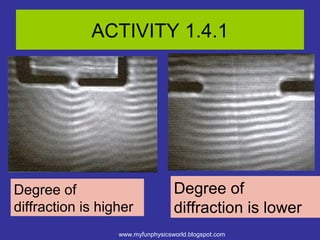
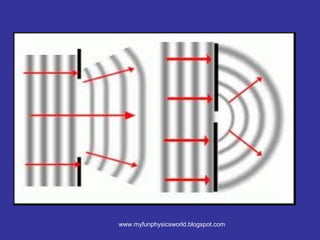
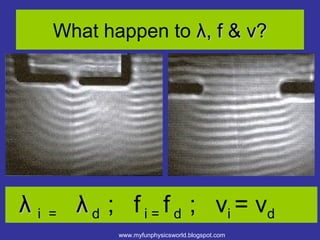
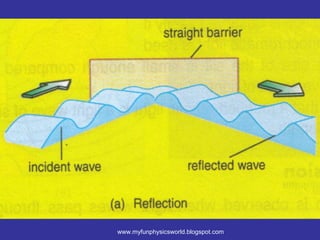
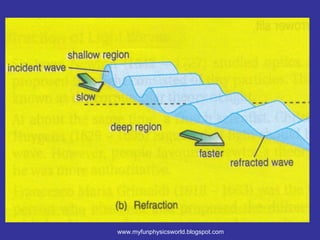
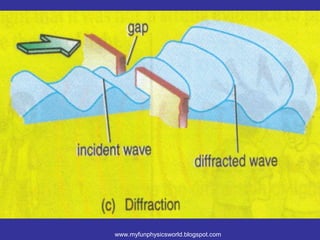
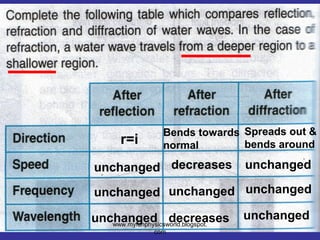
The document describes the concept of diffraction of waves. It discusses how diffraction causes waves to bend or spread out when passing through an obstacle or gap. It provides examples of diffraction of water waves and discusses how the degree of diffraction depends on factors like the size of the obstacle or gap relative to the wavelength. The document also discusses how diffraction causes the shape, direction and amplitude of waves to change while keeping the wavelength and frequency the same. It poses sample questions assessing understanding of diffraction concepts.