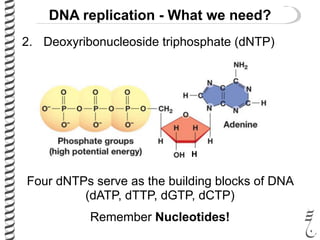
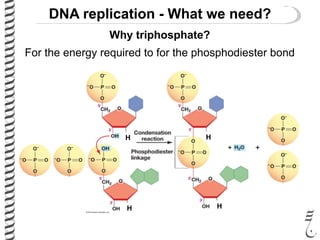
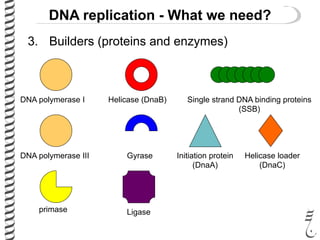
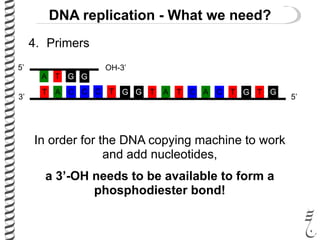
This document introduces the key elements needed for DNA replication in prokaryotes. It discusses the DNA template, building blocks (dNTPs), and proteins/enzymes involved. The main proteins/enzymes that are introduced are: DNA polymerase, which adds new nucleotides; helicase, which unwinds the DNA; single-stranded DNA binding proteins, which prevent rewinding; primase, which adds RNA primers for initiation; and ligase, which seals nicks in the newly synthesized strand. The goal is to explain the chemistry and functions of each component to introduce how prokaryotic DNA replication occurs.