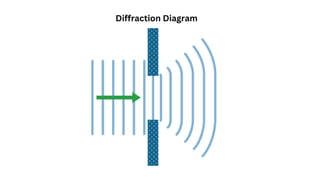
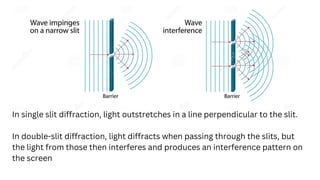
Diffraction is the bending and spreading of waves around obstacles or through openings. It occurs for all types of waves including light, water, and sound waves. The amount of diffraction increases with wavelength and decreases with aperture size. Huygens' principle and the Huygens-Fresnel principle describe how each point on a wavefront can be seen as a secondary source of waves, helping to explain diffraction. Practical examples of diffraction include interference patterns from double slits and its role in technologies like communication systems and medical imaging.