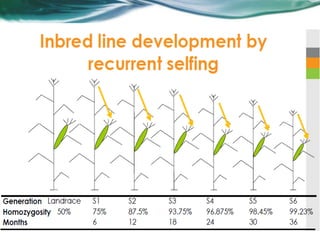
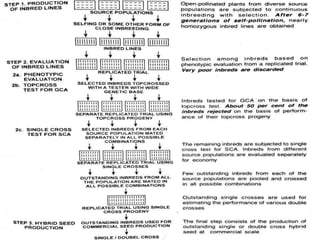
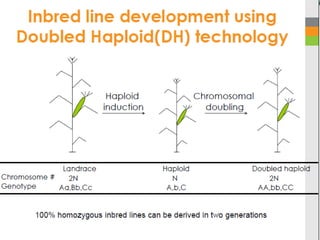
The document discusses the development of hybrid varieties in cross-pollinated crops, highlighting the importance of inbreeding depression and heterosis. It details the three main steps in maize hybrid production: inbred development, evaluation, and hybrid seed production, including methods such as top cross and single cross for assessing inbred performance. Furthermore, it outlines the procedures for hybrid seed production while emphasizing the need for isolation to maintain genetic purity.