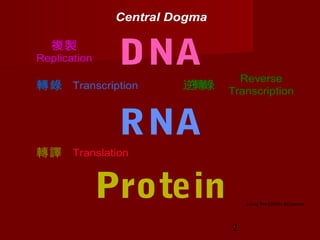
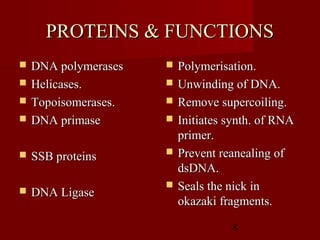
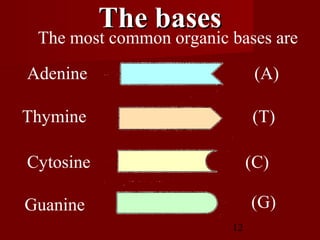
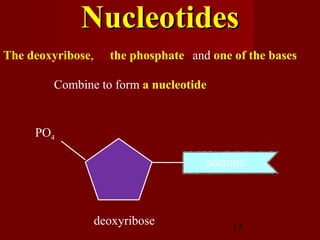
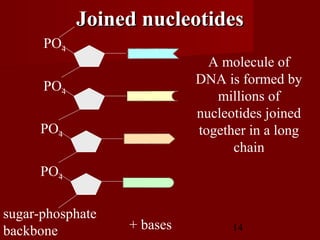
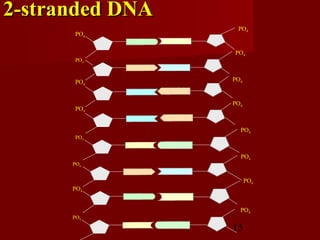
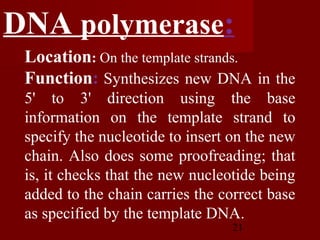
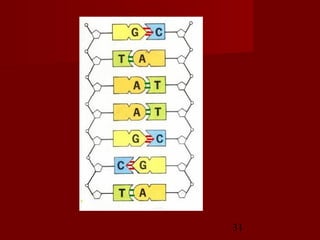
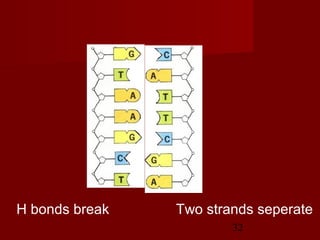
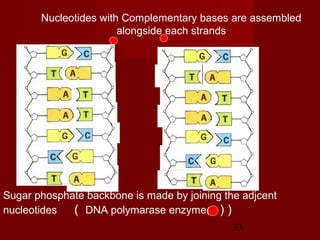
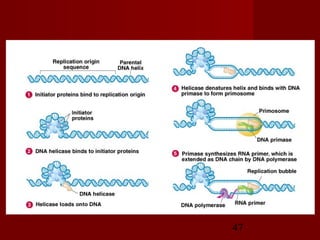
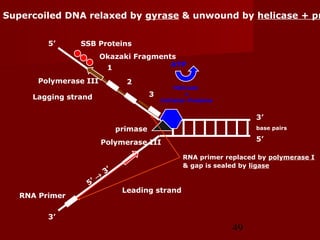
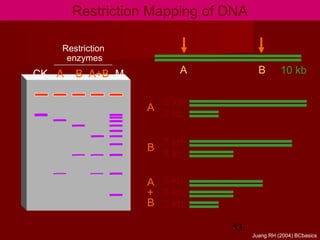
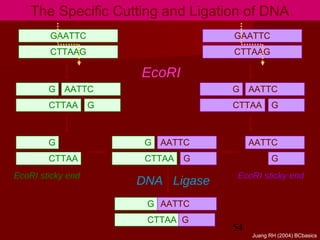
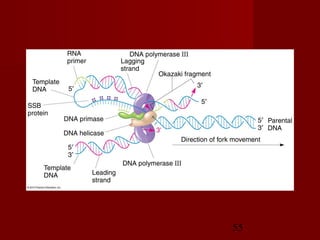
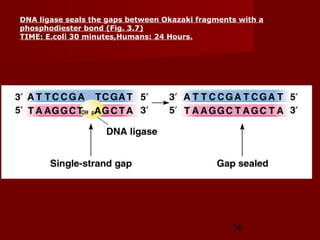
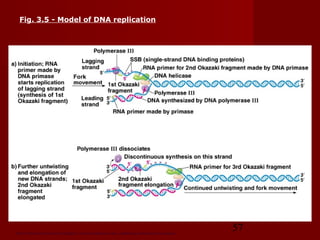
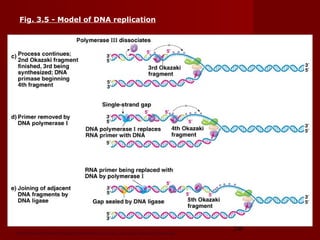
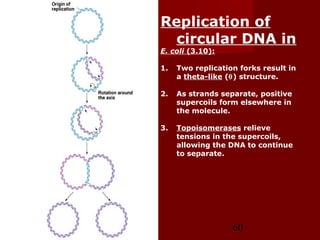
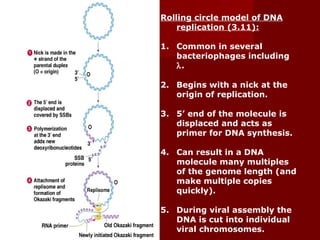
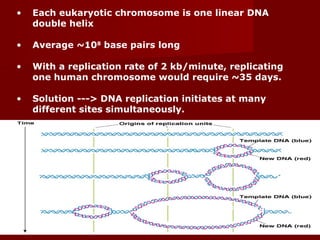
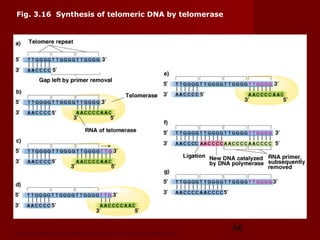
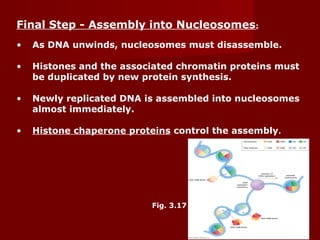
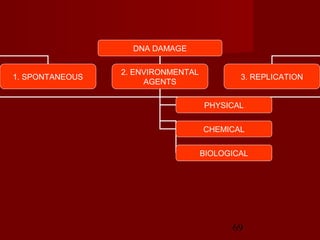
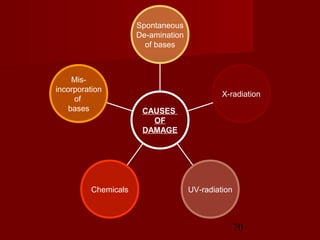
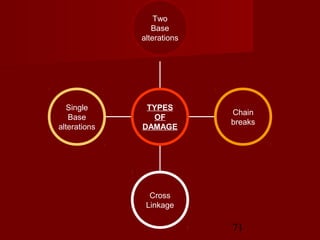
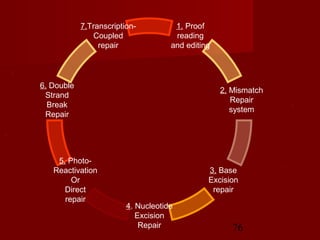
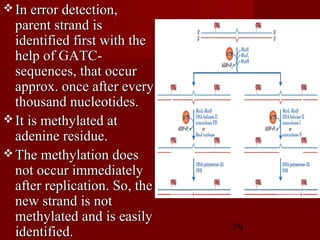
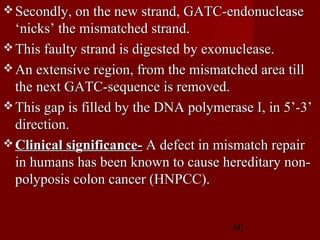
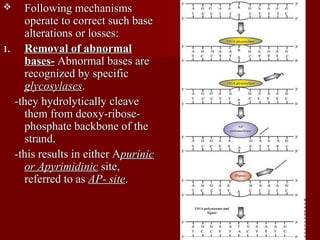
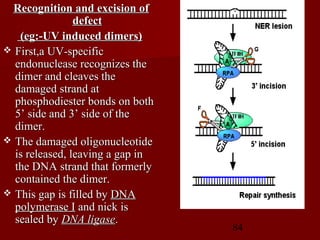
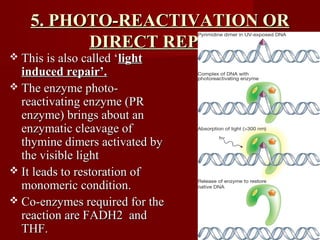
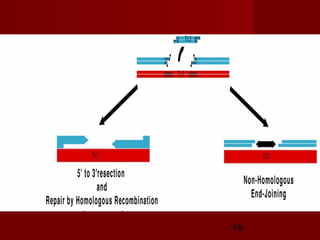
1. DNA replication is the process where a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It involves unwinding the DNA double helix into single strands and using DNA polymerases to synthesize new strands that are complementary to the original strands.
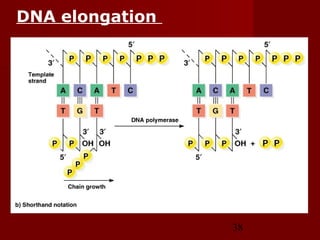
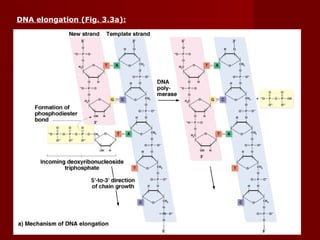
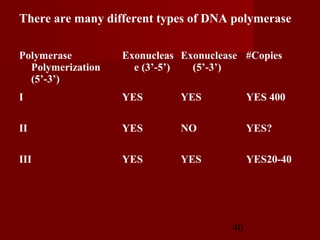
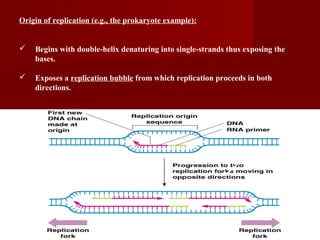
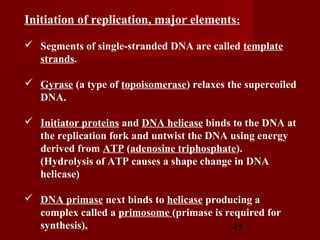
2. There are three main steps to DNA replication: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, enzymes help unwind the DNA at the origin of replication. In elongation, DNA polymerases add nucleotides to the 3' ends of the primers to extend the new DNA strands. Termination occurs when the replication forks meet at the end of the DNA molecule.
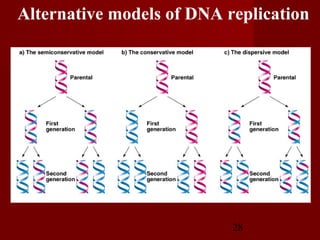
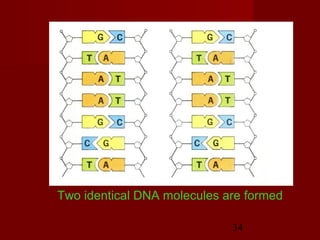
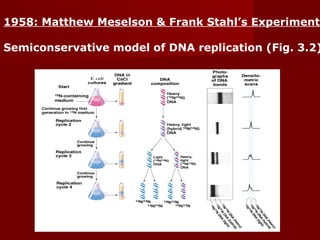
3. DNA replication is semiconservative, meaning the double helix splits into two double helices, with each