Embed presentation
Download to read offline

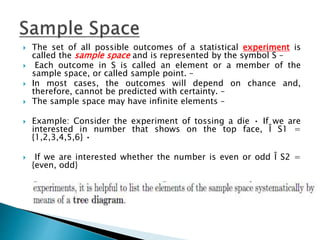
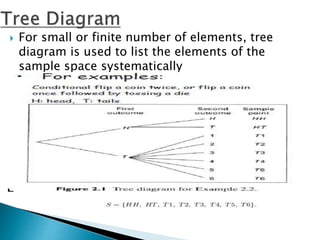
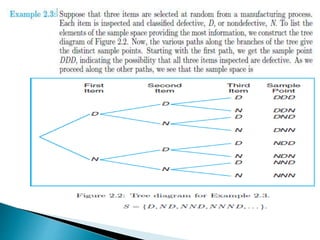
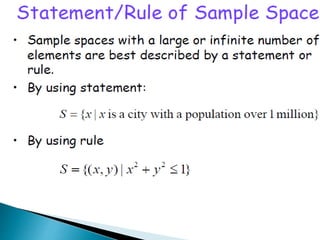

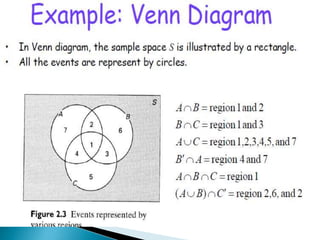

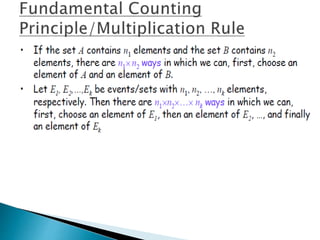







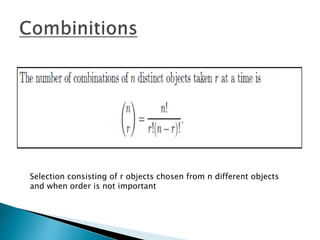


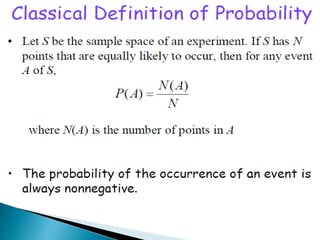











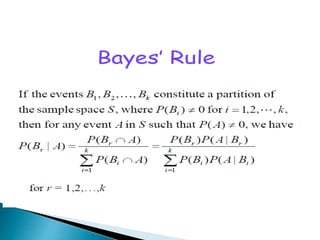



The document defines key concepts in probability and statistics including sample space, sample points, permutations, combinations, dependent and independent events, and conditional probability. It provides examples of calculating the number of possible outcomes for experiments like tossing a die, answering true/false questions, and creating license plates. Sample space represents all possible results of an experiment and can include finite or infinite elements. Permutations and combinations are used to calculate arrangements and selections of objects. Conditional probability expresses the likelihood of one event given another event.


































