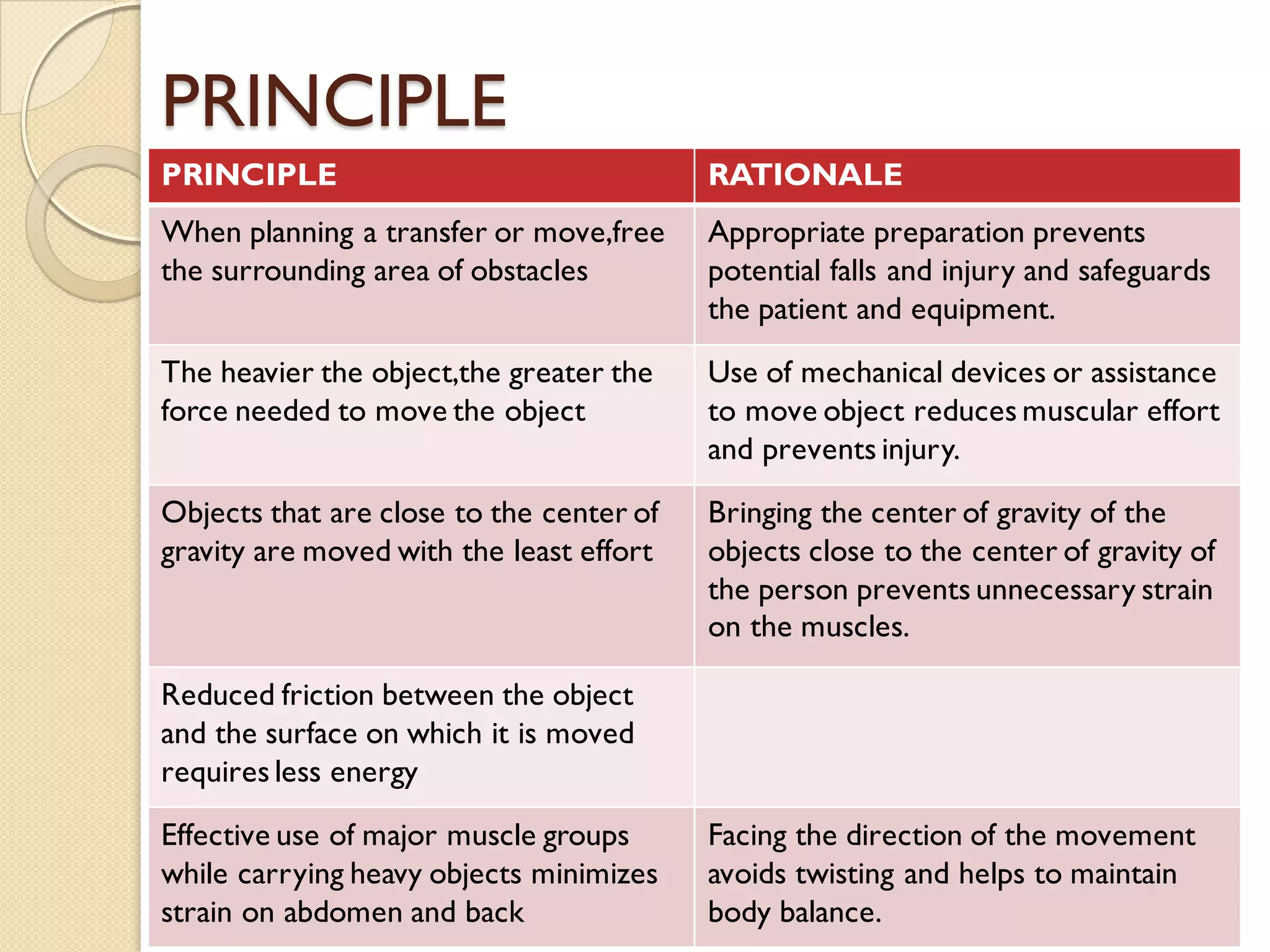
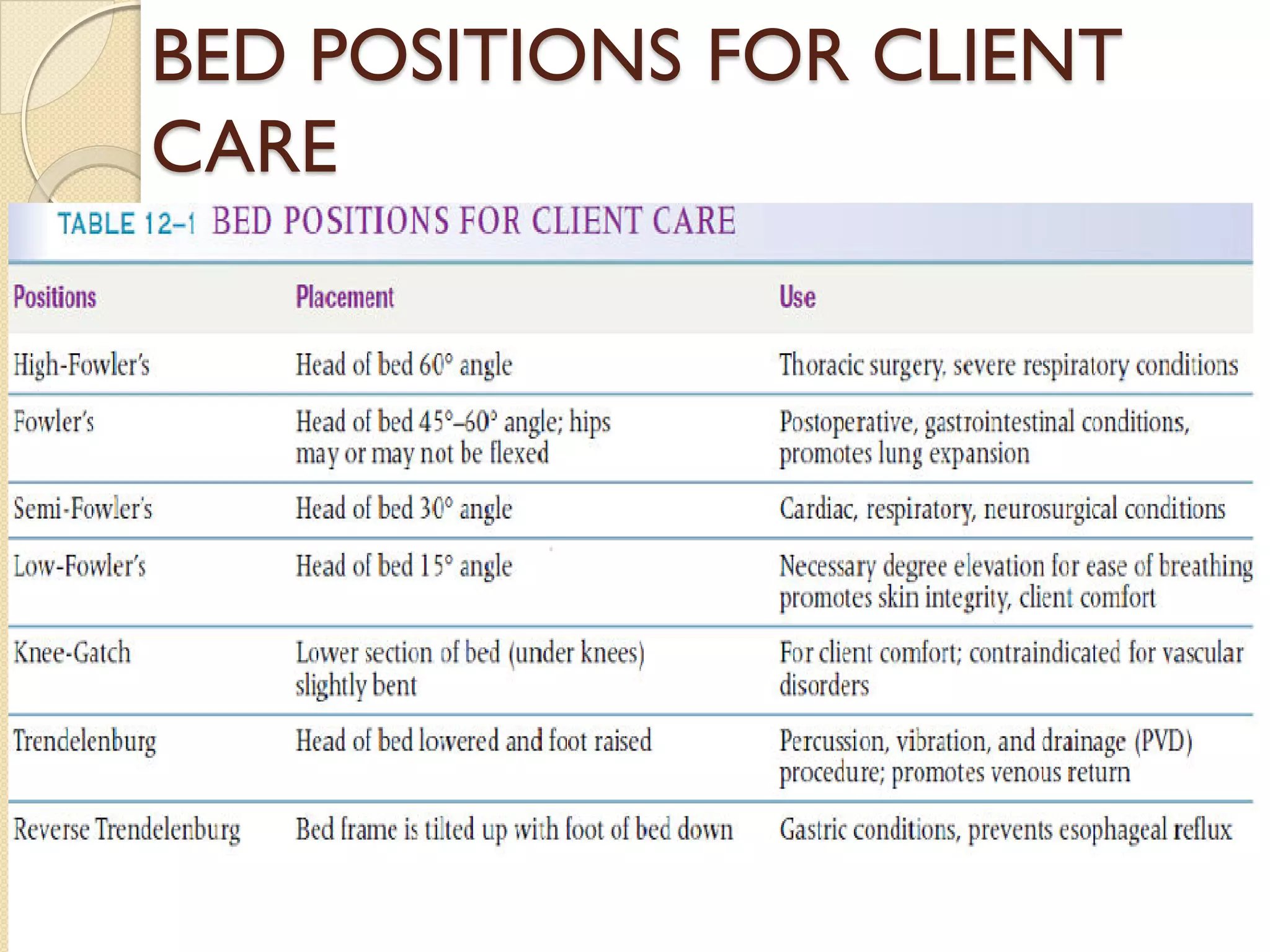
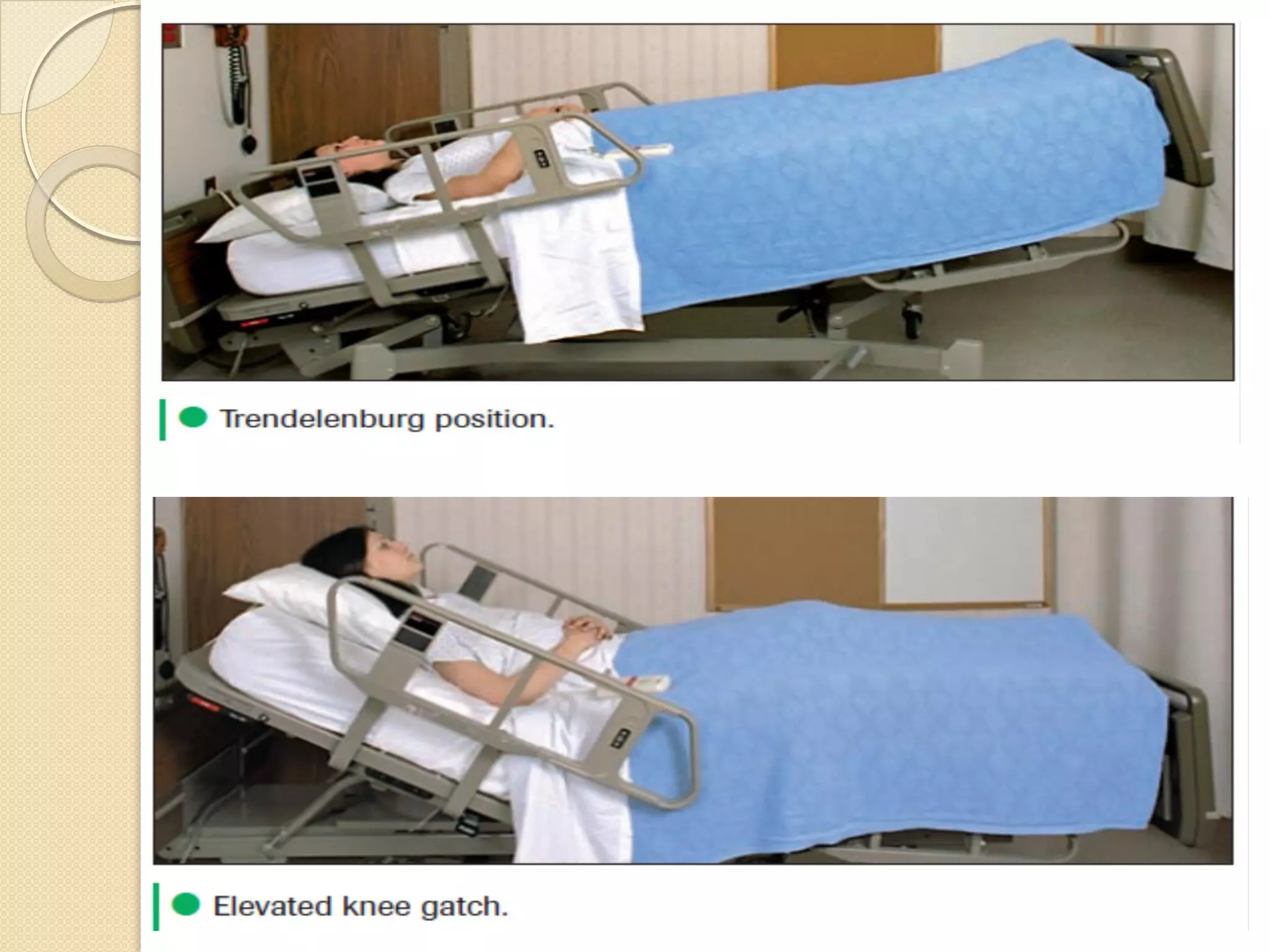
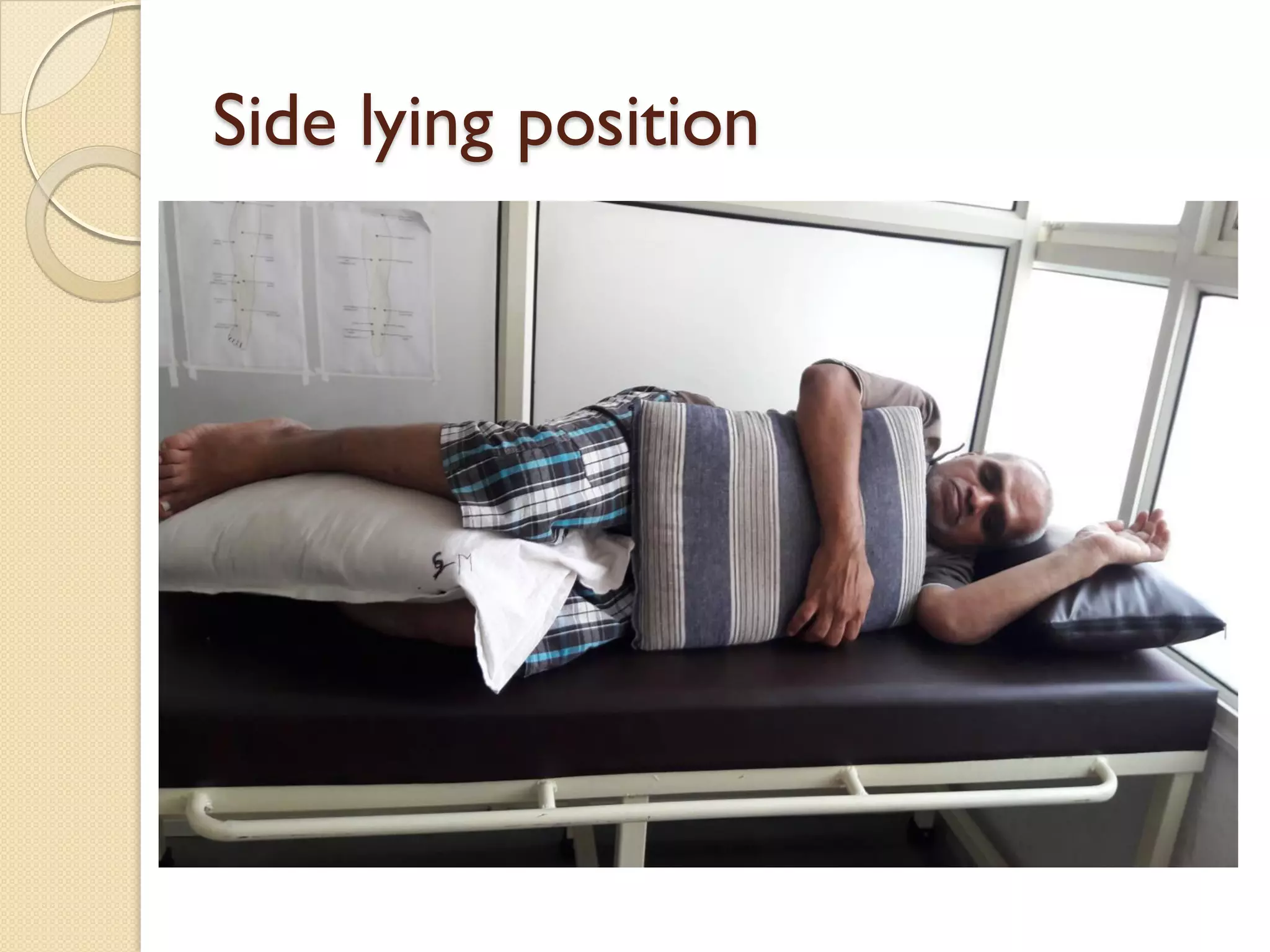
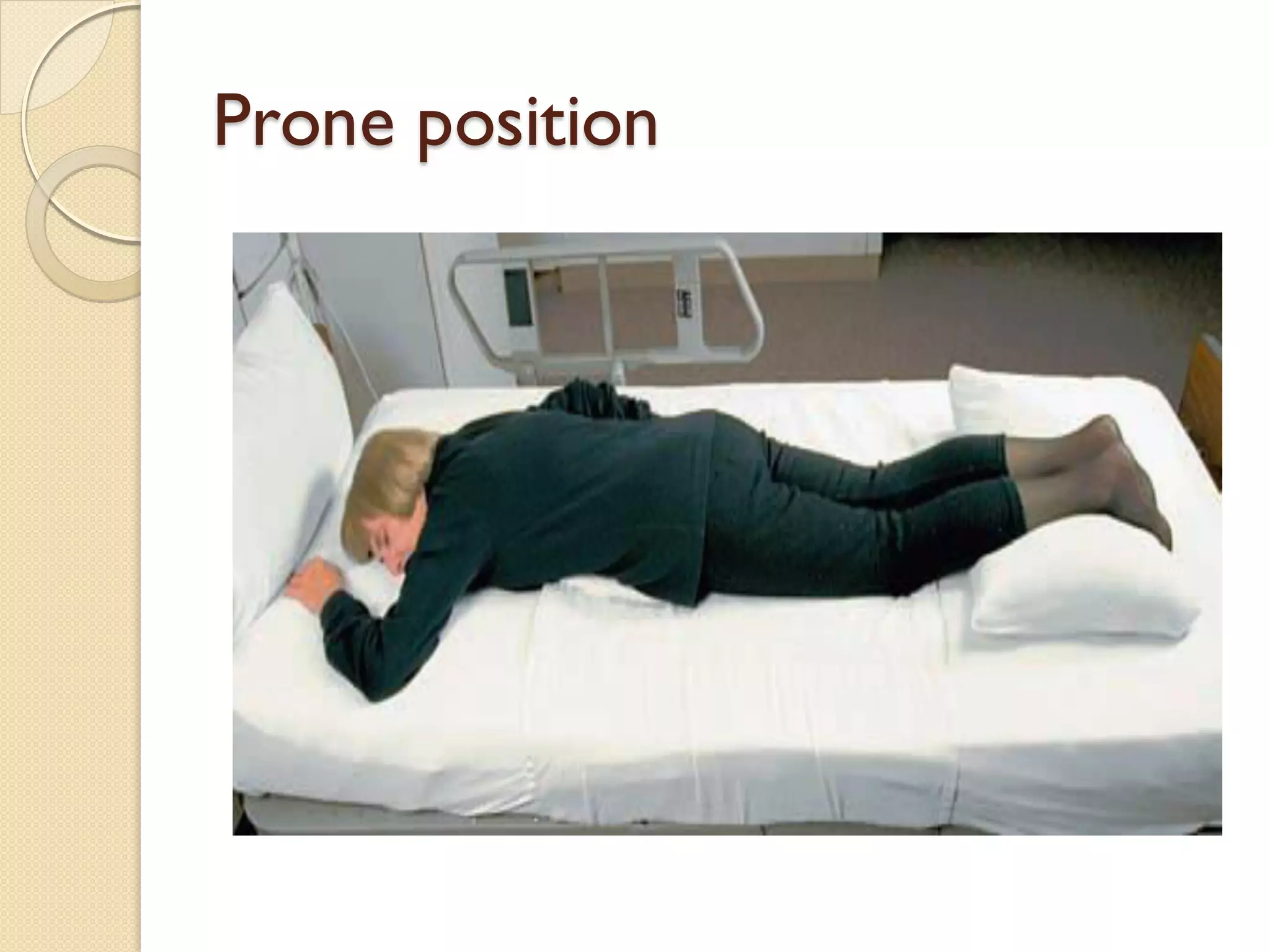
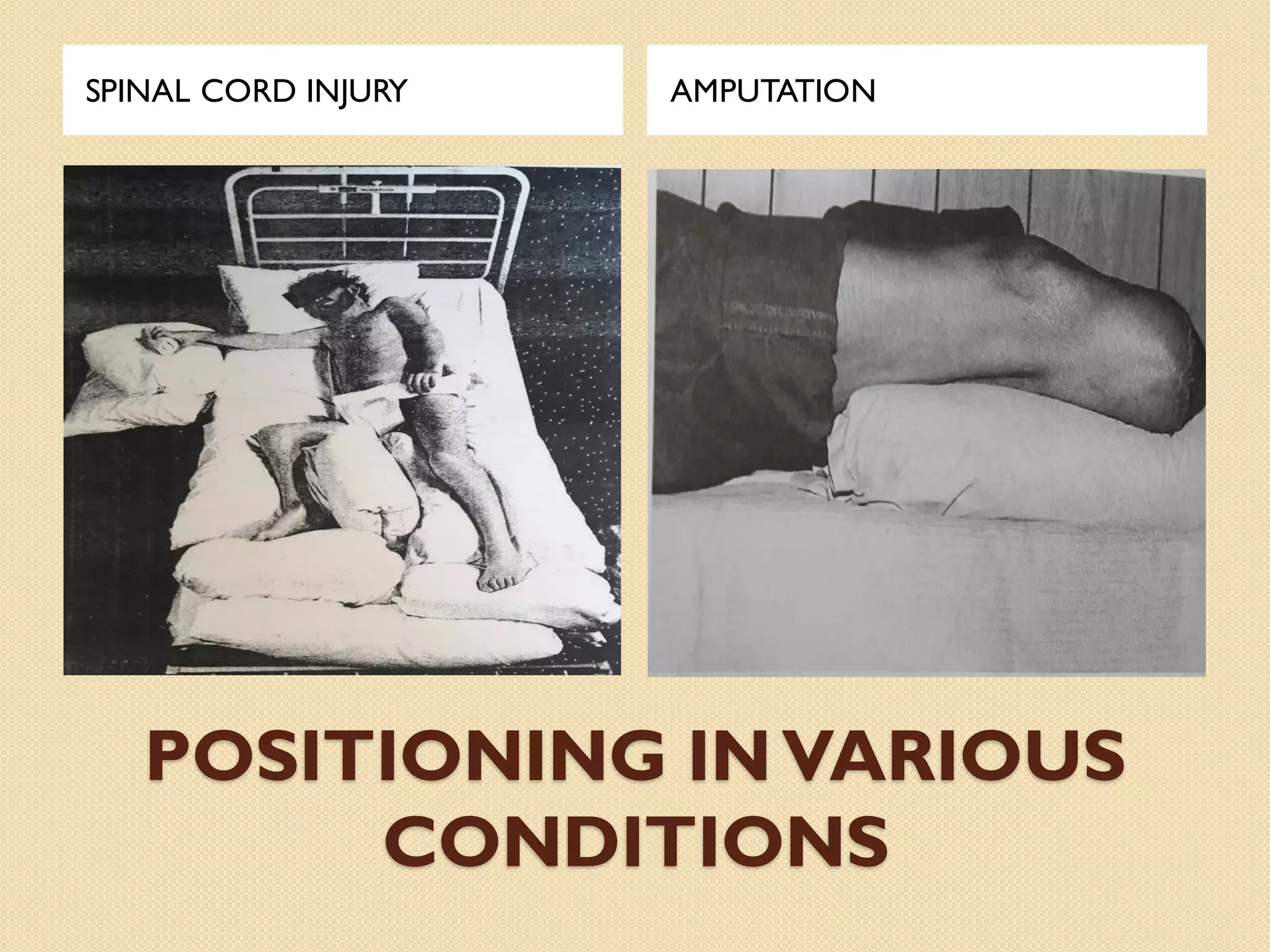
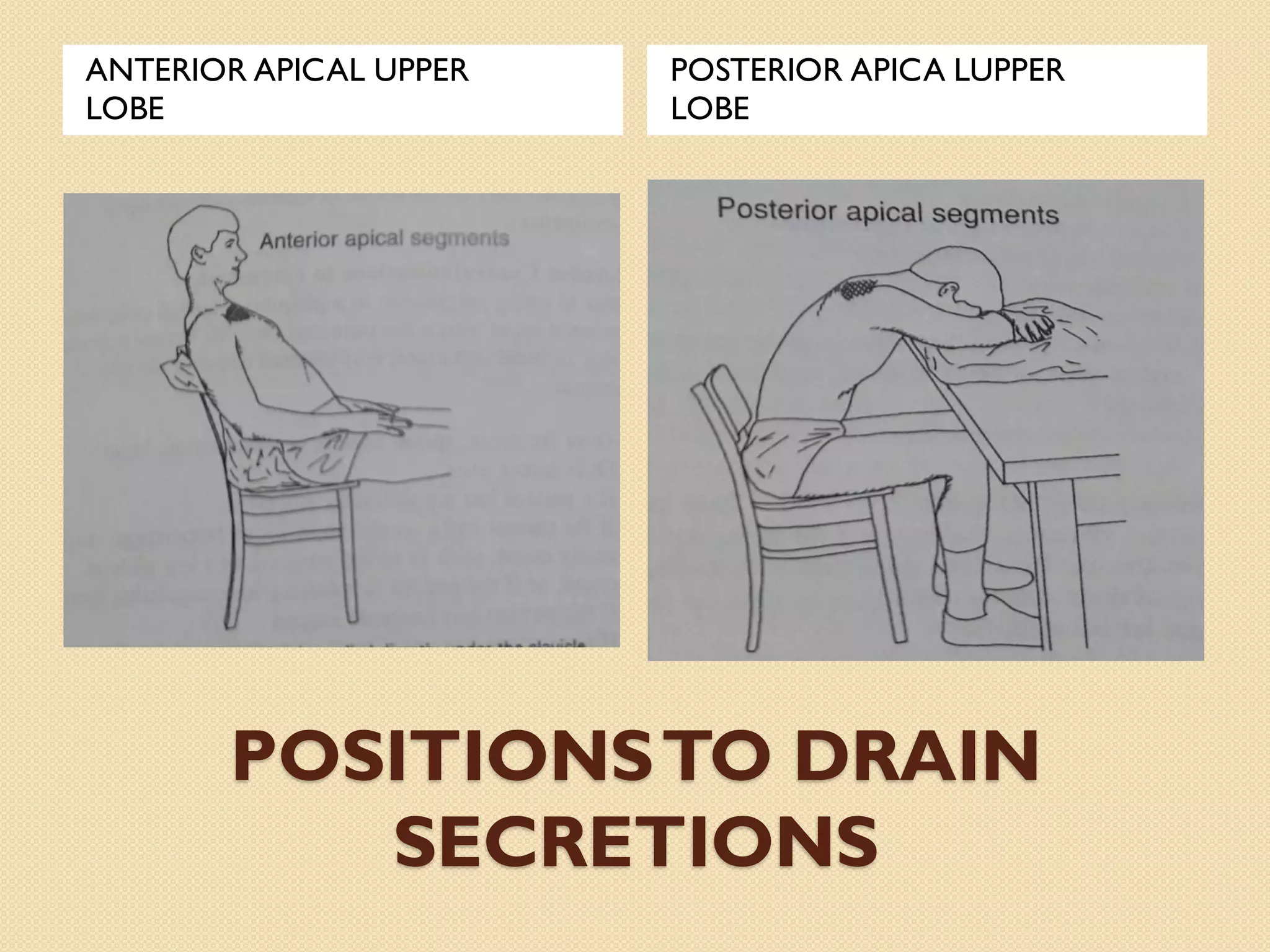
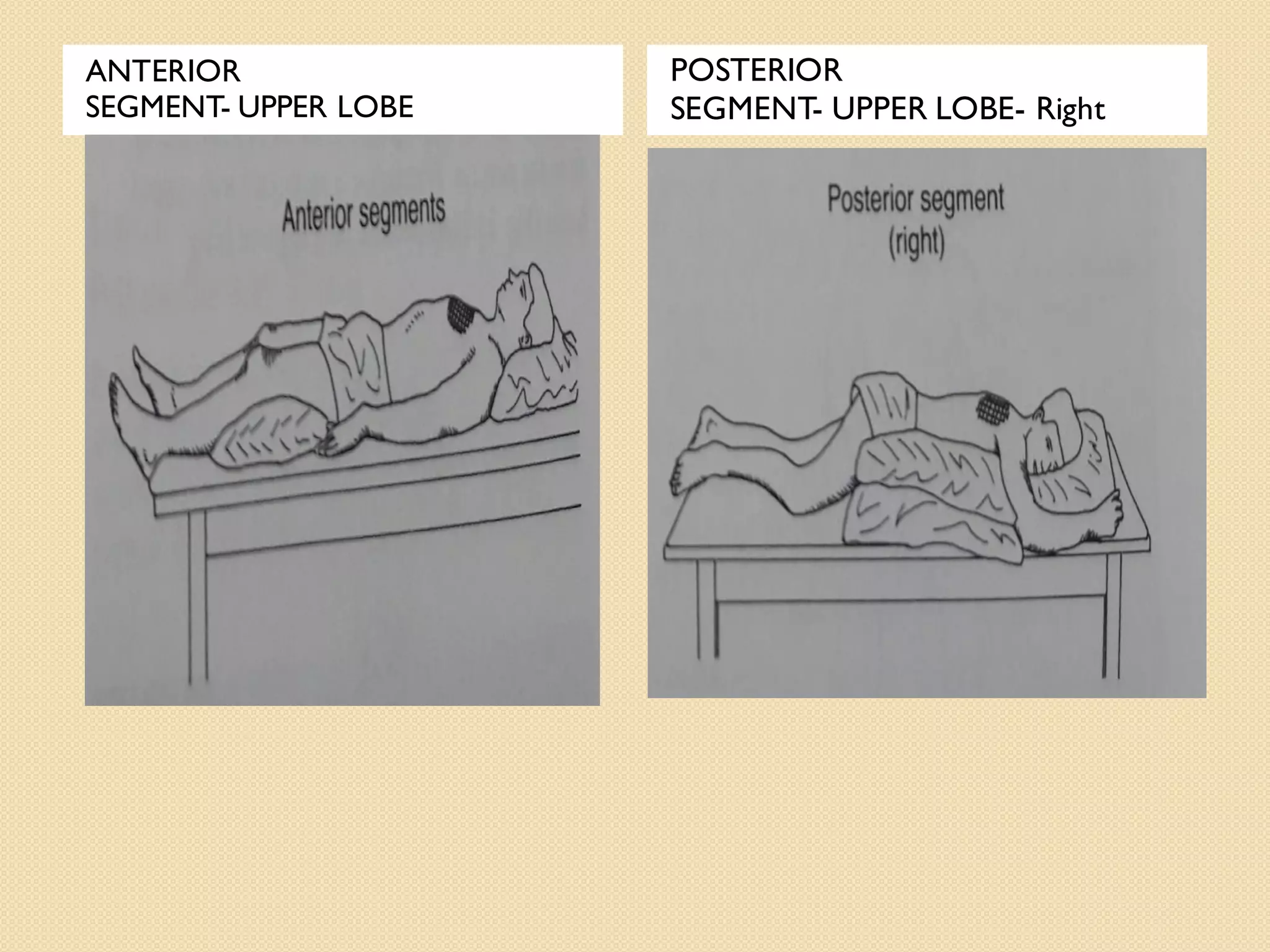
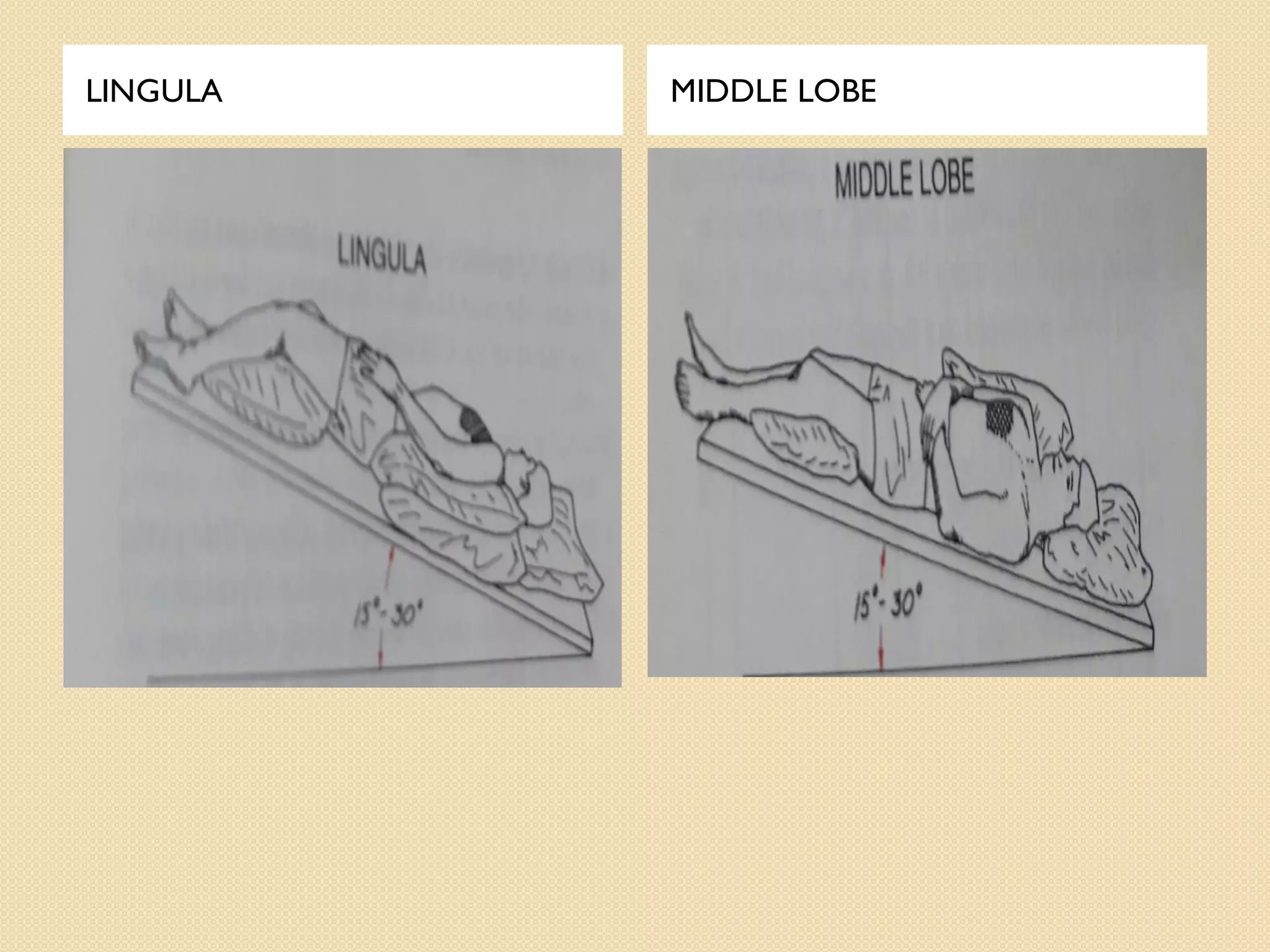
This document discusses body mechanics, patient positioning, and transfer techniques for healthcare providers. It covers principles of body mechanics like maintaining good alignment and balance to prevent injury. It also describes different bed positions like supine, lateral, and prone and how to move a patient between positions safely. Finally, it outlines various transfer techniques like bed to chair and use of assistive devices to move patients while protecting caregiver and patient safety.