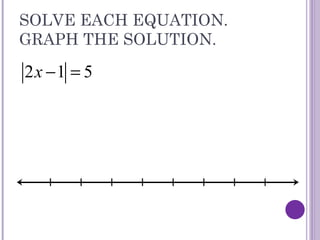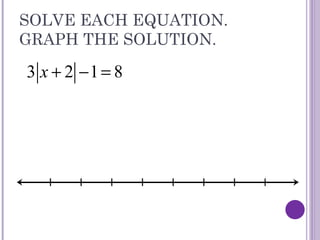Embed presentation
Downloaded 116 times

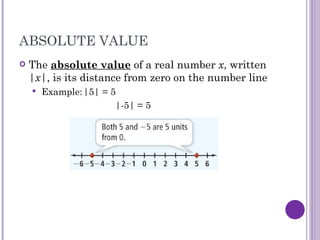


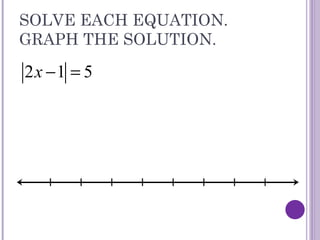

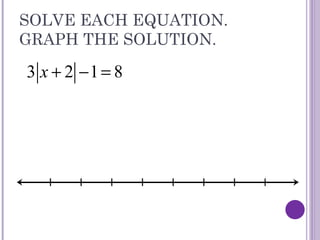









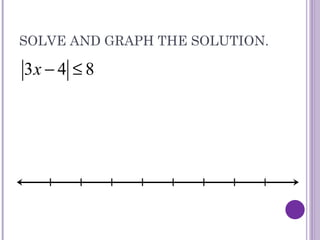

This document discusses absolute value equations and inequalities. It explains that absolute value equations can have two solutions because opposites have the same absolute value. It provides steps for solving absolute value equations which include isolating the absolute value and removing the absolute value signs. Solutions then need to be checked for extraneous solutions, which are solutions that do not satisfy the original equation. The document also covers absolute value inequalities and how to write them as compound inequalities without absolute value symbols in order to solve and graph the solutions.