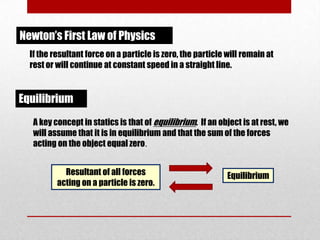
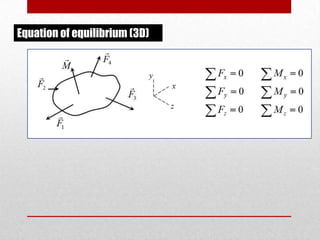
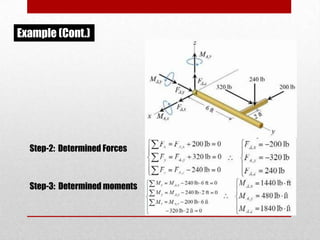
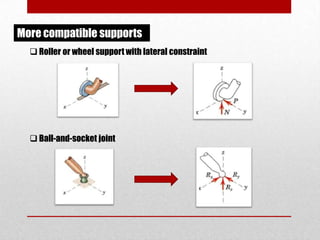
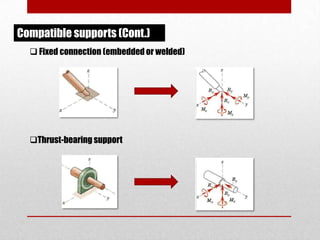
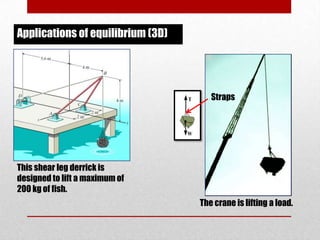
This presentation discusses equilibrium and the equation of equilibrium in 3 dimensions. It defines static and dynamic equilibrium, with static equilibrium occurring when the net force on a body is zero and it is at rest, and dynamic equilibrium occurring when the net force is zero and a body is in uniform motion. It presents the two conditions for equilibrium: 1) the vector sum of all forces is equal to zero, and 2) the algebraic sum of all clockwise and counterclockwise torques is equal to zero. An example problem is shown to demonstrate solving the 3D equation of equilibrium to determine unknown support reactions on a structure. Applications to lifting structures like cranes are also briefly discussed.