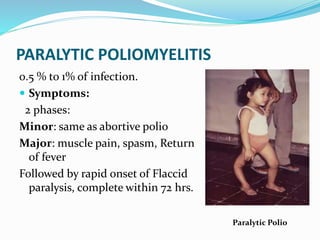
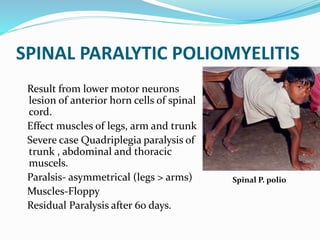
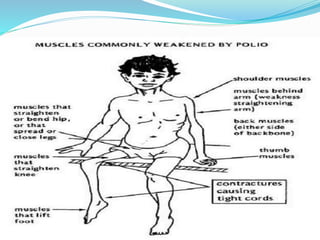
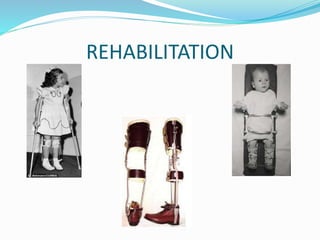
Poliomyelitis is an acute viral infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. It has affected humans for thousands of years. While effective vaccines were developed by the mid-20th century, polio outbreaks were still common worldwide. The presentation provides an overview of the history, epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment, prognosis, and prevention of poliomyelitis. It also describes rehabilitation programs and case studies of polio survivors.