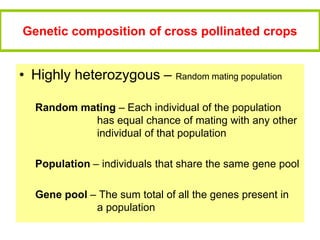
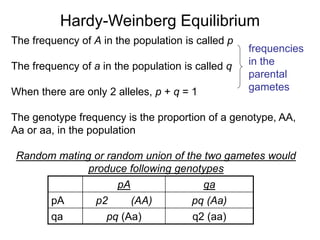
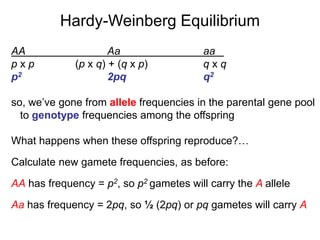
1) The document discusses Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, which states that allele and genotype frequencies in a population remain constant from generation to generation if the population is large, randomly mating, and not experiencing selection, migration, mutation or genetic drift.
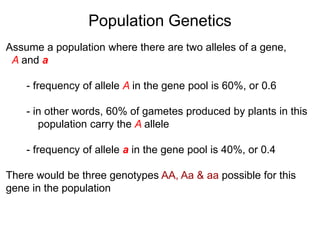
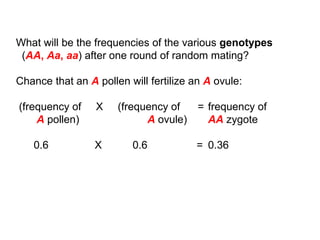
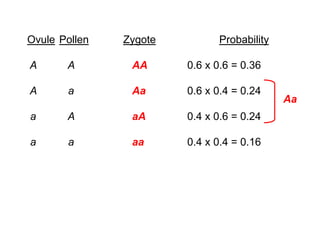
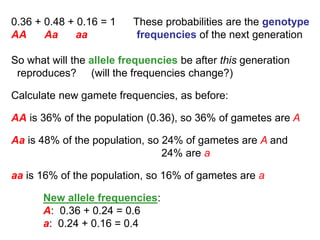
2) It provides an example showing how the frequencies of genotypes AA, Aa and aa are calculated based on the allele frequencies p and q in the parental generation.
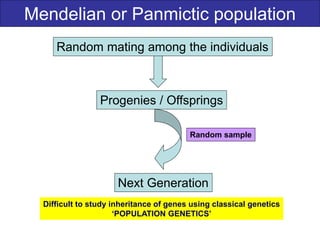
3) The document explains that under Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the allele frequencies p and q will remain the same in subsequent generations, even as the specific genotype frequencies may change during mating.