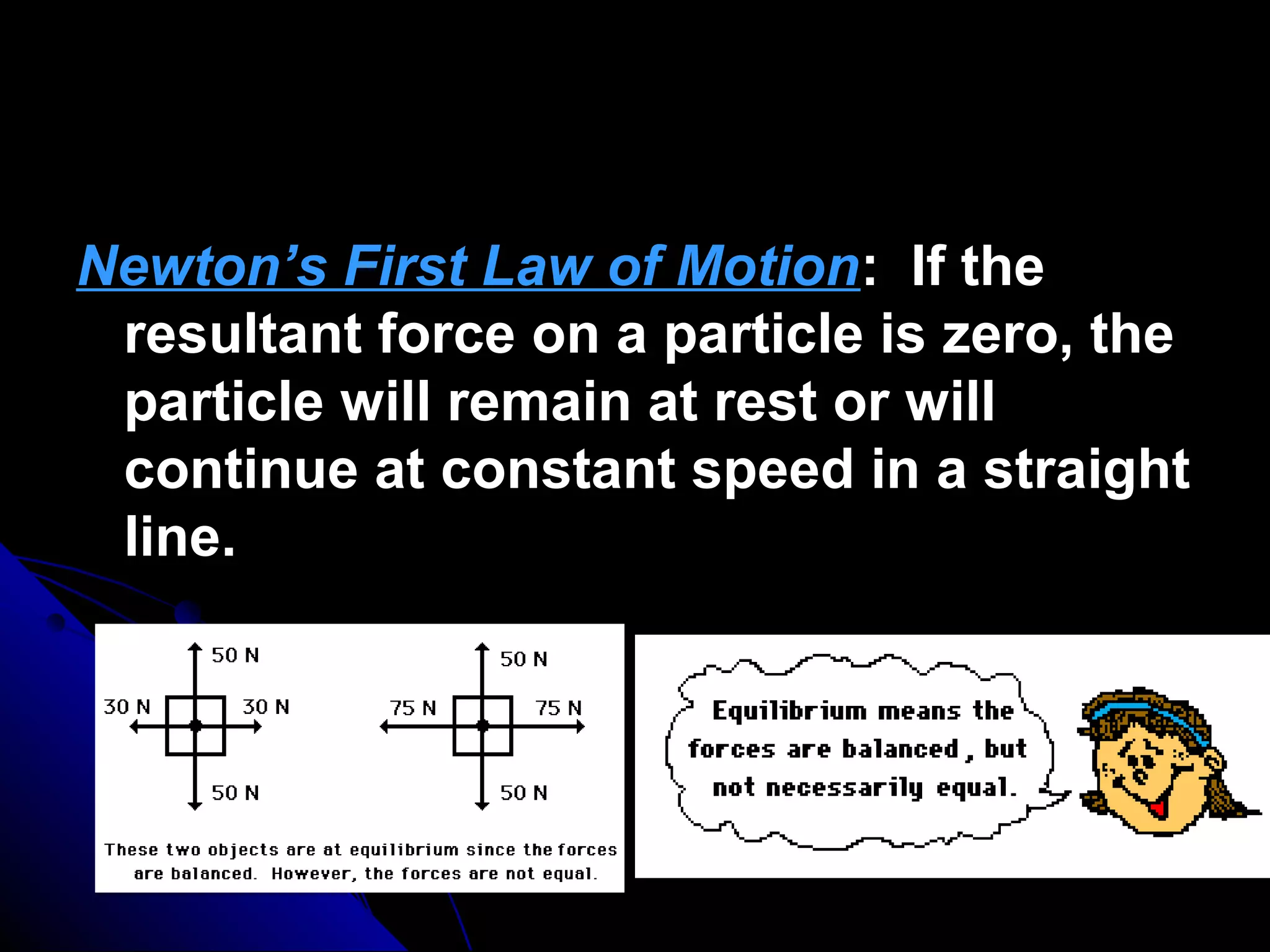
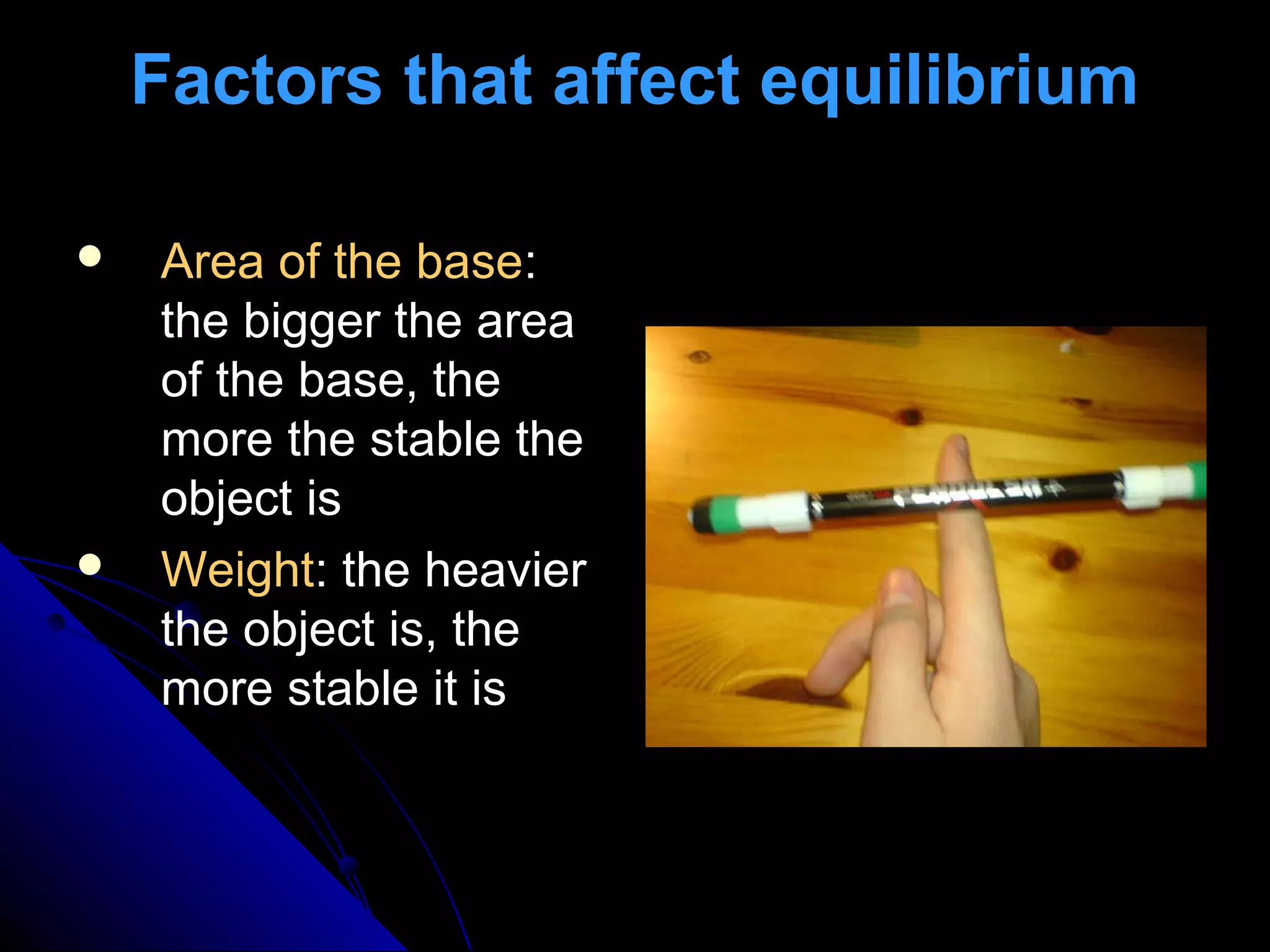
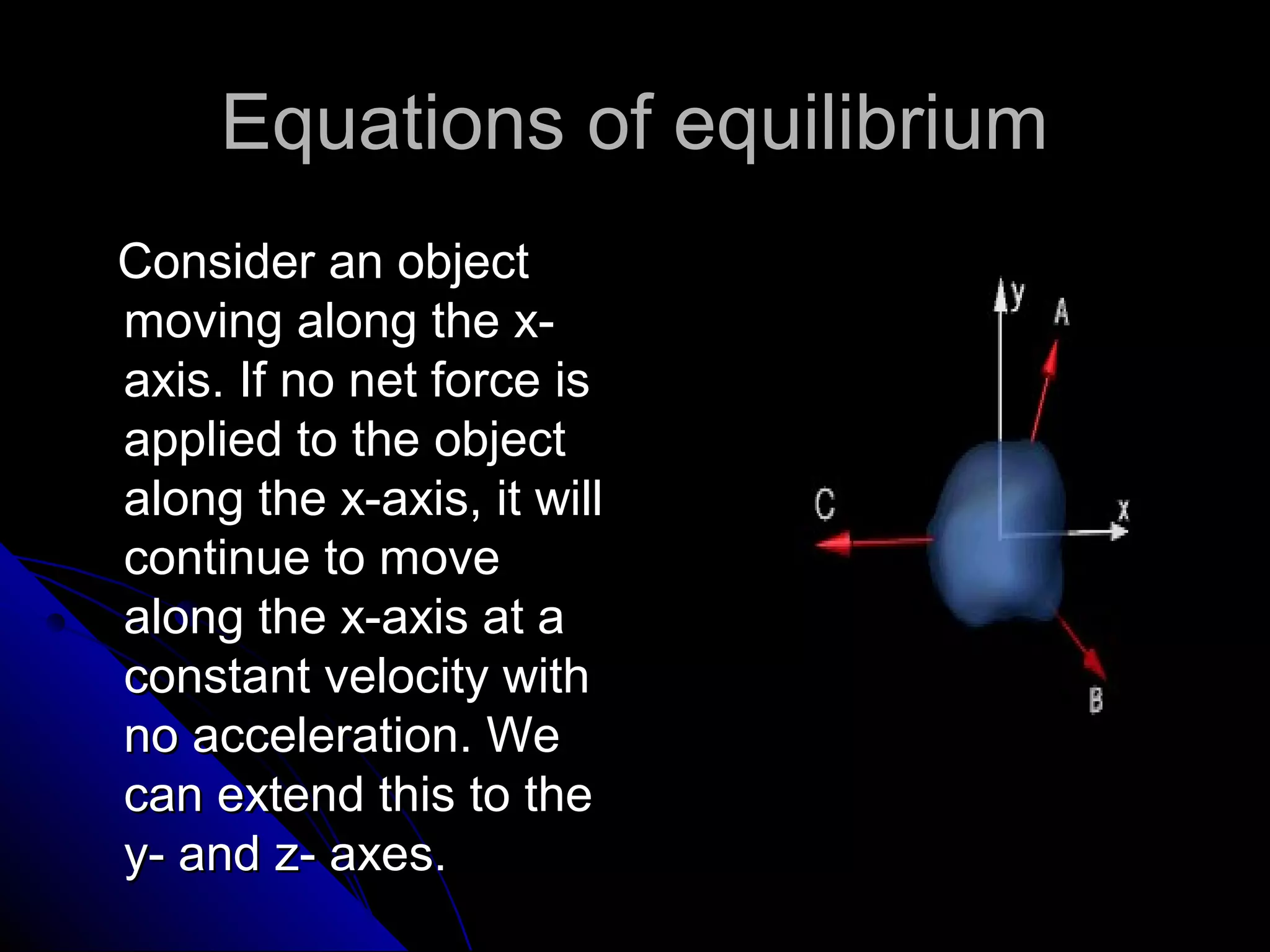
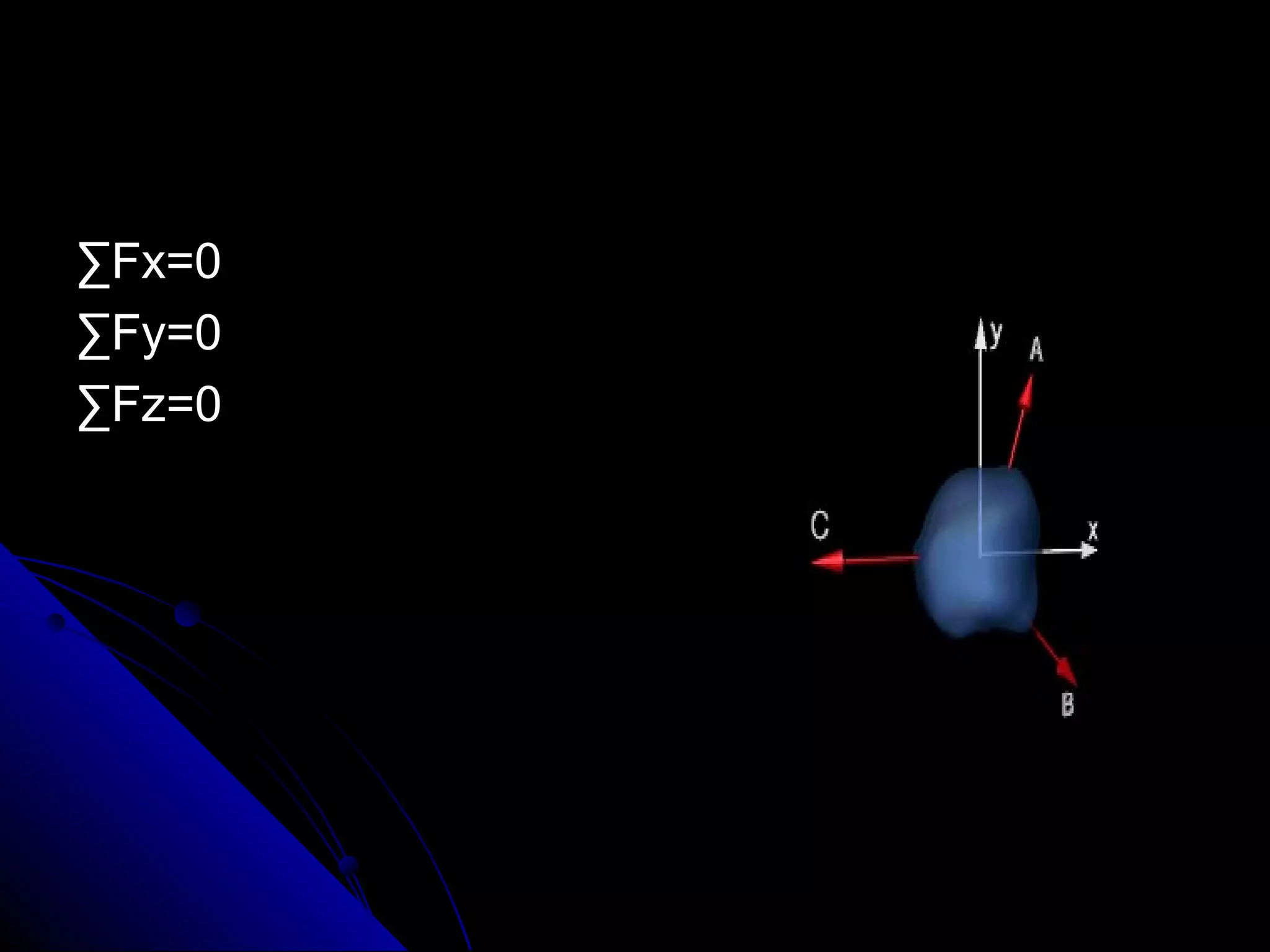
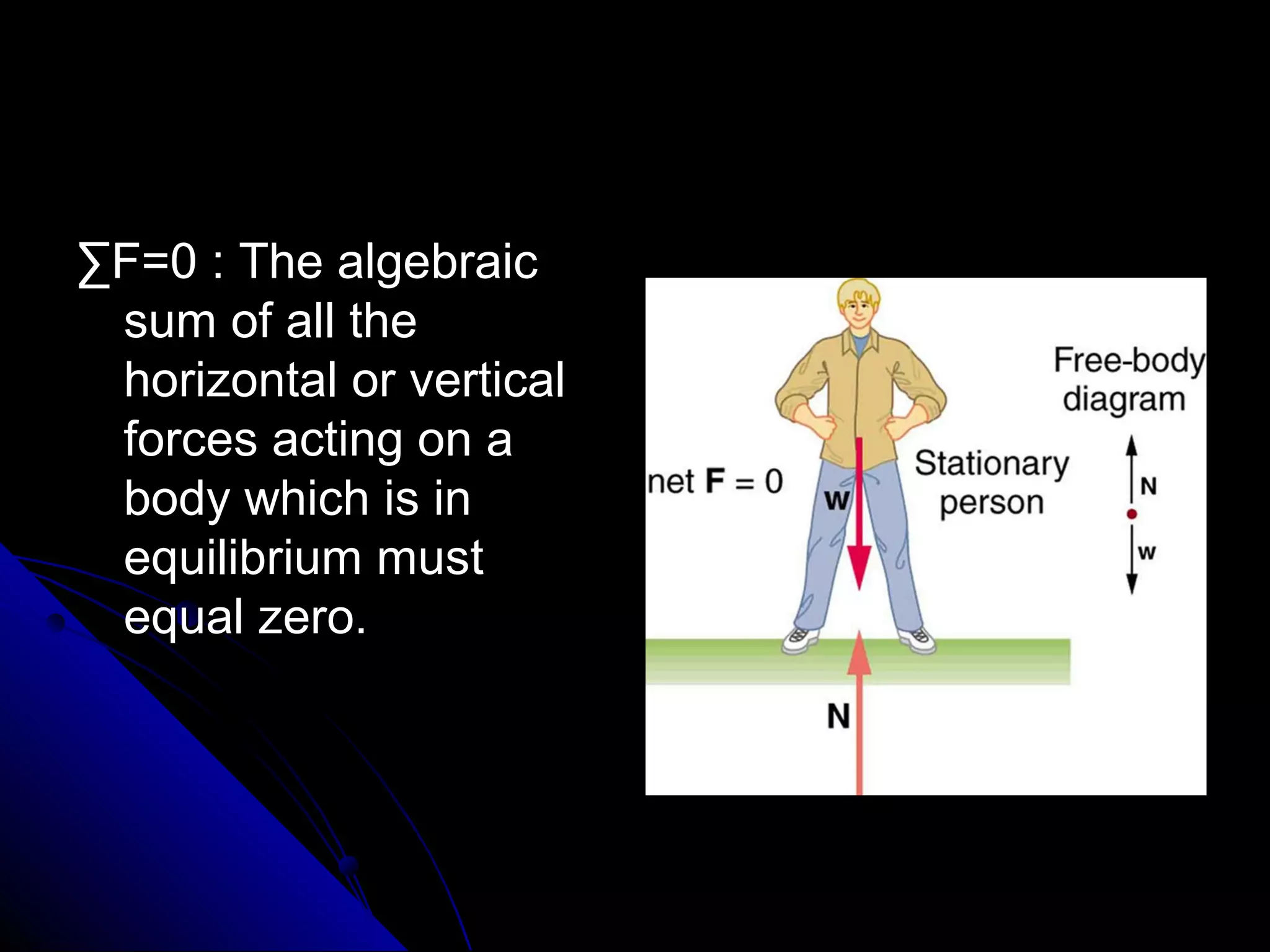
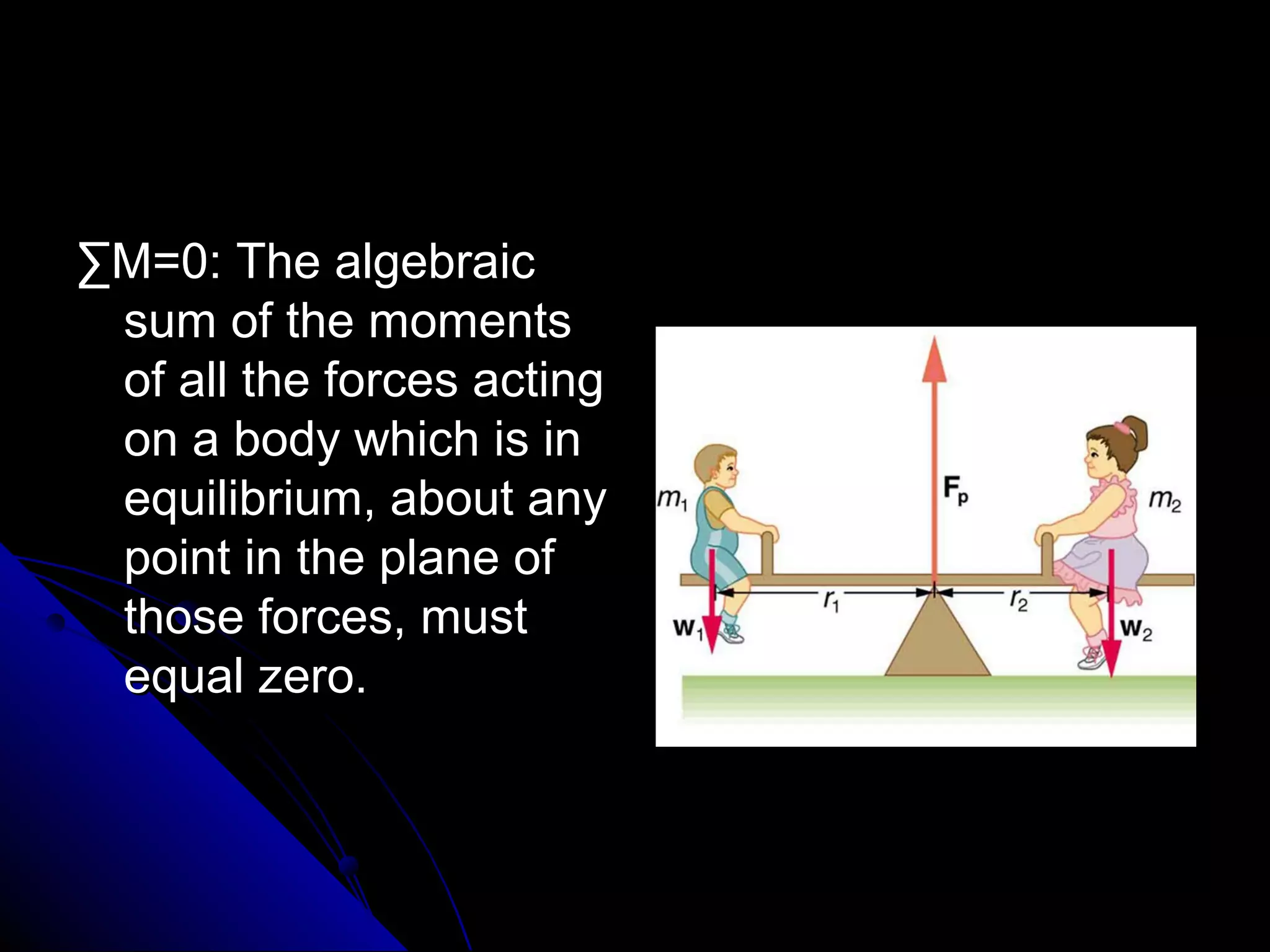
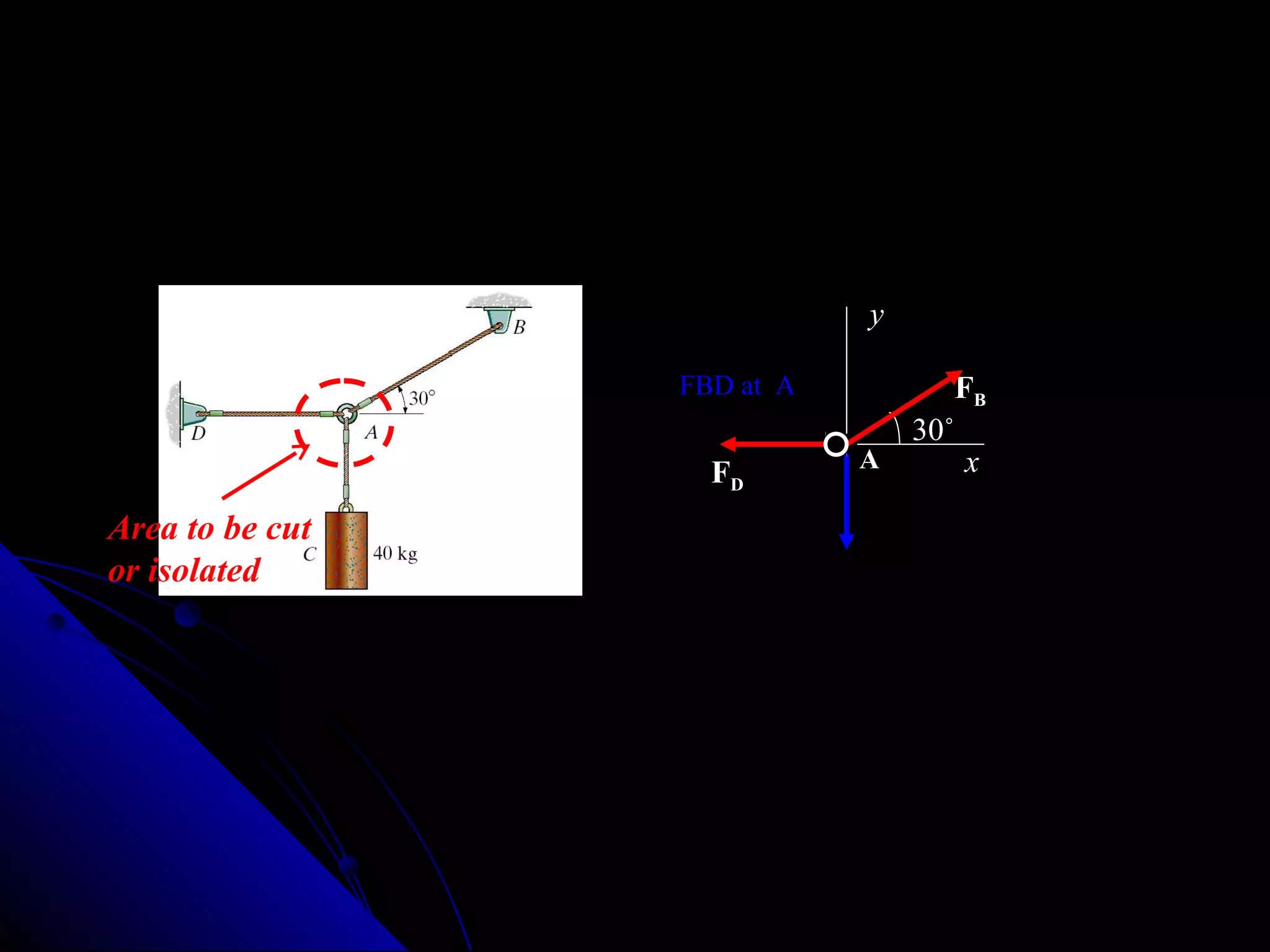
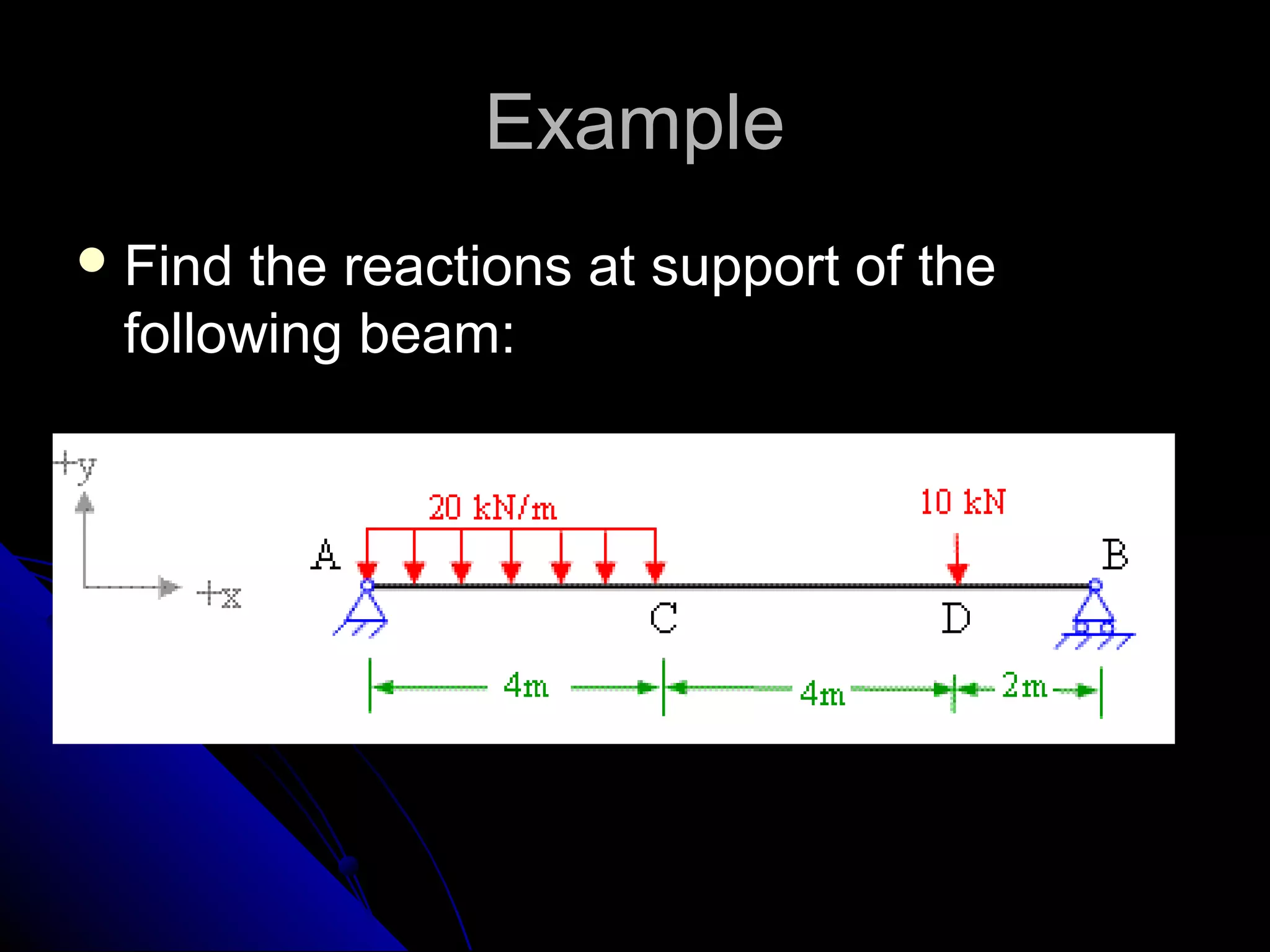
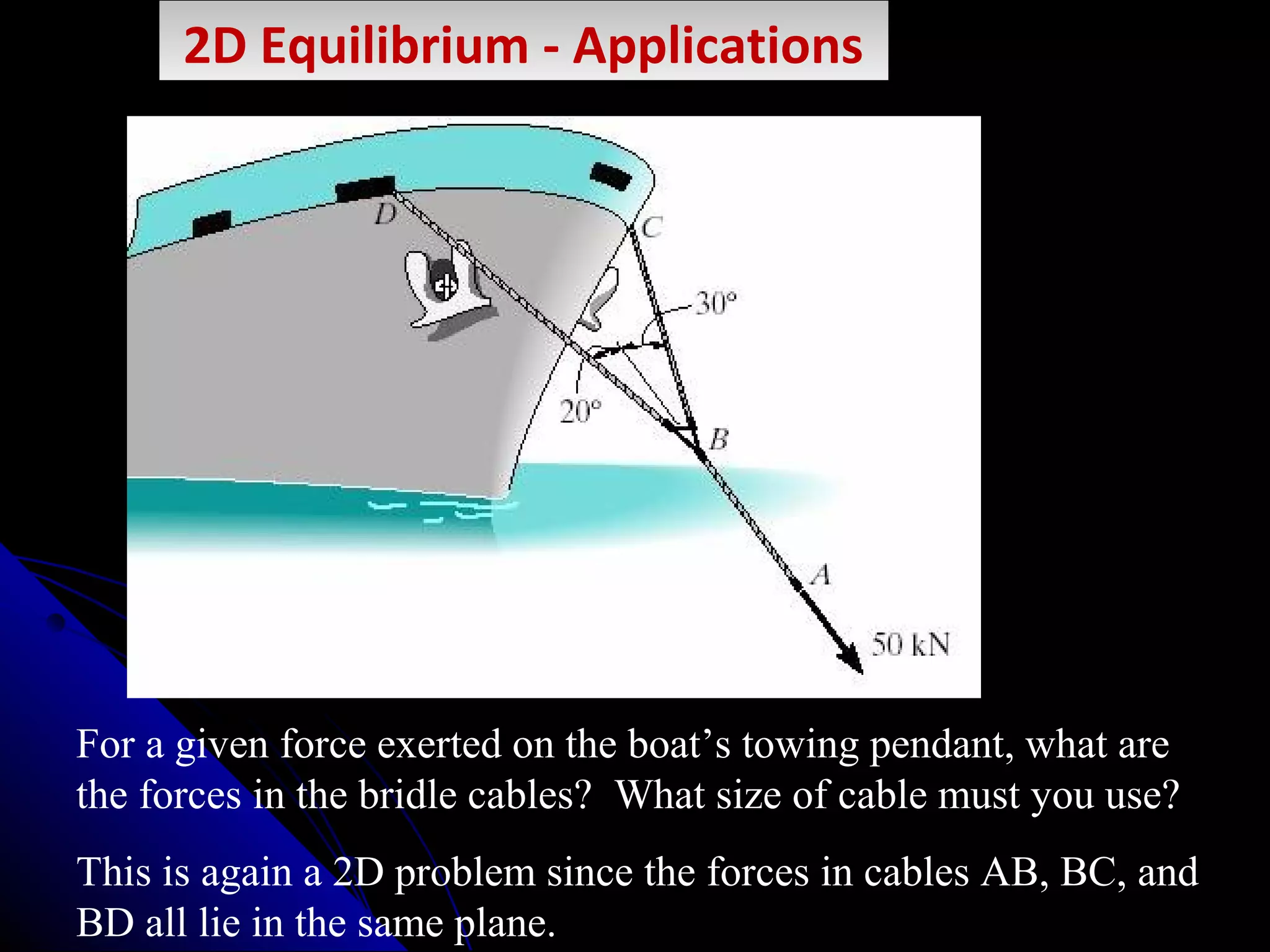
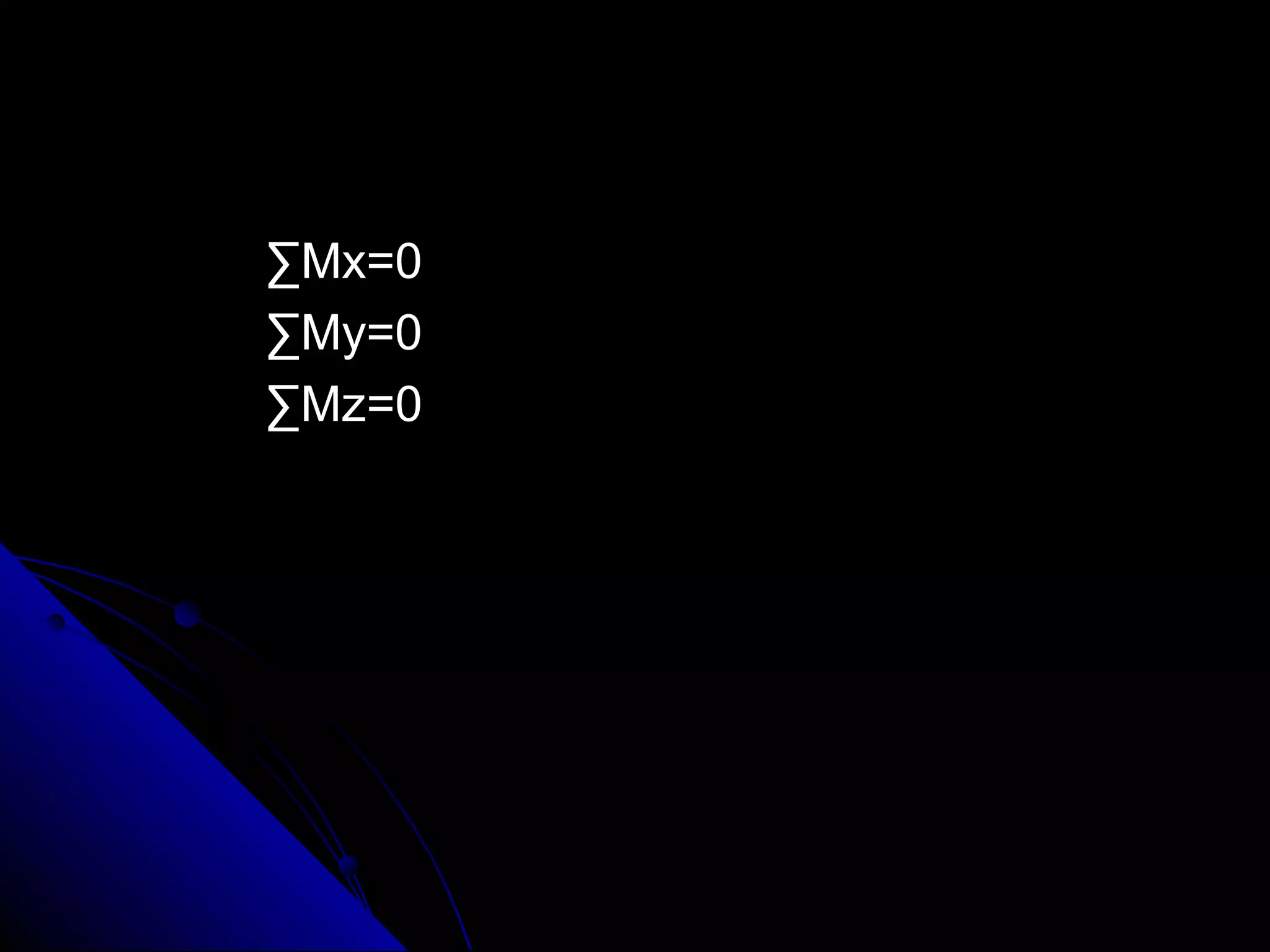This presentation discusses the concept of equilibrium in 2 dimensions. Equilibrium occurs when the net force and net torque on an object are both zero. This allows the object to remain at rest or in uniform motion. The key equations of equilibrium in 2D are: the sum of the horizontal forces equals 0 (ΣFx=0), the sum of the vertical forces equals 0 (ΣFy=0), and the sum of torques about the z-axis equals 0 (ΣMz=0). Examples are provided to demonstrate how to apply these equations to solve for unknown forces by drawing a free body diagram and setting up the appropriate equilibrium equations.