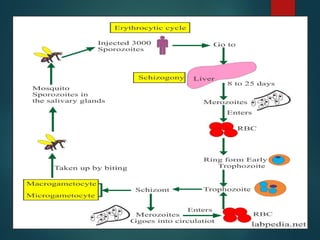
This document defines malaria and discusses its transmission, pathogenesis, clinical features, complications, diagnosis, and management. Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites transmitted via mosquito bites and characterized by periodic fevers. P. falciparum can cause potentially fatal malaria. Complications include tropical splenomegaly syndrome, nephropathy, and anemia. Diagnosis involves blood smears to identify parasites and antigen testing. Management consists of antimalarial drugs like quinine, addressing complications, and specific treatment for children and pregnant women in high-risk areas.







![PATHOGENESIS
Clinical symptoms and signs are caused by the
asexual forms of the parasite
Invade and destroy RBCs,
Localise in tissues and organs by binding to
endothelial cells (cytoadherence)
Induce release of many pro-inflammatory cytokines
[e.G. Tumour necrosis factor-α (tnf-α)].
Initiating step when merozoites invade RBCs
trophozoite schizont stage bind to epithelial
cells in post capillary venules microvascular
obstruction (cytoadherent) toxins produced
cytokine release
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/malaria-220803042906-8165253d/85/Malaria-pdf-9-320.jpg)








