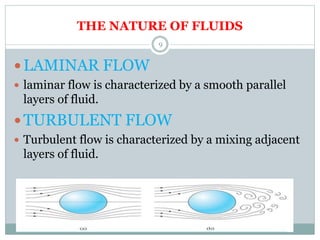
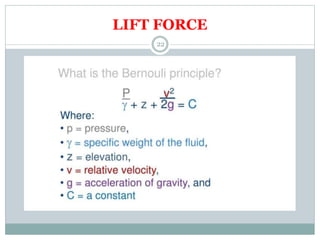
This document defines key concepts related to fluids, including definitions of fluid, density, viscosity, temperature, pressure, and other fluid properties. It explains that fluids include both liquids and gases, and that they continuously deform under shear stress. It also discusses fluid flow regimes including laminar and turbulent flow. Additional concepts covered include buoyancy, drag, and lift forces. Buoyancy is defined as a vertical force that can be positive, negative, or neutral. The three types of drag - frictional, form, and wave drag - are explained. Finally, it notes that lift is a force perpendicular to fluid flow, and that factors like density, viscosity, and flow speed affect lift.