Embed presentation




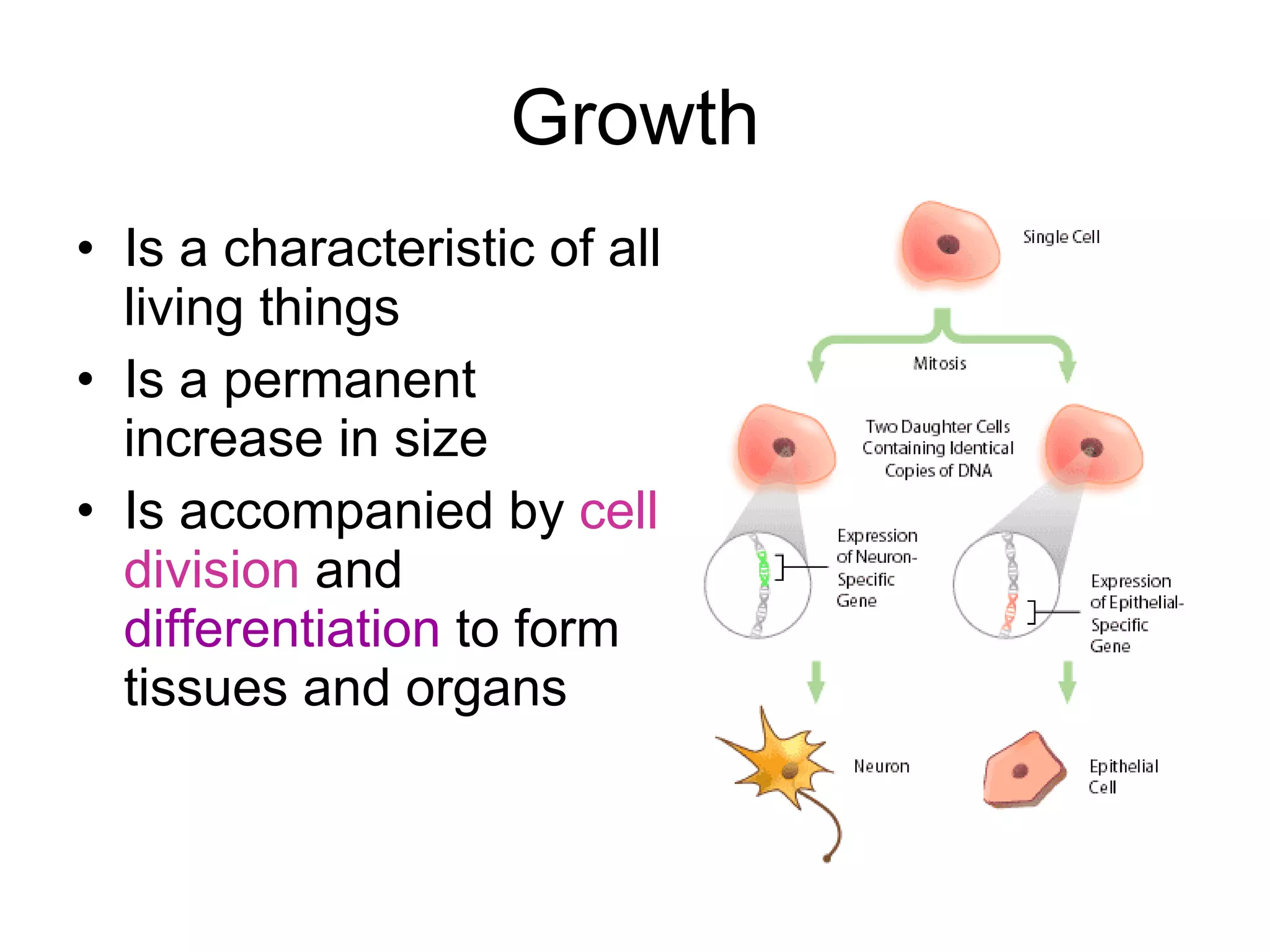
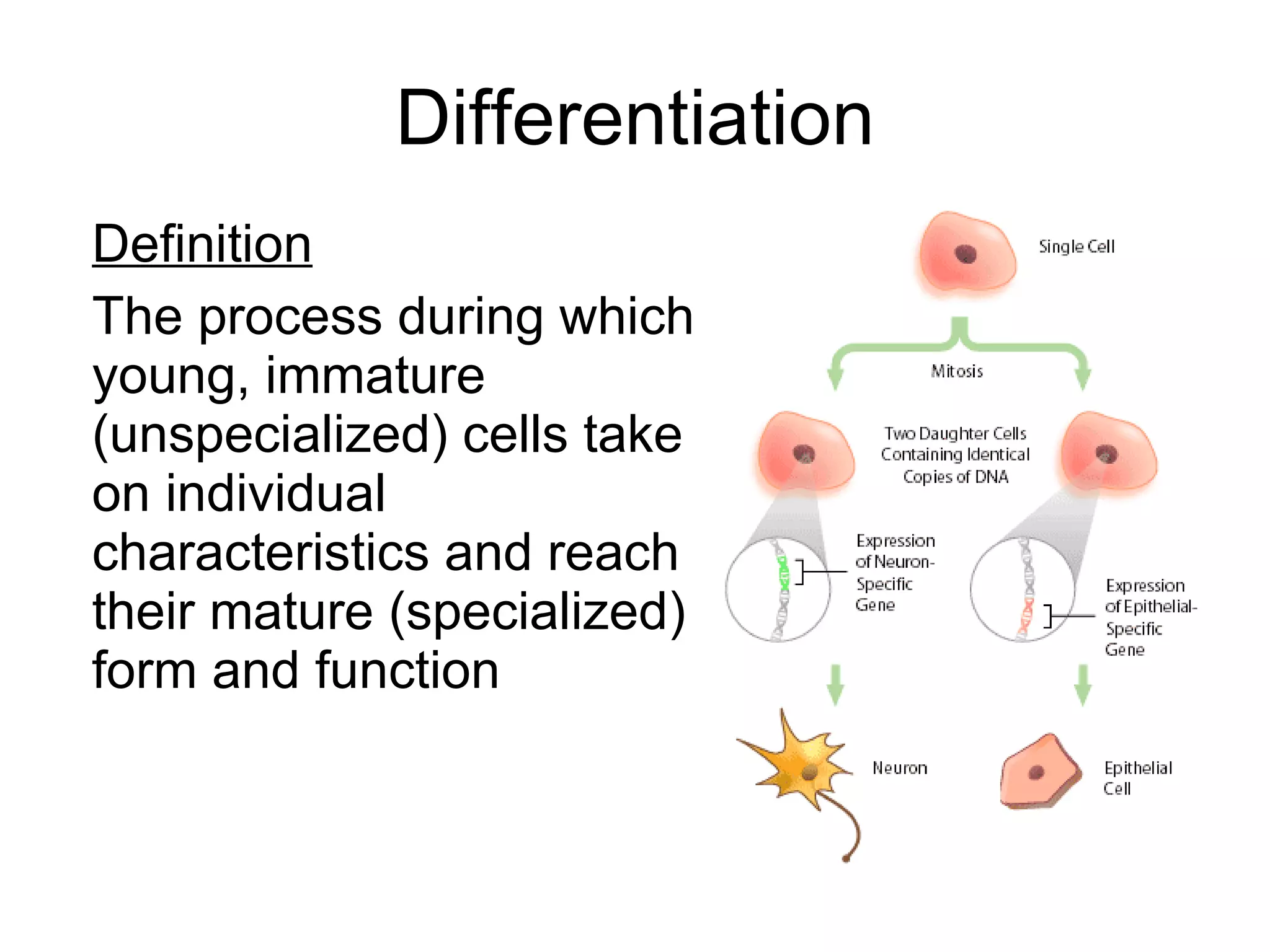
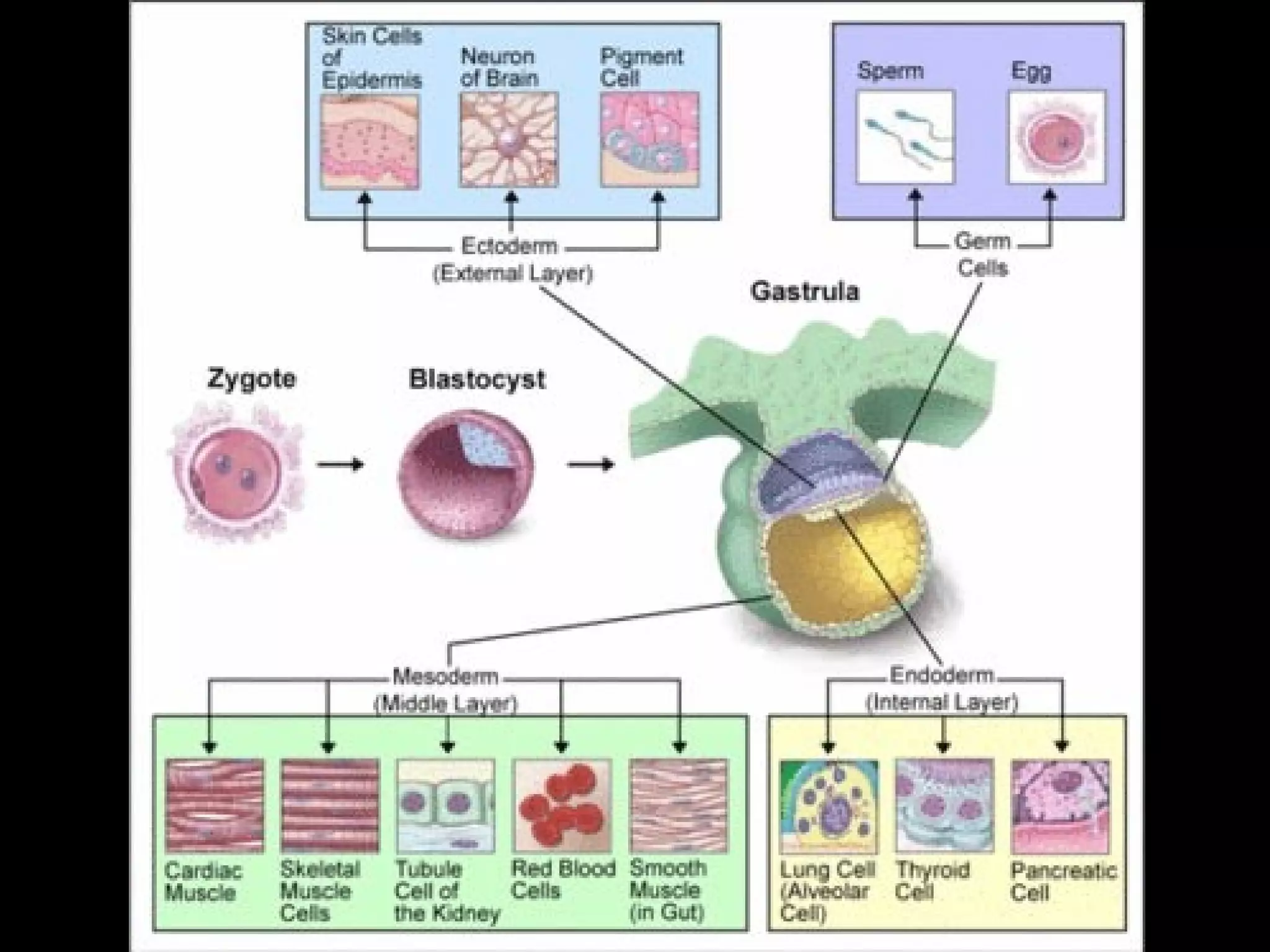

Cell division is important for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction. Mitosis produces genetically identical cells through carefully controlled replication. Meiosis results in haploid cells and leads to genetic variation important for sexual reproduction. The stages of mitosis and meiosis are identified through diagrams.







