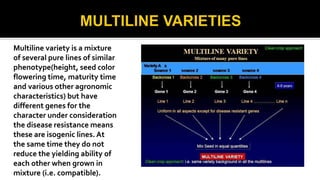
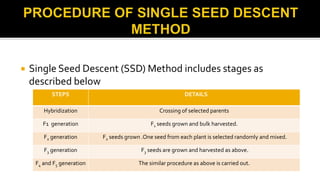
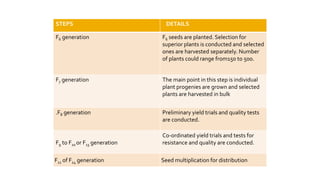
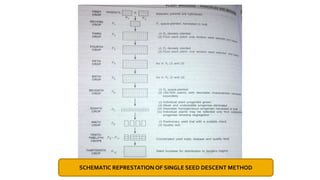
The document discusses single seed descent (SSD) method and multiline varieties. It begins by explaining the SSD method, which involves selecting a single seed randomly from selected plants at each generation to make the bulk, instead of bulking the whole seed lot. This method is useful for improving quantitative traits like yield rather than qualitative traits. It then describes the steps involved in the SSD method from hybridization to seed multiplication. The document also discusses advantages and disadvantages of the SSD method and multiline varieties. It provides examples of crops developed using these methods like wheat varieties Kalyan Sona and KML7404.






![Author(s): Kulbhushan Saxena; Rachit K Saxena; Rajeev KVarshney; M Prasad International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics,
Patancheru, India
Abstract –
•Long duration required for generation advancement in pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp] is one of the major
bottlenecks in realizing rapid genetic gains.
•Therefore, a technology for rapid generation turnover is warranted to facilitate the development of new cultivars and
recombinant inbred lines.
•Breeding of early‐maturing cultivars has now opened up the possibility of rapid generation advance (RGA) in this crop.
•This paper reports the development of an RGA technology that integrates the germination of immature seeds with single
seed descent method of breeding.
•RESULT-The results showed that immature 35‐day‐old seeds can be used successfully to turn over a generation of
pigeonpea with 100% seed germination. These way 3/4 successive generations can be grown within a year.The
methodology presented in this study will accelerate the breeding process for breeding cultivars and develop rapidly the
materials required for genomics research in pigeonpea.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ssdppt-220130065923/85/Single-seed-descent-and-multilines-varieties-ppt-10-320.jpg)