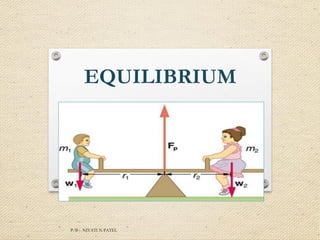
A rigid body is in equilibrium if both the net force and net torque acting on it are zero. For translational equilibrium, the net force must be zero so that the linear acceleration is zero and the body is either at rest or moving with constant velocity. For rotational equilibrium, the net torque must be zero so that the angular acceleration is zero and the body is either stationary or rotating with constant angular velocity. A body is in static equilibrium if it satisfies both conditions and is stationary, or it is in dynamic equilibrium if it satisfies both conditions and is moving.