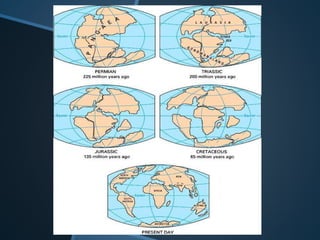
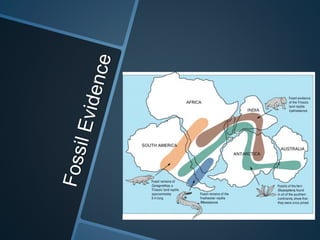
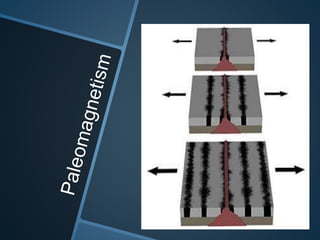
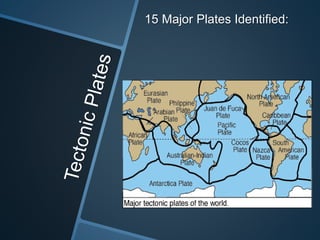
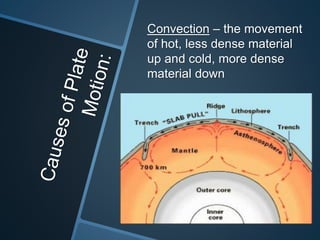
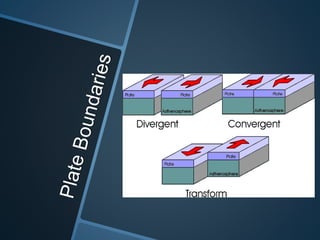
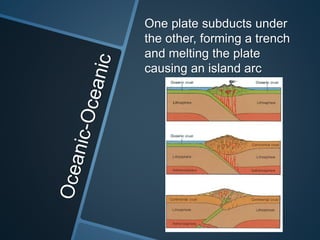
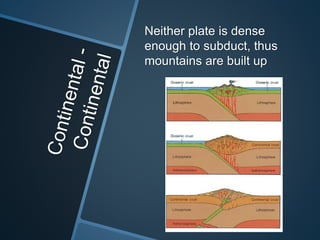
The document summarizes Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift from 1912. It proposed that the continents were once joined together in a supercontinent called Pangea, which later broke apart and drifted to their current positions. Wegener noted evidence supporting this, like matching fossil and rock formations across oceans, but did not know the mechanisms that caused the drift. Later studies discovered plate tectonics, including sea floor spreading at mid-ocean ridges, which provided the explanation for how and why the continents moved over time.