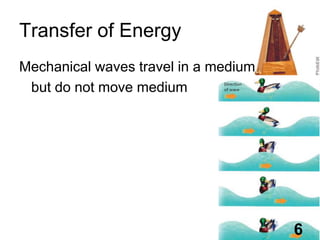
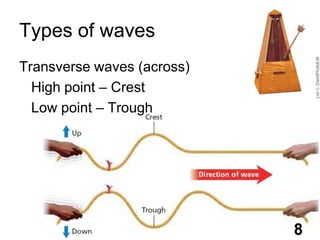
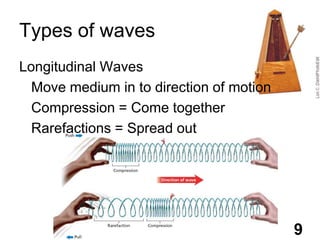
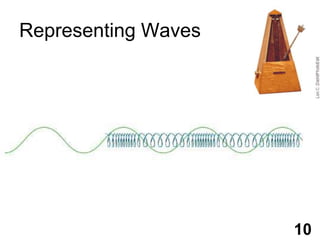
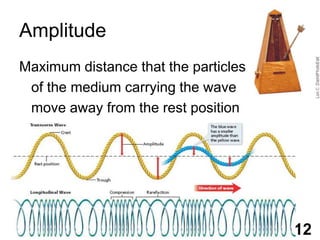
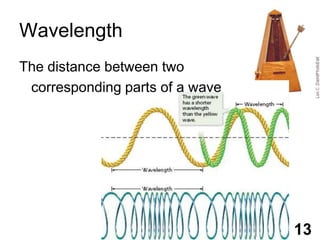
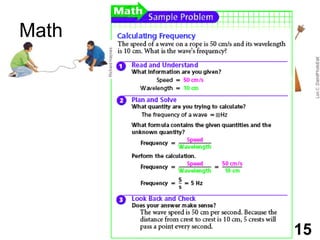
Students will learn about different types of waves including transverse waves, longitudinal waves, and electromagnetic waves. The key properties of waves that will be discussed are amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed. Waves transfer energy through a medium and can be described by their height, how often they occur, and how fast they travel.