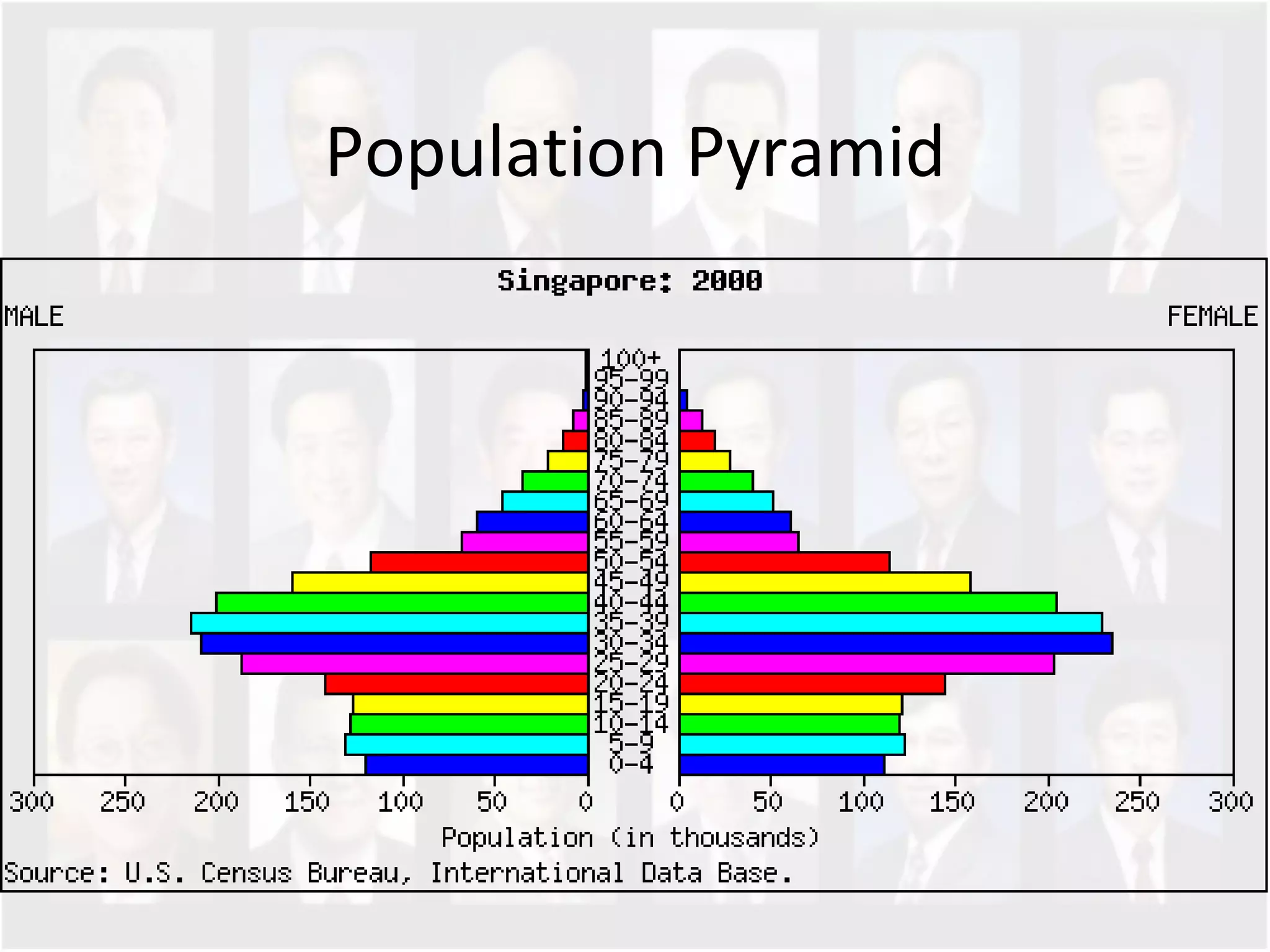
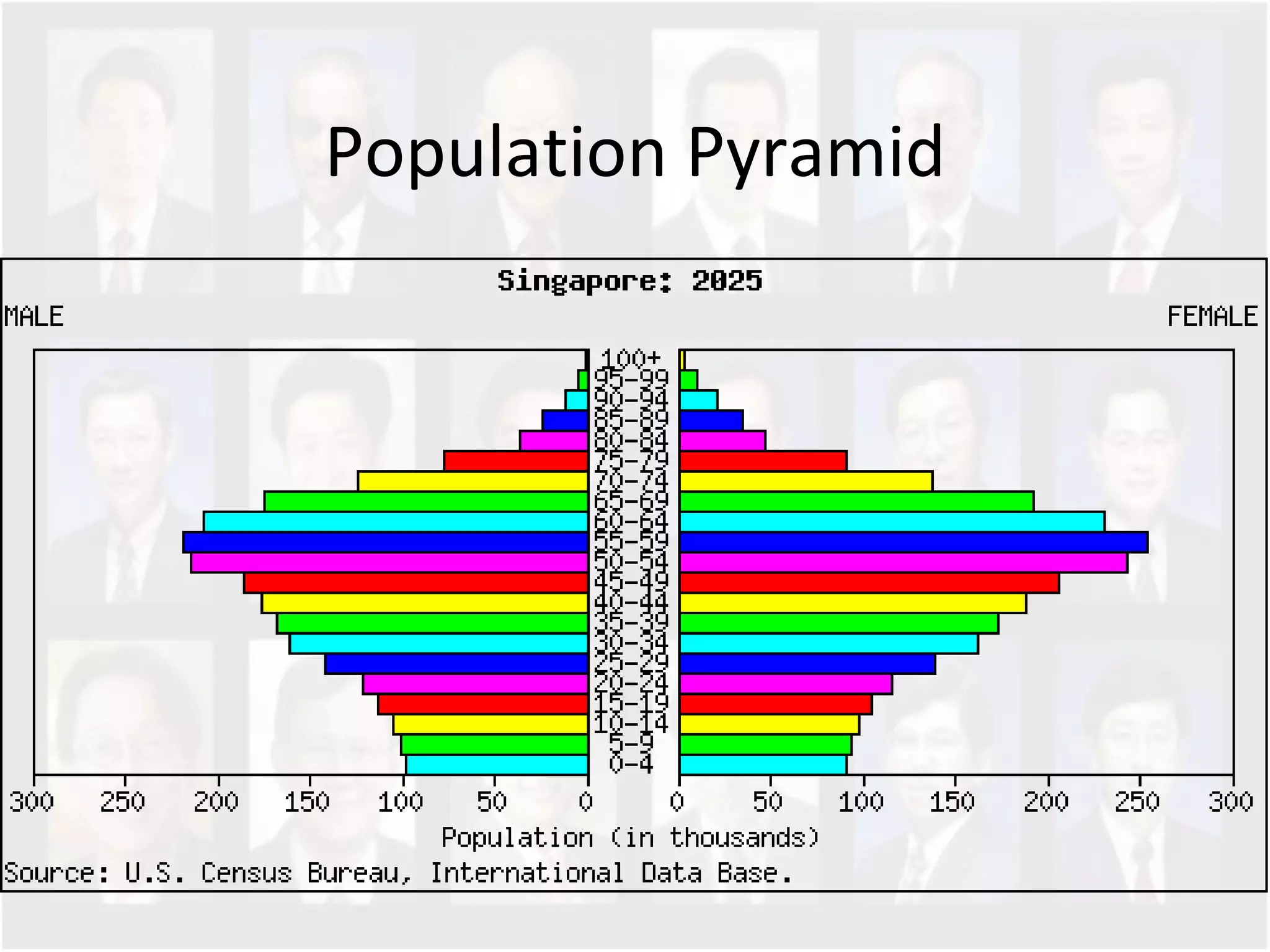
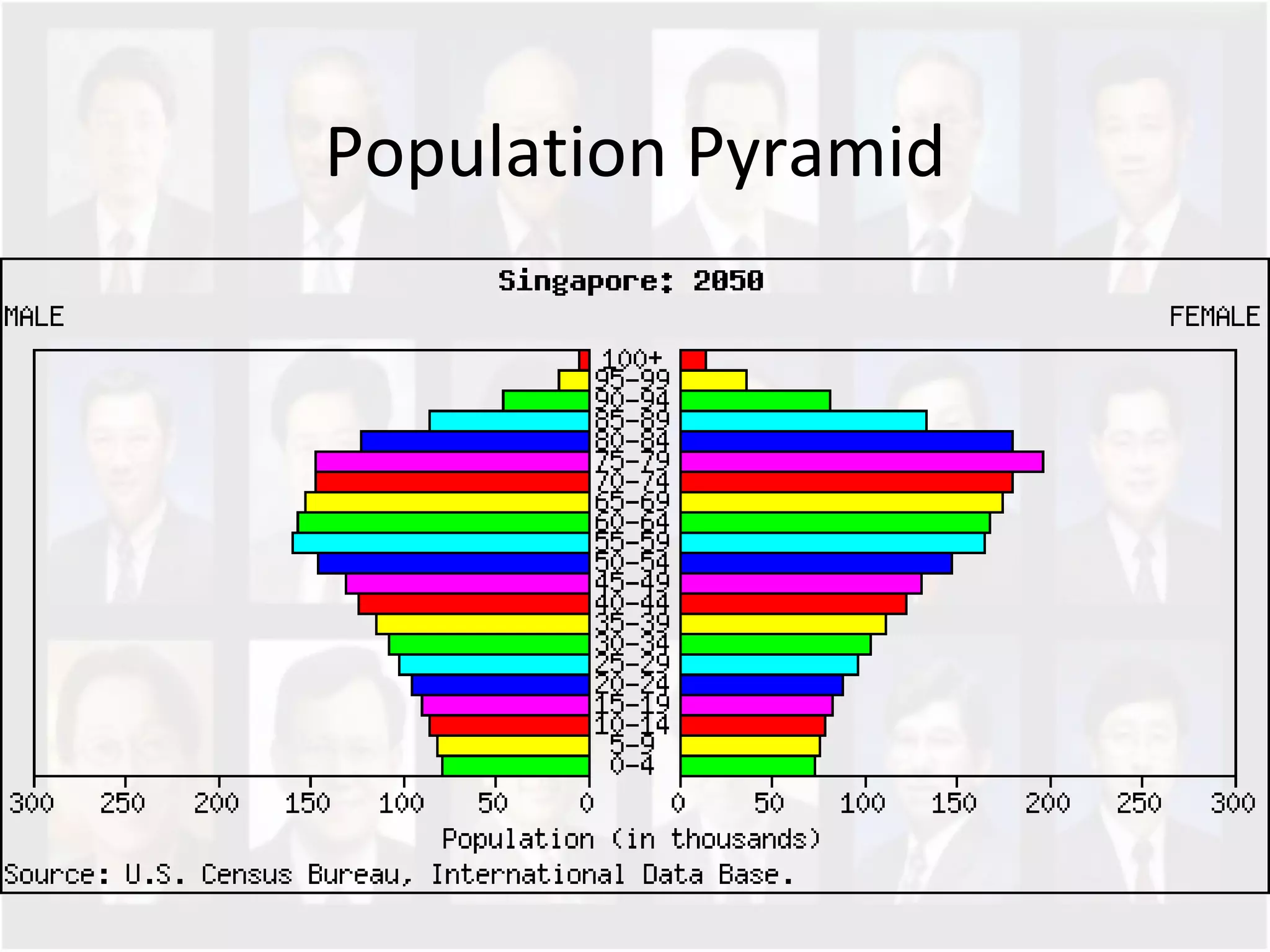
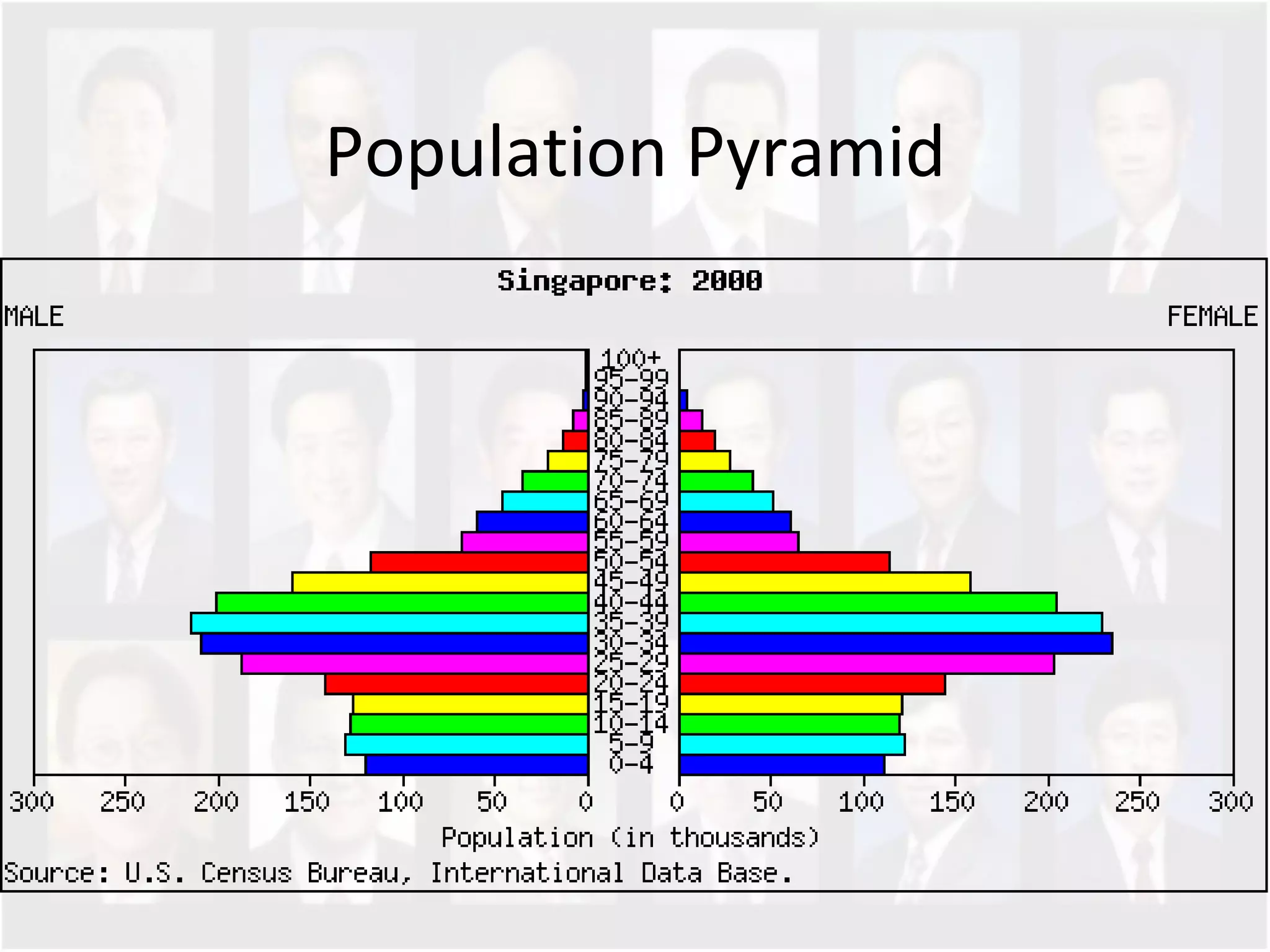
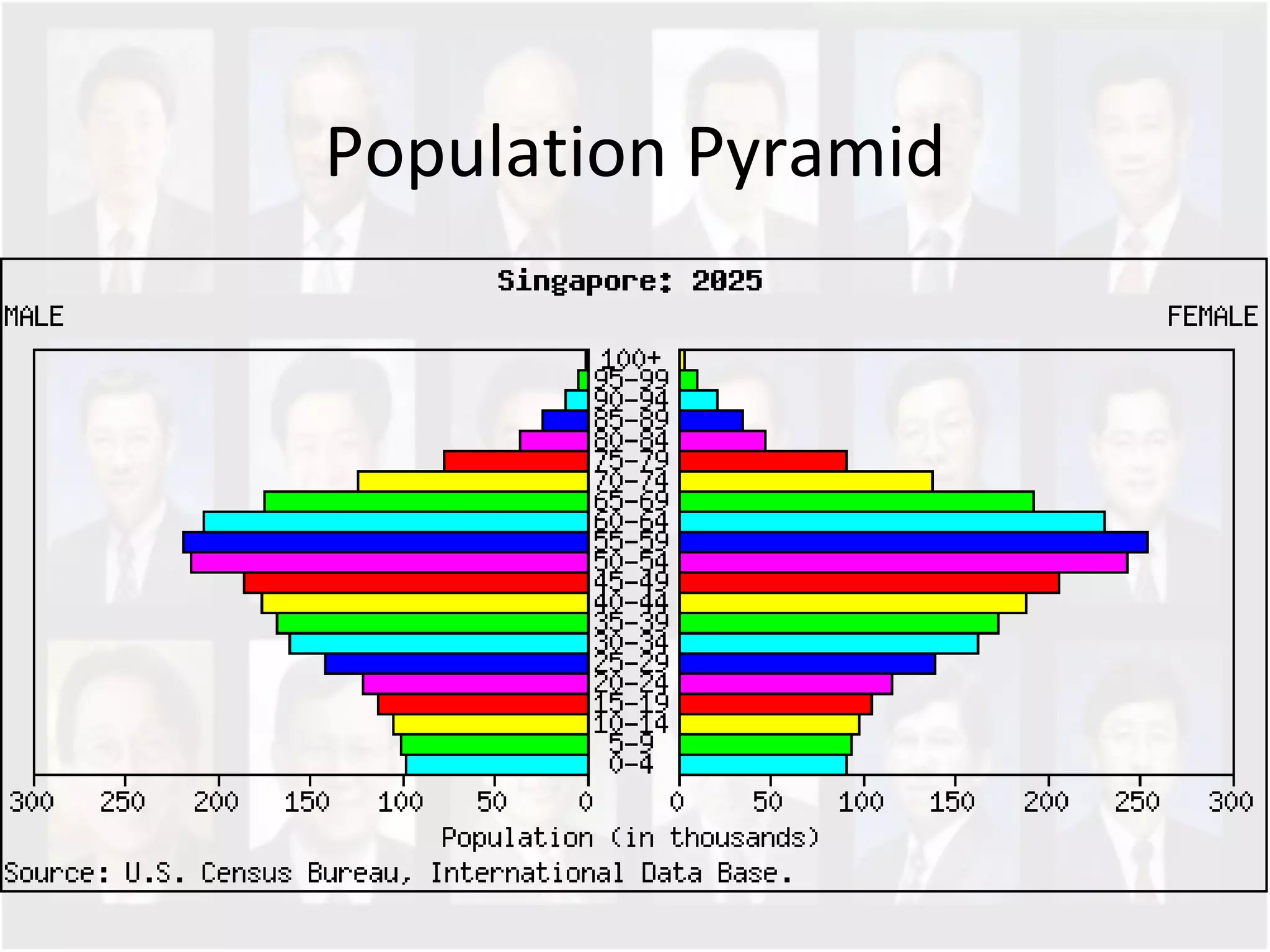
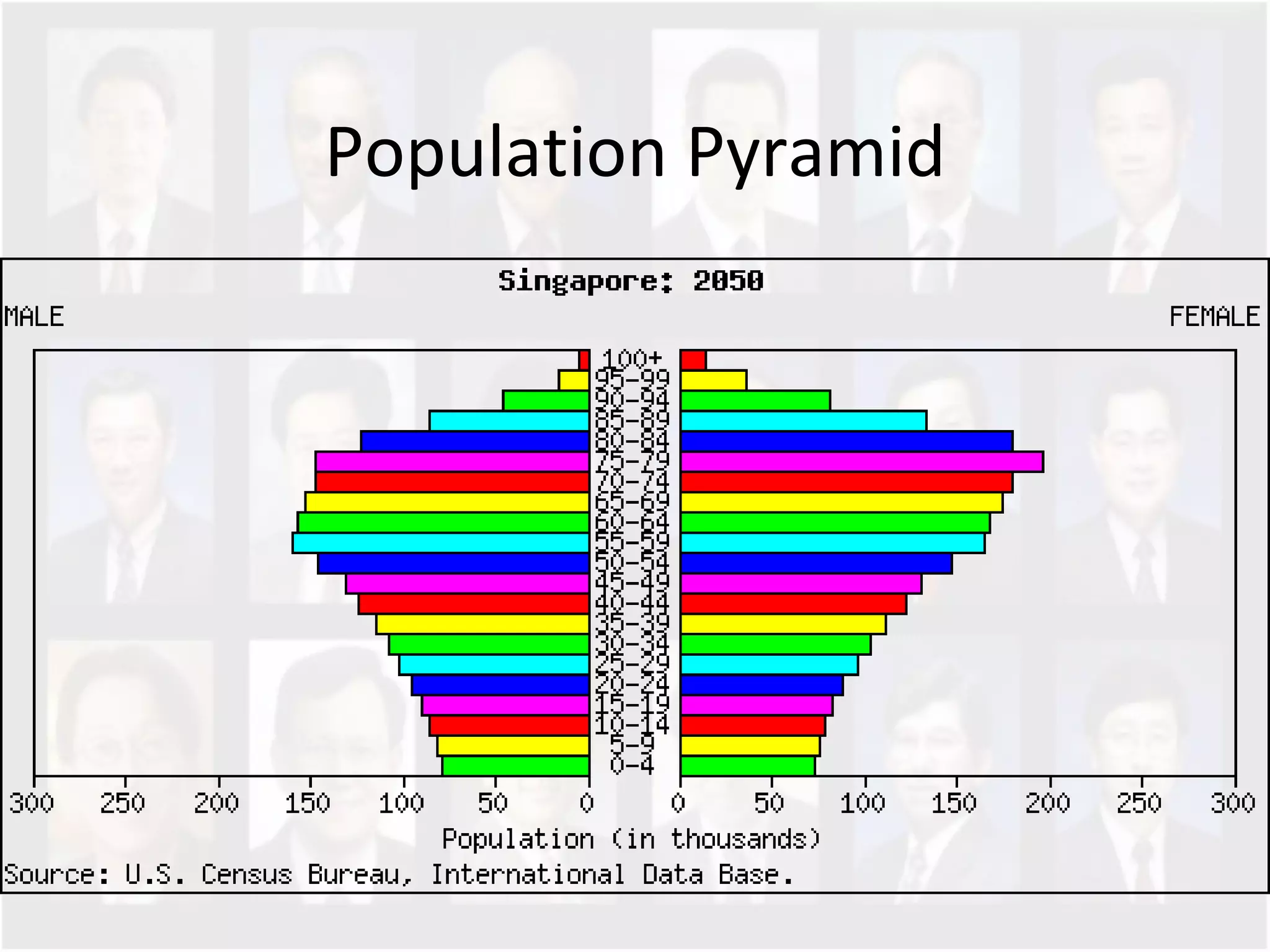
The document discusses Singapore's population policy and the government's approach to population management. It notes that in the 1960s-1980s, Singapore's growing population led to issues like unemployment, housing shortages, and lack of healthcare and education services due to limited resources. Both large and small families were problematic. The government thus implemented population policies to achieve a balanced population size that supports economic growth without overburdening resources.