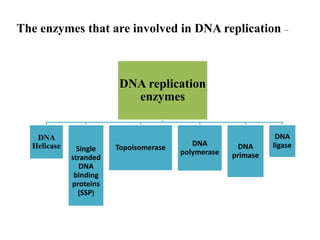
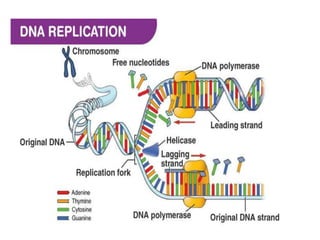
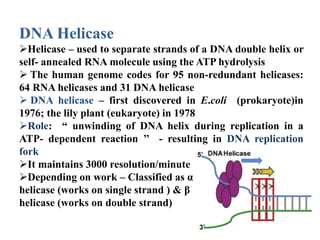
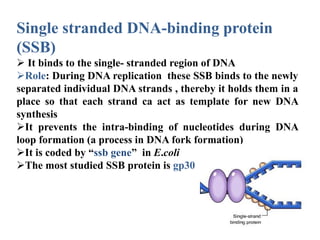
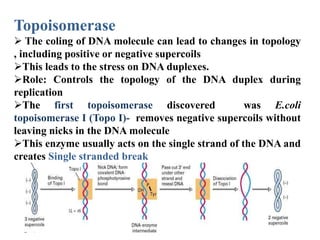
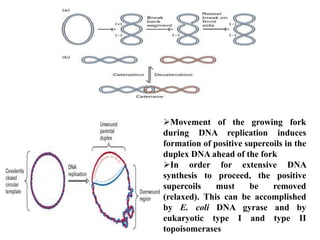
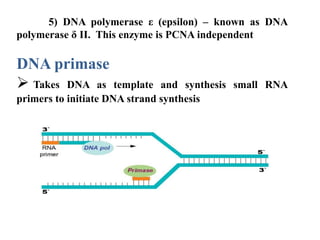
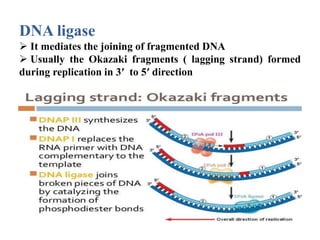
The key enzymes involved in DNA replication are helicase, single-stranded DNA binding proteins, topoisomerase, DNA polymerase, DNA primase, and DNA ligase. Helicase unwinds the DNA double helix using ATP hydrolysis. Single-stranded DNA binding proteins bind to the separated strands and prevent them from reannealing. Topoisomerase controls the topology of the DNA duplex during replication. DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands using the old strands as templates. DNA primase synthesizes RNA primers for DNA polymerase. And DNA ligase joins the DNA fragments produced during lagging strand synthesis.