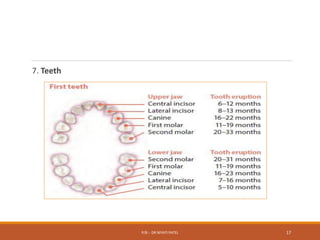
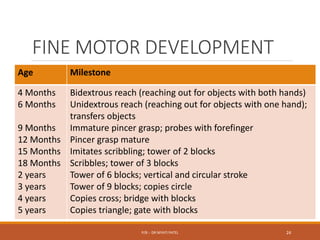
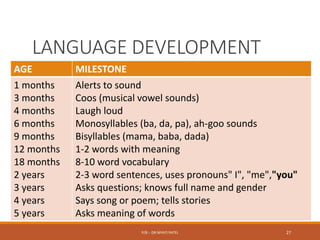
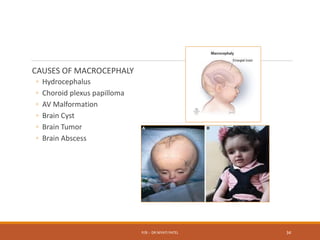
The document discusses normal growth and development from conception through childhood. It describes the stages of growth from the ovum and embryo stages through infancy, childhood and adolescence. It outlines the factors that can affect growth and development such as genetics, hormones, nutrition, socioeconomic status and intellectual stimulation. Key growth parameters like weight, height and head circumference are provided for each stage of development. Milestones for gross motor, fine motor, social and language development are also outlined. Abnormal growth such as low birth weight, microcephaly and macrocephaly are defined and their potential causes discussed.