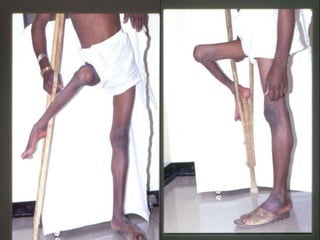
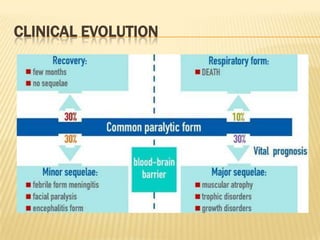
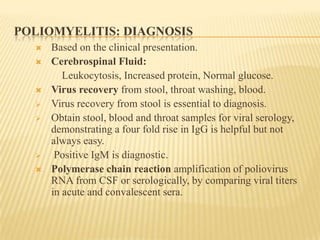
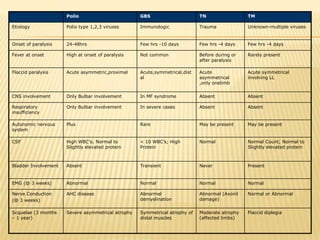
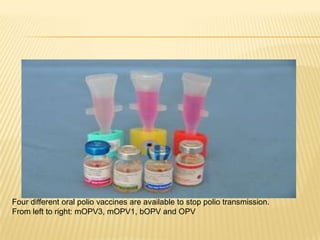
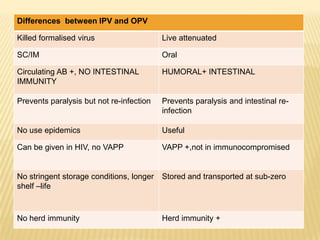
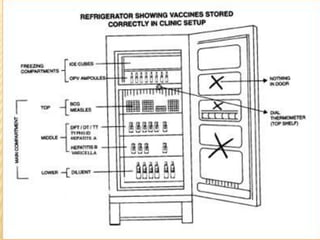
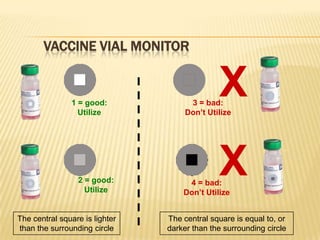
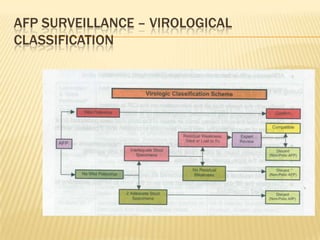
The document summarizes key information about acute poliomyelitis including its clinical diagnosis, cycle of infection, transmission, pathogenesis, immunity, risk factors, types of infection, treatment, vaccines, and strategies for eradication. Poliomyelitis is caused by three serotypes of poliovirus and spreads primarily through the fecal-oral route. It can cause abortive infection or paralytic disease. Treatment focuses on supportive care and vaccines aim to build immunity to stop transmission and eradicate the virus globally through high vaccination coverage and surveillance.