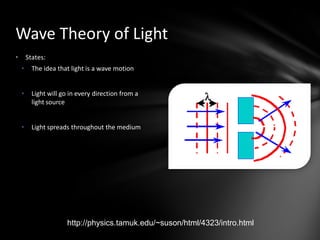
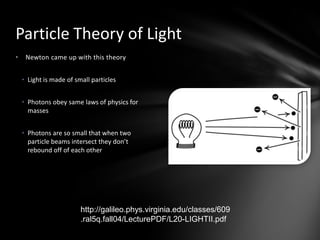
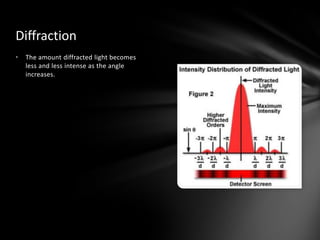
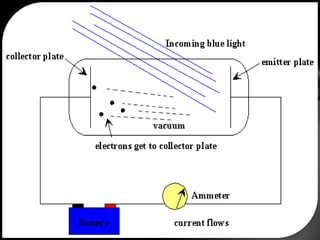
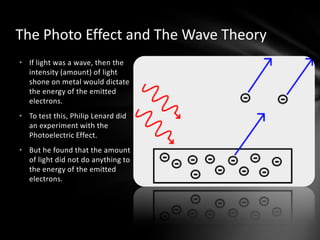
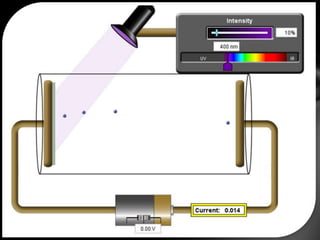
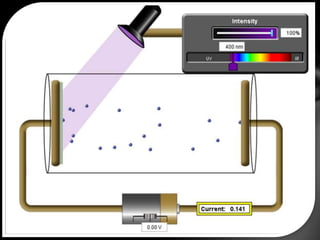
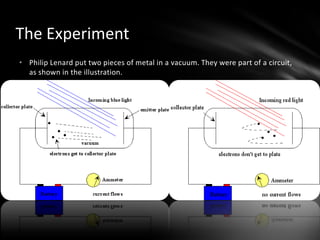
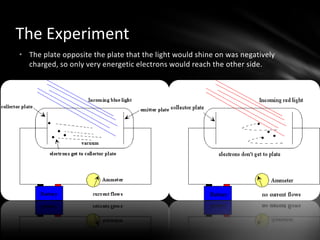
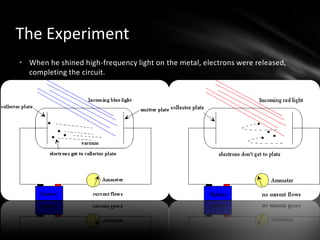
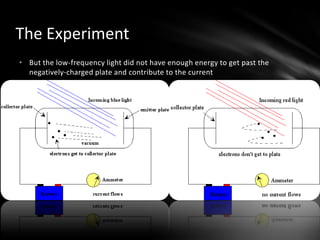
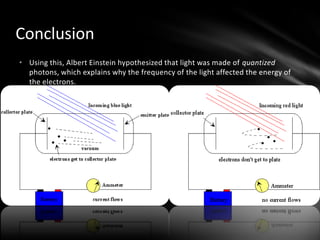
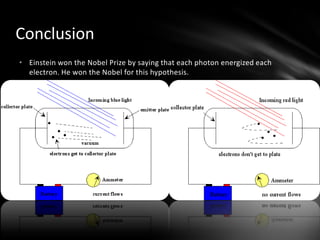
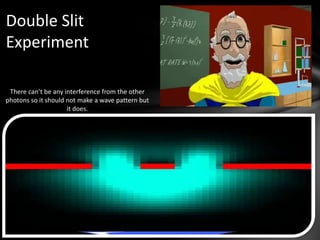
This document discusses the wave-particle duality of light. It describes early theories that light was either a wave (wave theory) or particle (particle theory). Later, Max Planck and Albert Einstein provided evidence that light exhibits both wave-like and particle-like properties. The photoelectric effect and double slit experiment showed that light behaves as particles in some cases and waves in others, demonstrating its dual nature.