Embed presentation
Download to read offline



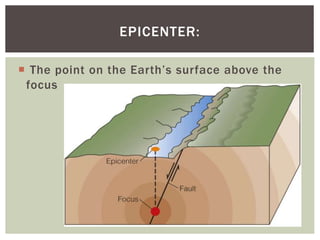





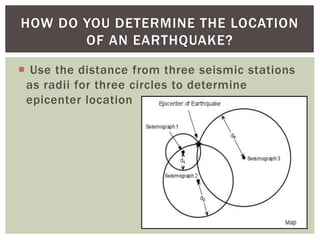
This document defines key terms related to earthquakes and seismic waves. It explains that earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy along fault lines in the earth. The focus is the location within the earth where the earthquake starts, while the epicenter is the point on the surface directly above the focus. There are three main types of seismic waves: P-waves which move in the direction of travel, S-waves which move sideways, and surface waves which cause the most damage. The timing and speed of P and S waves detected by seismic stations can be used to locate the epicenter of an earthquake.









