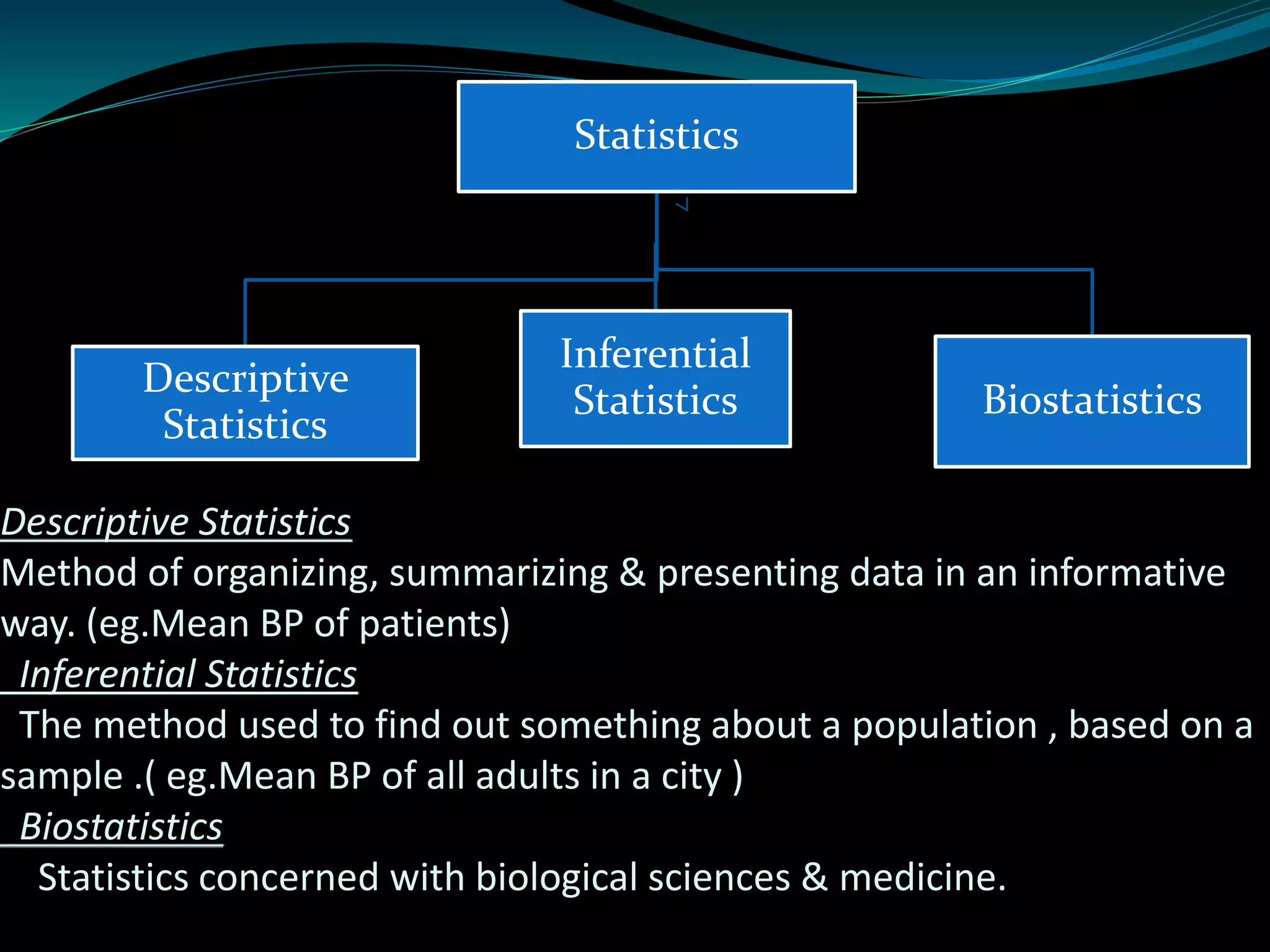
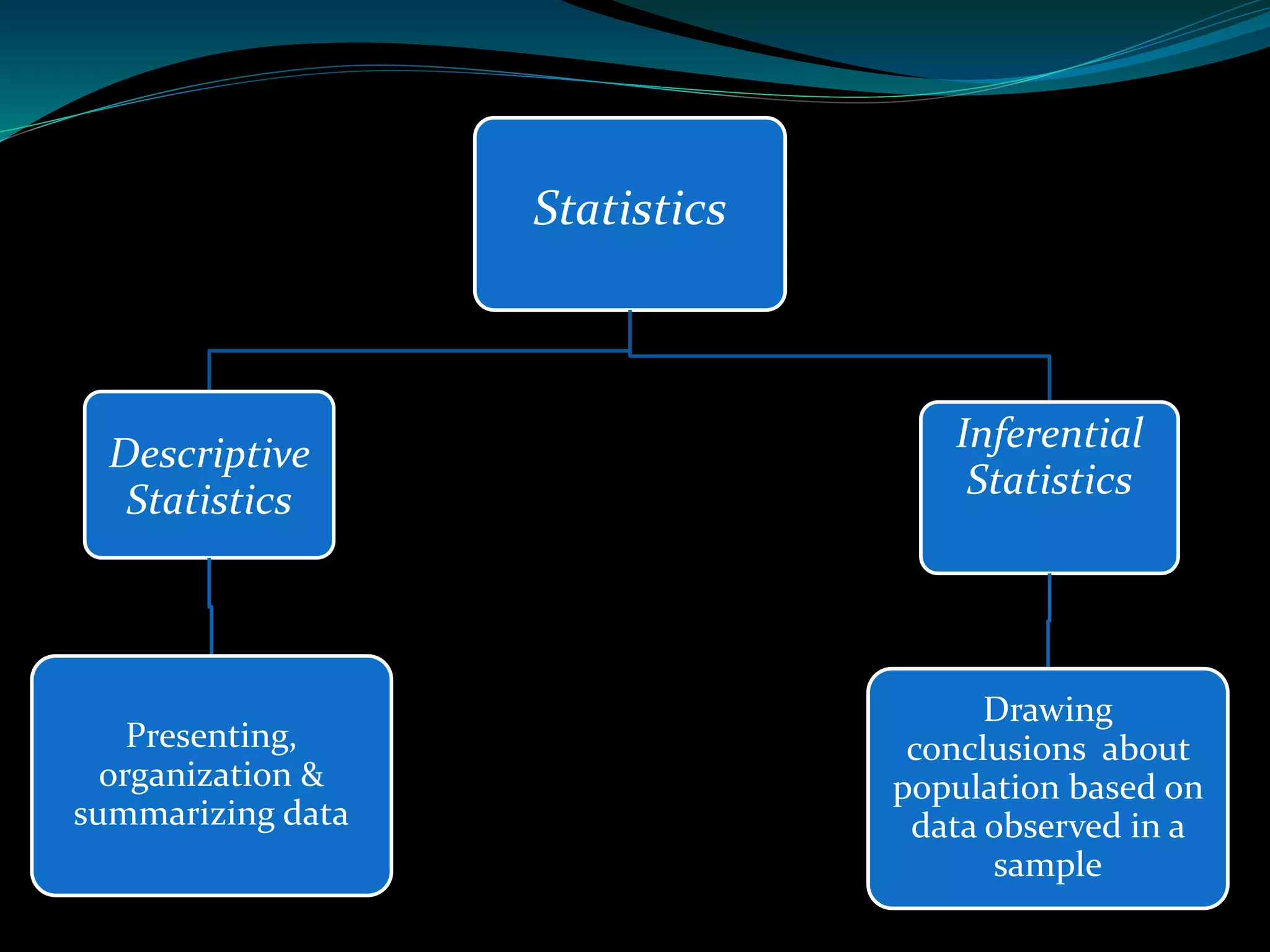
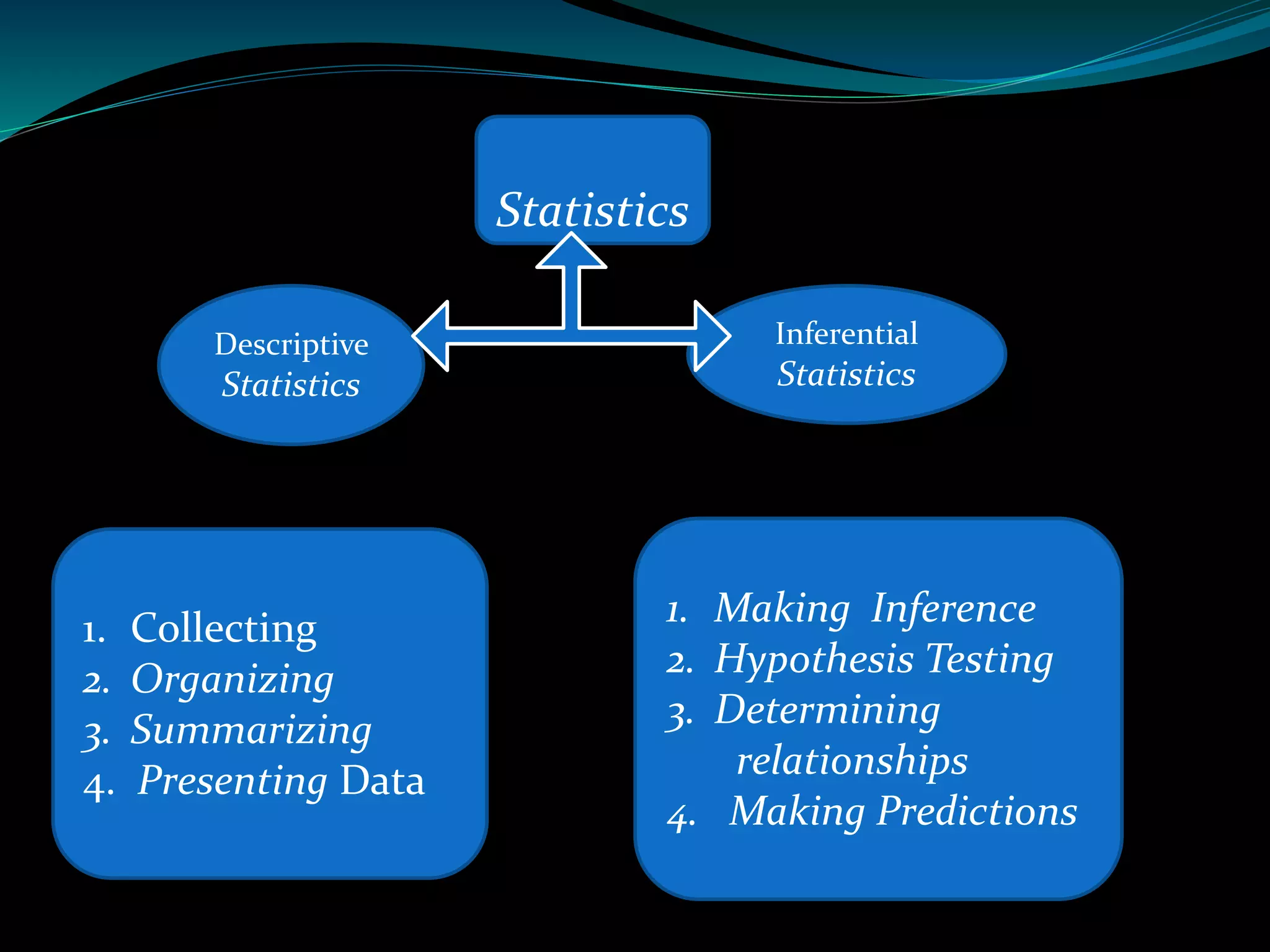
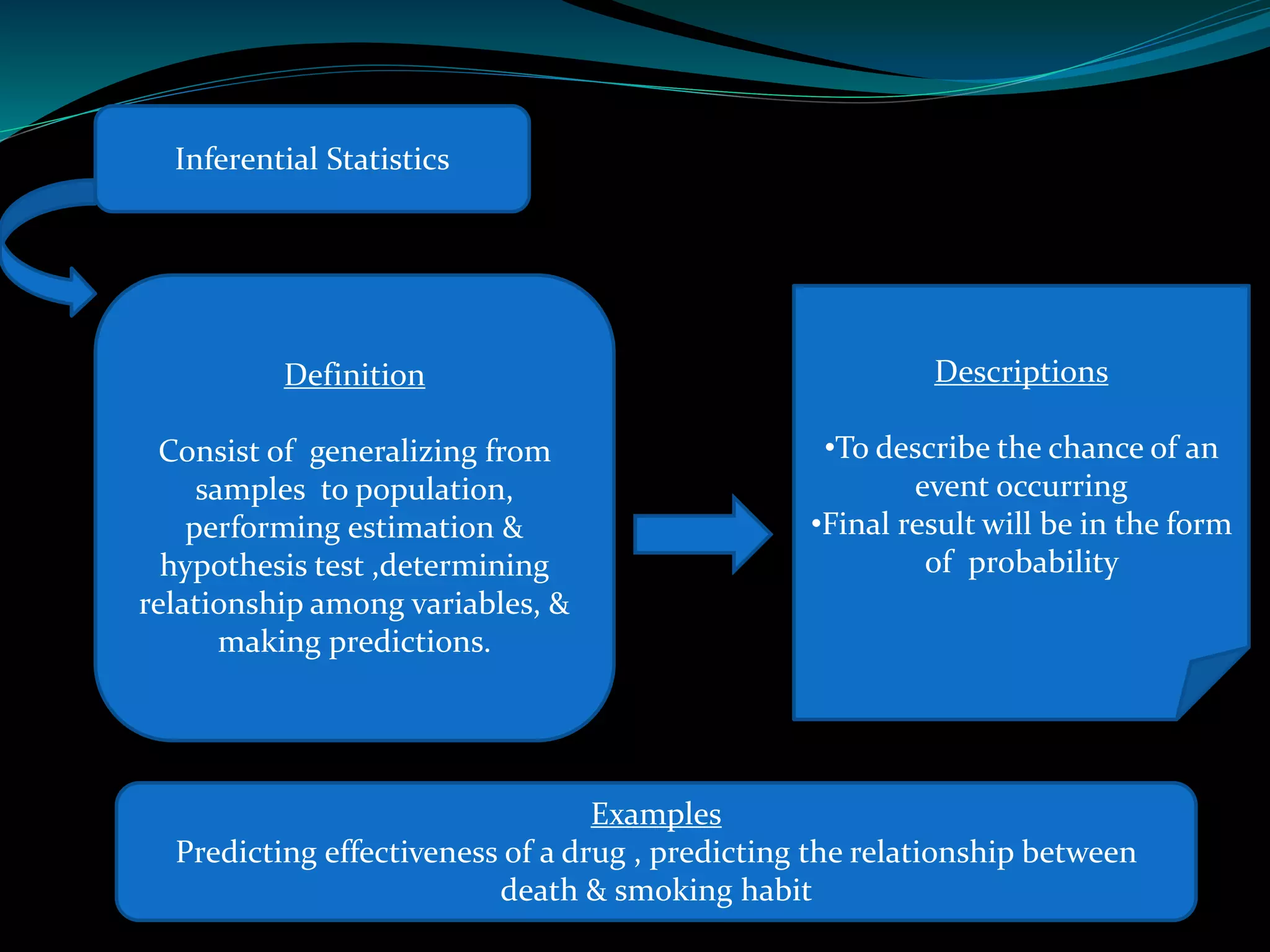
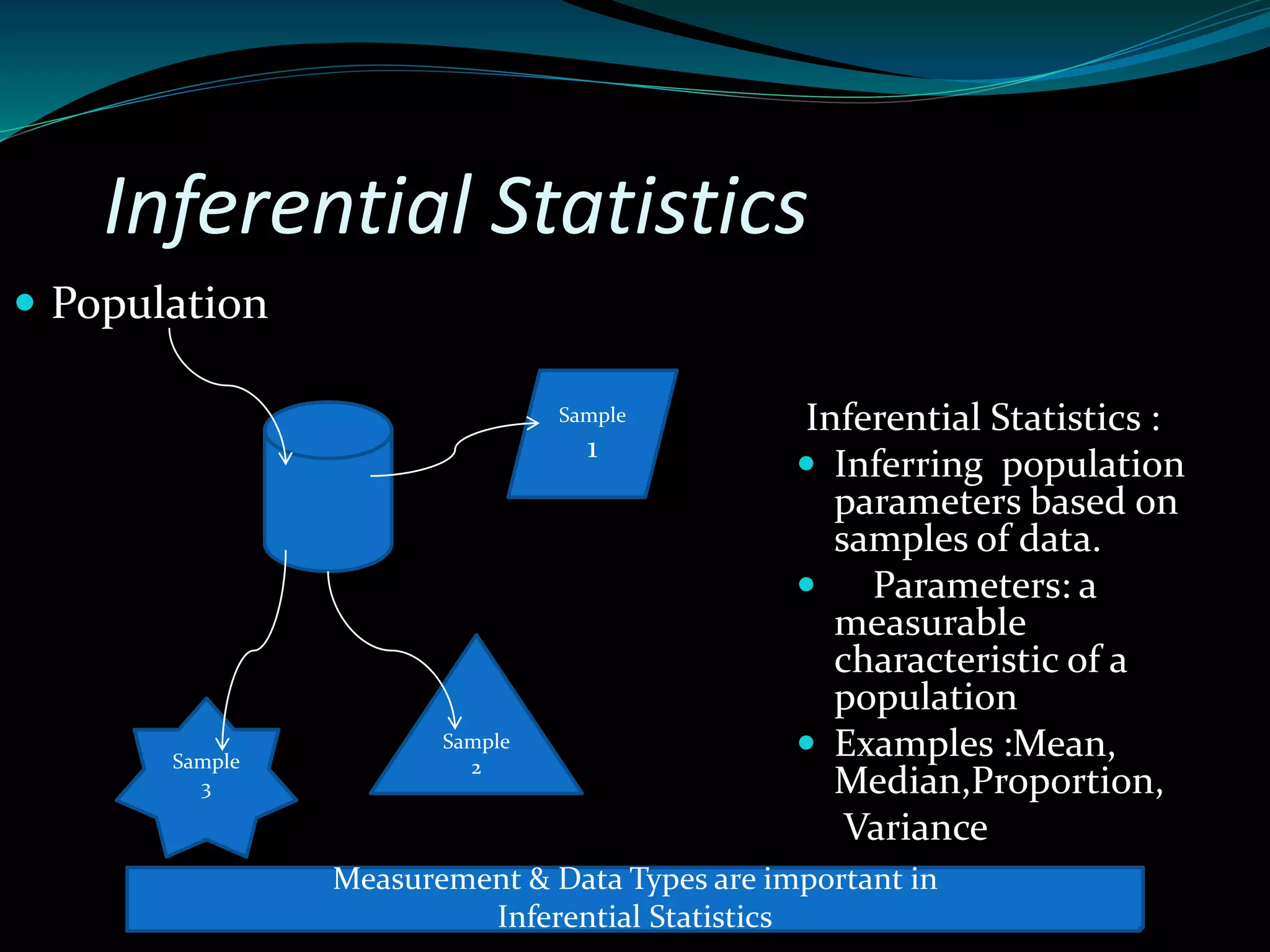
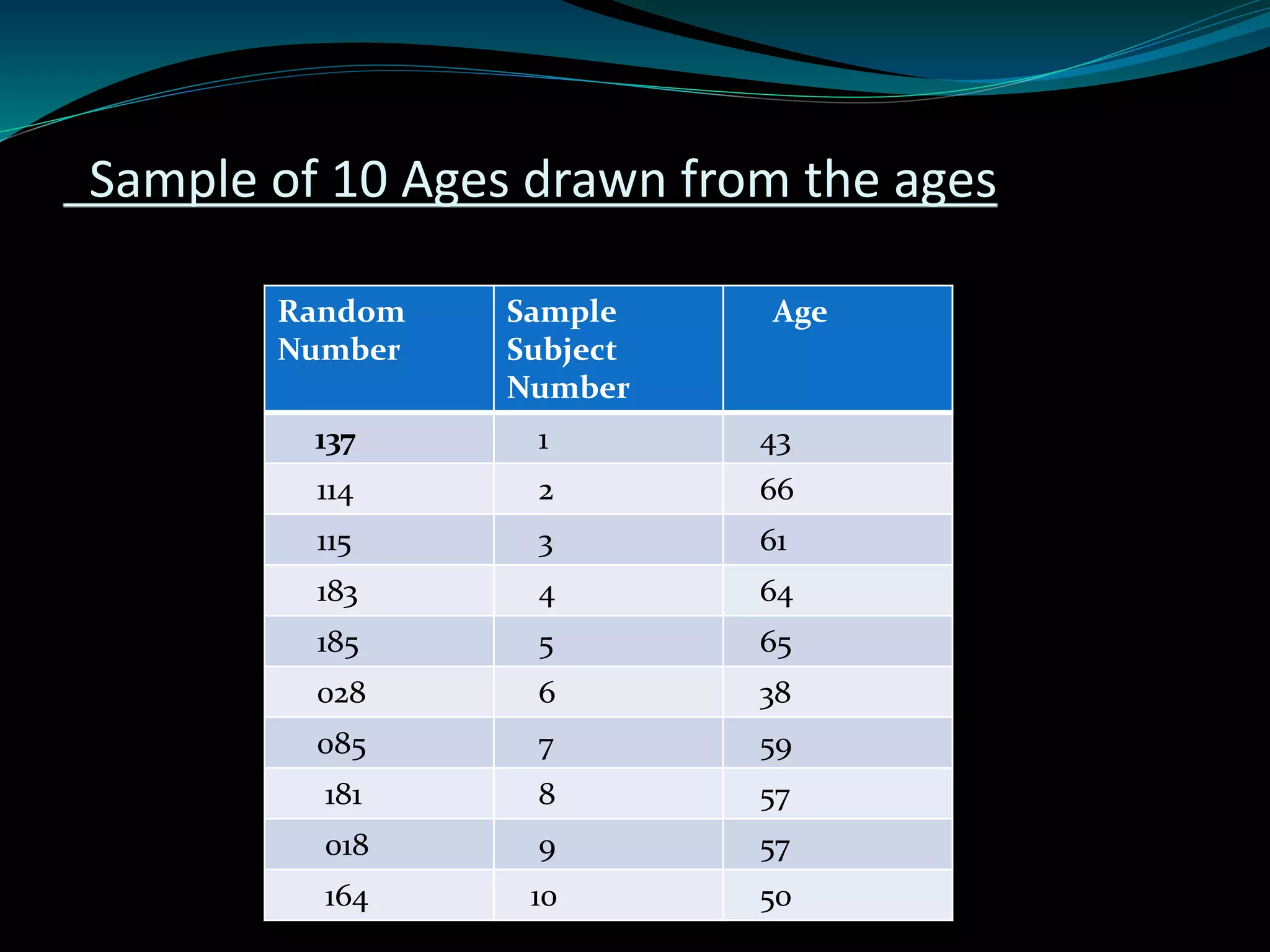
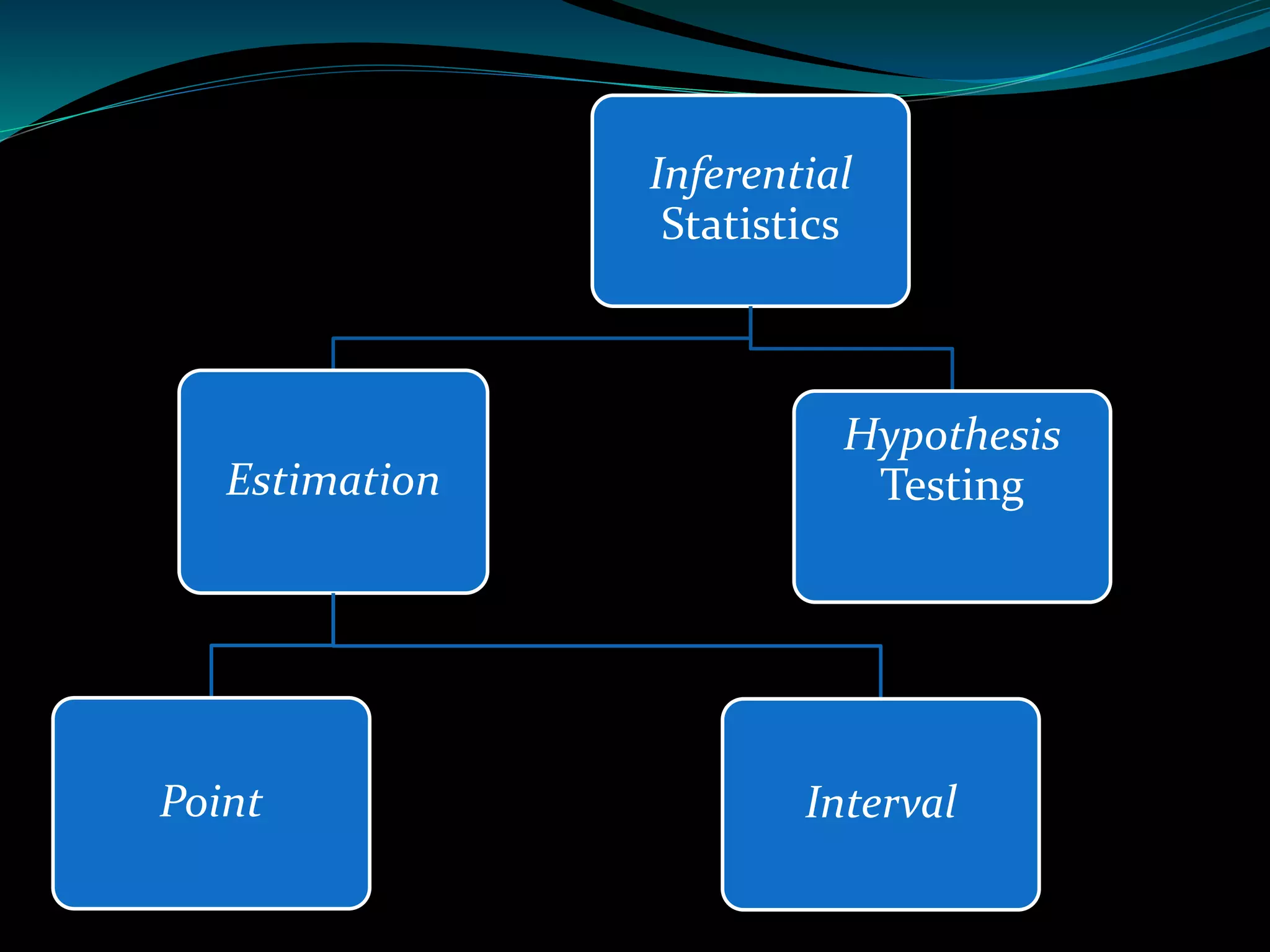
This document discusses inferential statistics and different types of samples that can be drawn from a population. Inferential statistics involves making inferences about a population based on a sample. It consists of generalizing from samples to populations, estimating parameters, hypothesis testing, and determining relationships. Two main methods are estimation, which uses a sample to estimate a parameter and construct a confidence interval, and hypothesis testing, which involves assuming and testing a null hypothesis against collected data. Types of samples discussed are simple random samples, systematic samples, and stratified random samples.