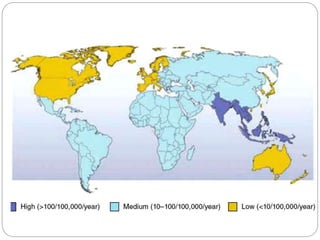
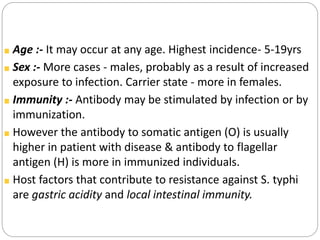
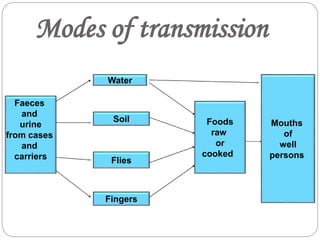
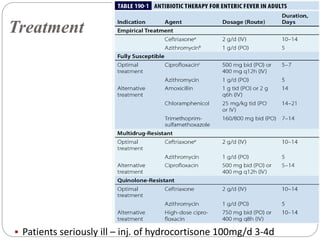
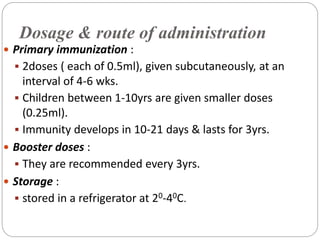
Typhoid fever is caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi. It remains a major public health problem worldwide, especially in parts of Asia, Africa and Latin America. In India, typhoid is endemic and a study showed 1% of children under 17 get typhoid each year. S. typhi only infects humans. People with typhoid can spread the infection through their feces and urine until they are treated. Carriers also spread infection asymptomatically. Prevention strategies include immunization, water purification, improved sanitation, and identifying and treating carriers. Symptoms include sustained fever, abdominal pain, and constipation or diarrhea. Complications can be serious without treatment.