Embed presentation
Downloaded 72 times



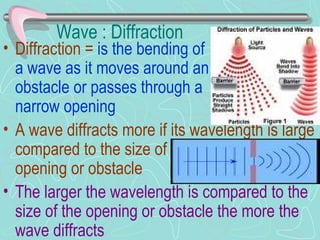


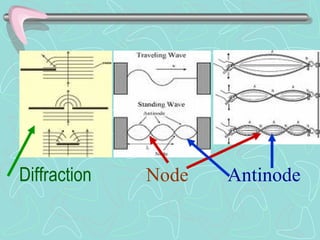
Reflection occurs when a wave bounces off a surface it cannot pass through and does not change the wave's speed or frequency but may flip it upside down. Refraction is the bending of a wave as it enters a new medium and occurs because the wave speed changes, with one side moving slower. Diffraction causes a wave to bend around obstacles, with larger wavelengths diffracting more. Interference results from waves combining constructively to make a larger displacement or destructively to make a smaller one. A standing wave appears stationary and has nodes of no displacement and antinodes halfway between nodes.






