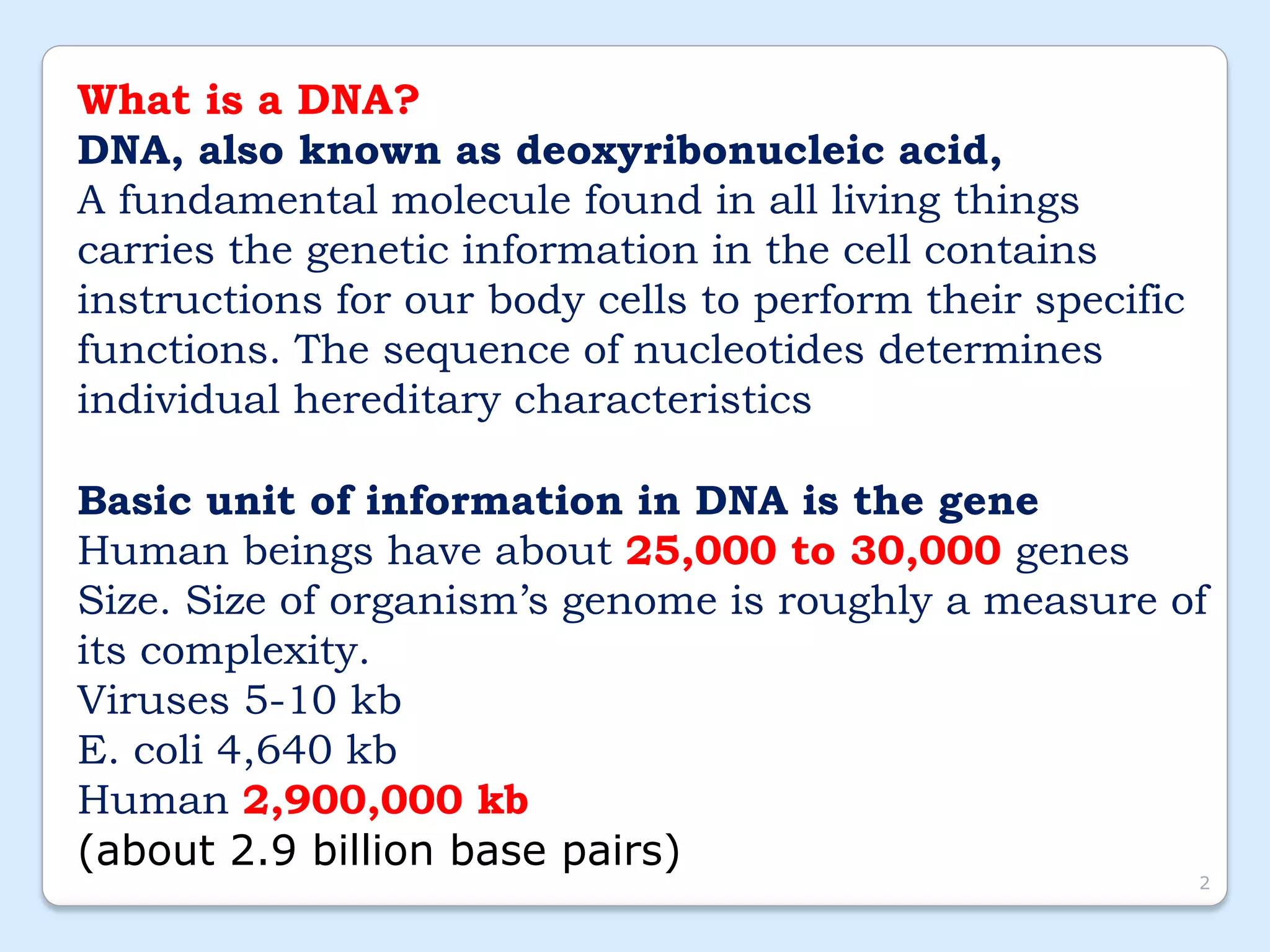
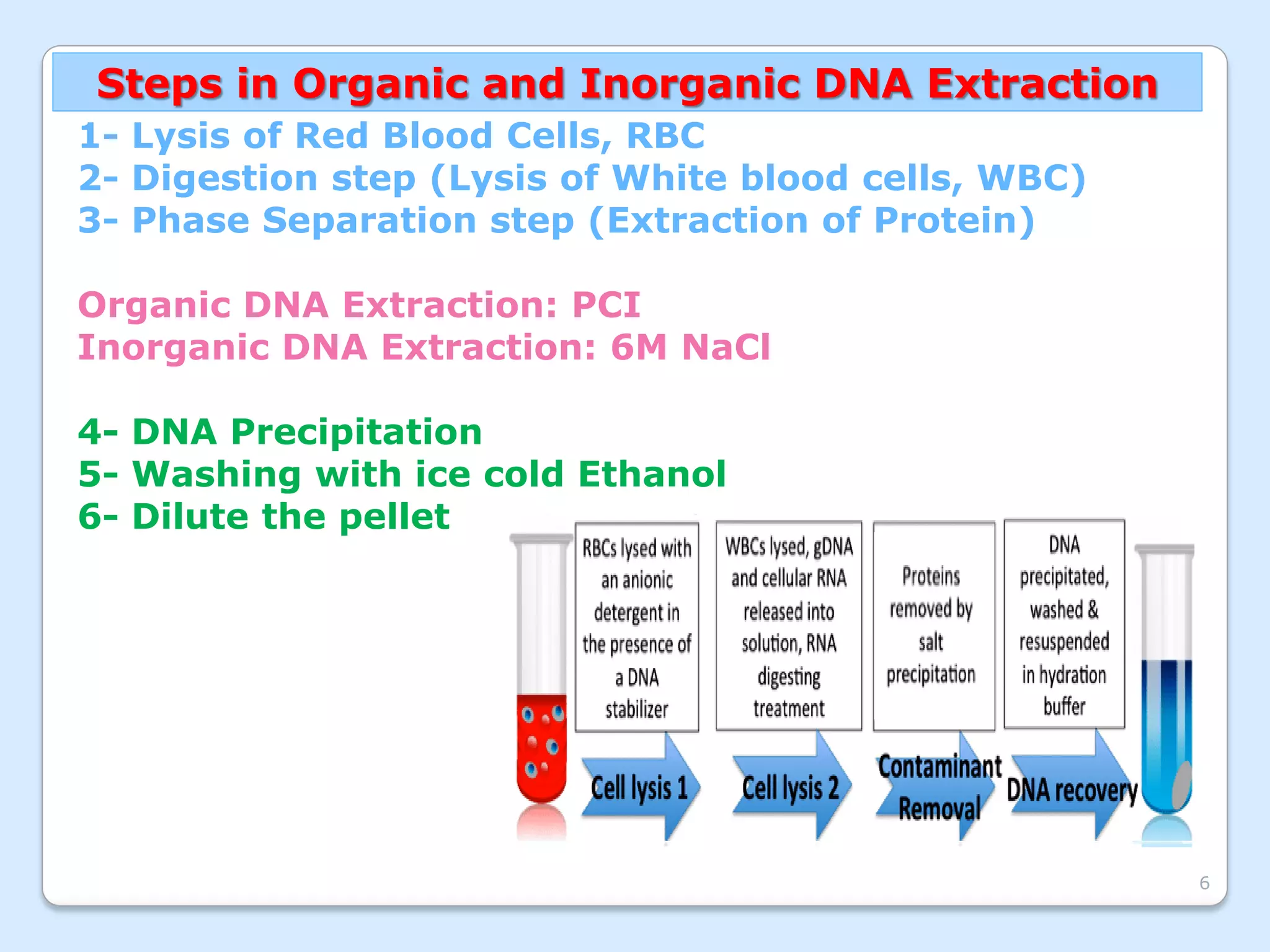
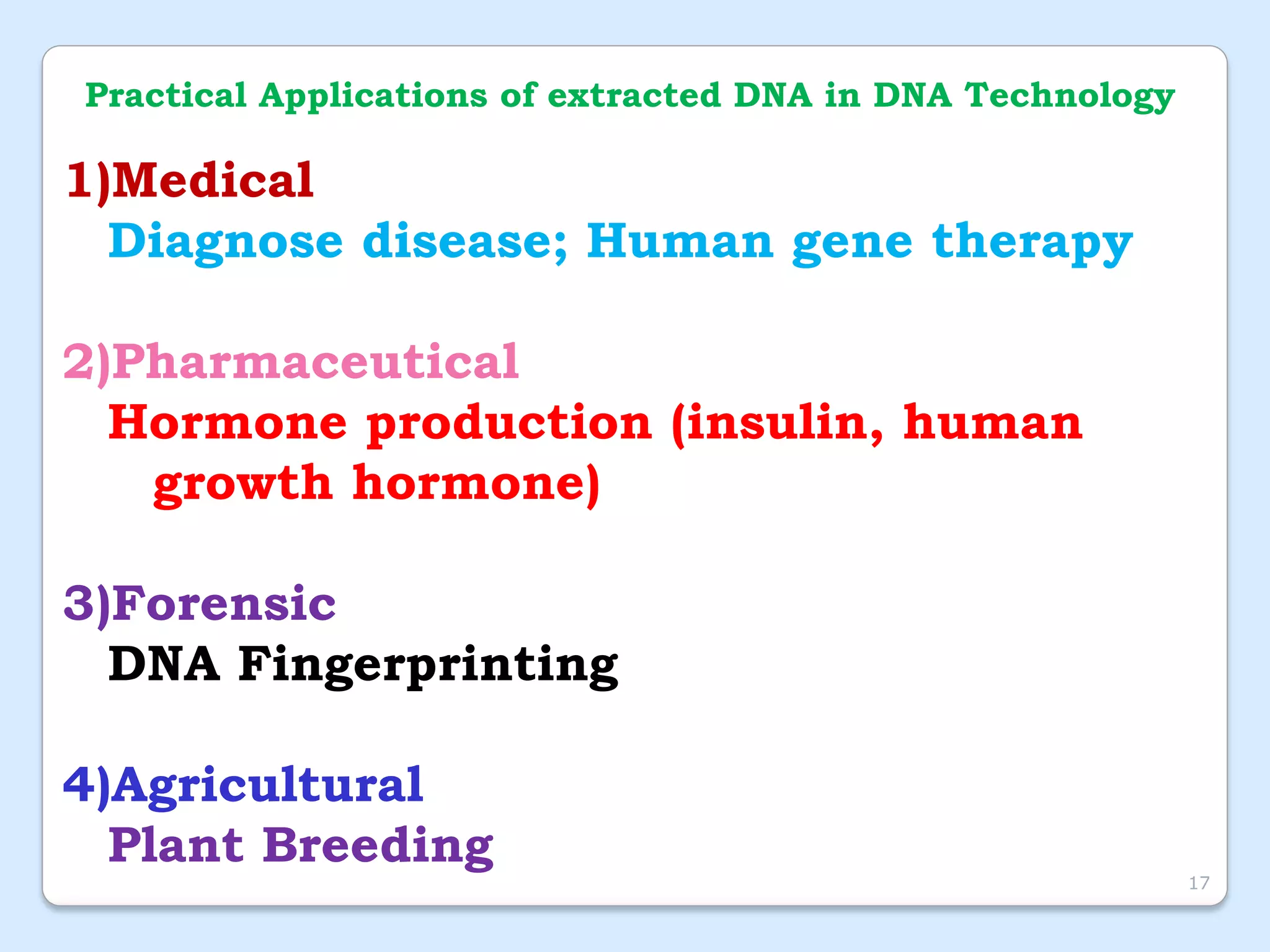
This document discusses DNA extraction methods. It defines DNA as the molecule that carries genetic information in cells. There are several common DNA extraction procedures, including organic phenol-chloroform extraction and non-organic proteinase K and salting out extraction. The organic extraction method uses phenol-chloroform to separate and purify DNA from other cellular components after cell lysis and protein digestion. It results in high-quality double-stranded DNA but is time-consuming and involves hazardous chemicals. Non-organic and chelex extractions are simpler alternatives that yield single-stranded DNA and remove PCR inhibitors. Extracted DNA has various applications, such as disease diagnosis, forensic DNA fingerprinting, and plant breeding.