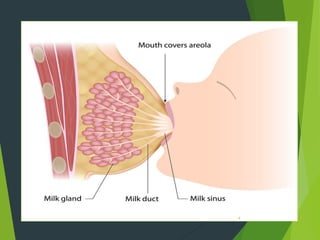
The document discusses breastfeeding, detailing its definition, mechanisms, and benefits for both baby and mother. It outlines various breastfeeding positions and techniques for successful latching and addresses common problems encountered during breastfeeding. Additionally, it highlights the nutritional advantages of breast milk and the importance of initiating breastfeeding shortly after delivery.