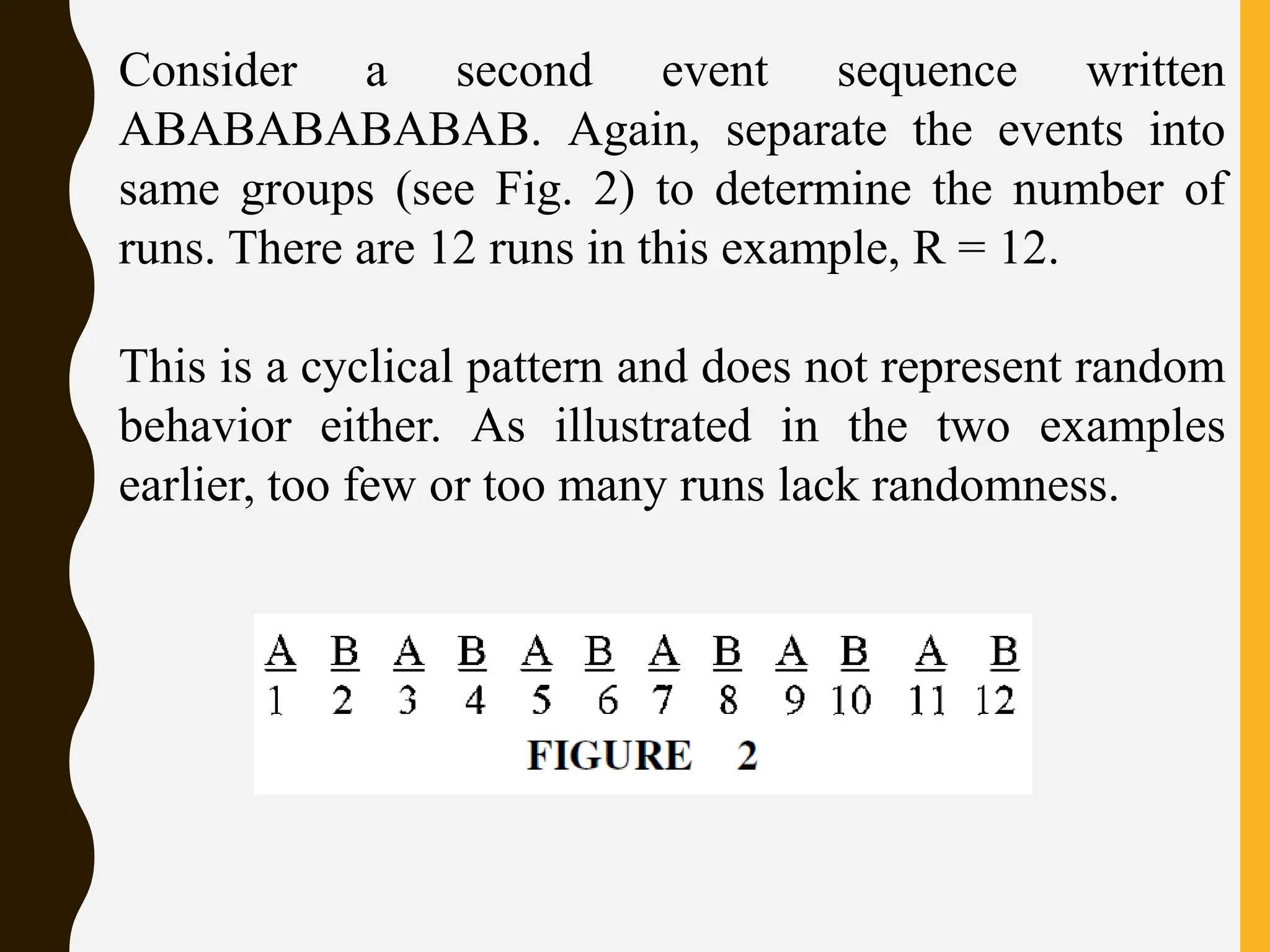
The runs test can be used to analyze a series of events for randomness. It involves separating a sequence into runs of the same event and counting the number of runs. For small sample sizes, the number of runs is compared to critical values in a table to determine if it falls within or outside the critical region, indicating whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis of randomness. Examples provided demonstrate applying the runs test to analyze whether a teacher called on students randomly by gender and whether a student's quiz scores were random.