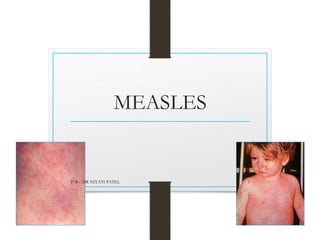
Measles is an acute viral respiratory illness characterized by fever, cough, conjunctivitis, and a maculopapular rash. It most commonly affects children between ages 3-5 years. The virus is highly infectious and spreads through direct contact or droplets. Clinical features include a prodromal stage with fever and Koplik's spots, followed by an exanthematous rash that begins behind the ears and spreads all over the body. Complications can include pneumonia, otitis media, and blindness. Prevention is through vaccination with the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine.