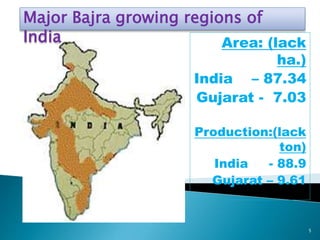
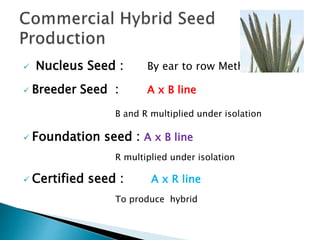
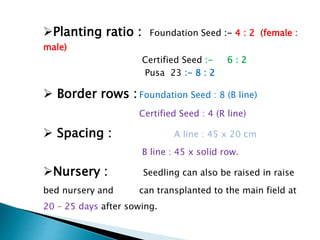
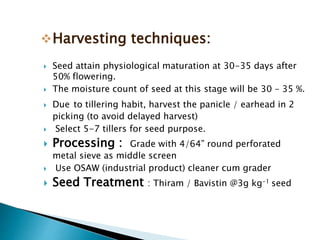
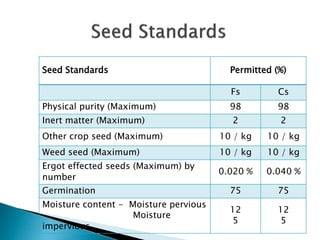
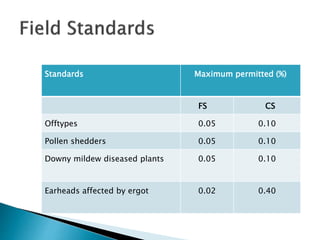
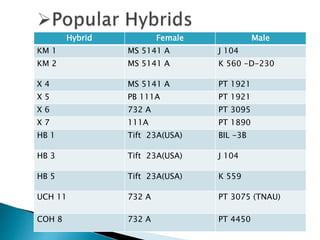
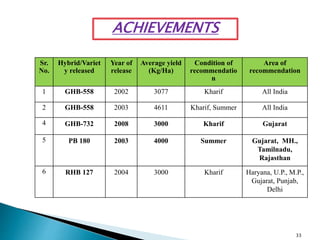
This document discusses hybrid seed production in bajra (Pennisetum glaucum). It begins with the botanical details of bajra and then discusses its taxonomy and floral biology. It describes the cytoplasmic genetic male sterility system used for hybrid seed production along with the different classes of seed (nucleus, breeder, foundation, certified). The document outlines the major bajra growing regions in India and details the steps involved in hybrid seed production, including isolation requirements, planting methods, rogueing, pollination synchronization techniques, and harvesting. It also provides information on pest and disease management, post-harvest processing, storage methods and seed standards. Finally, it lists some popular bajra hybrid