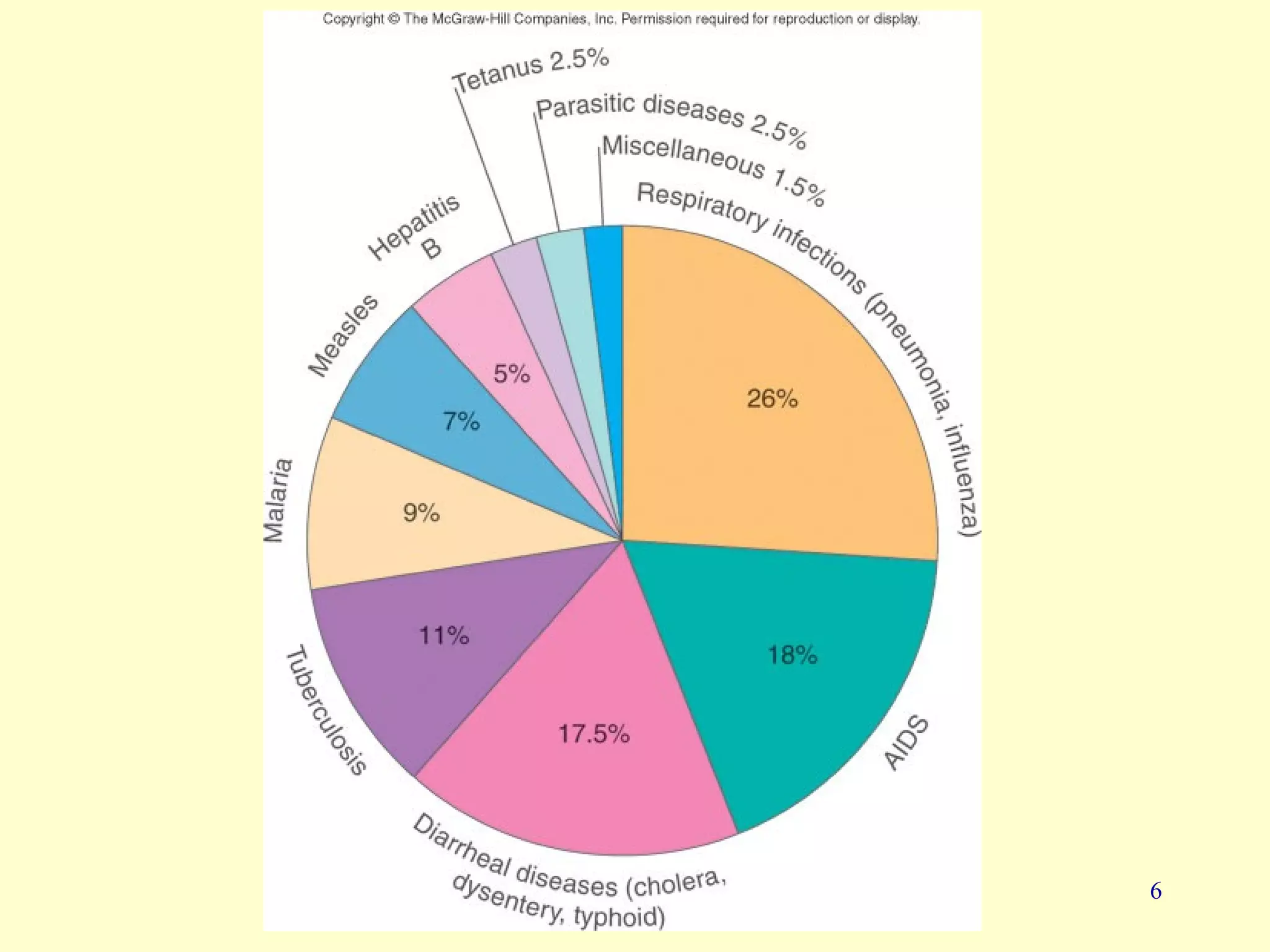
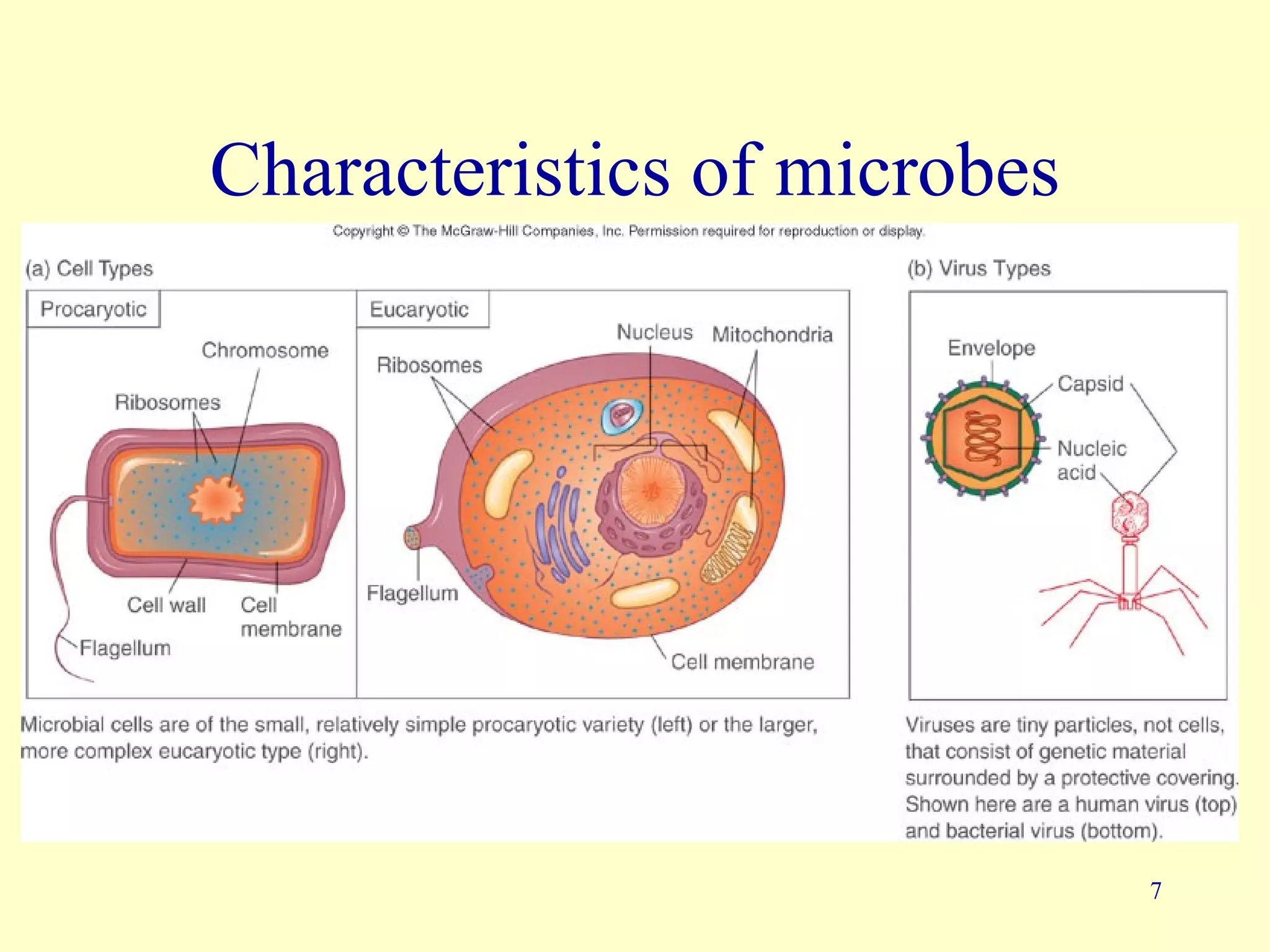
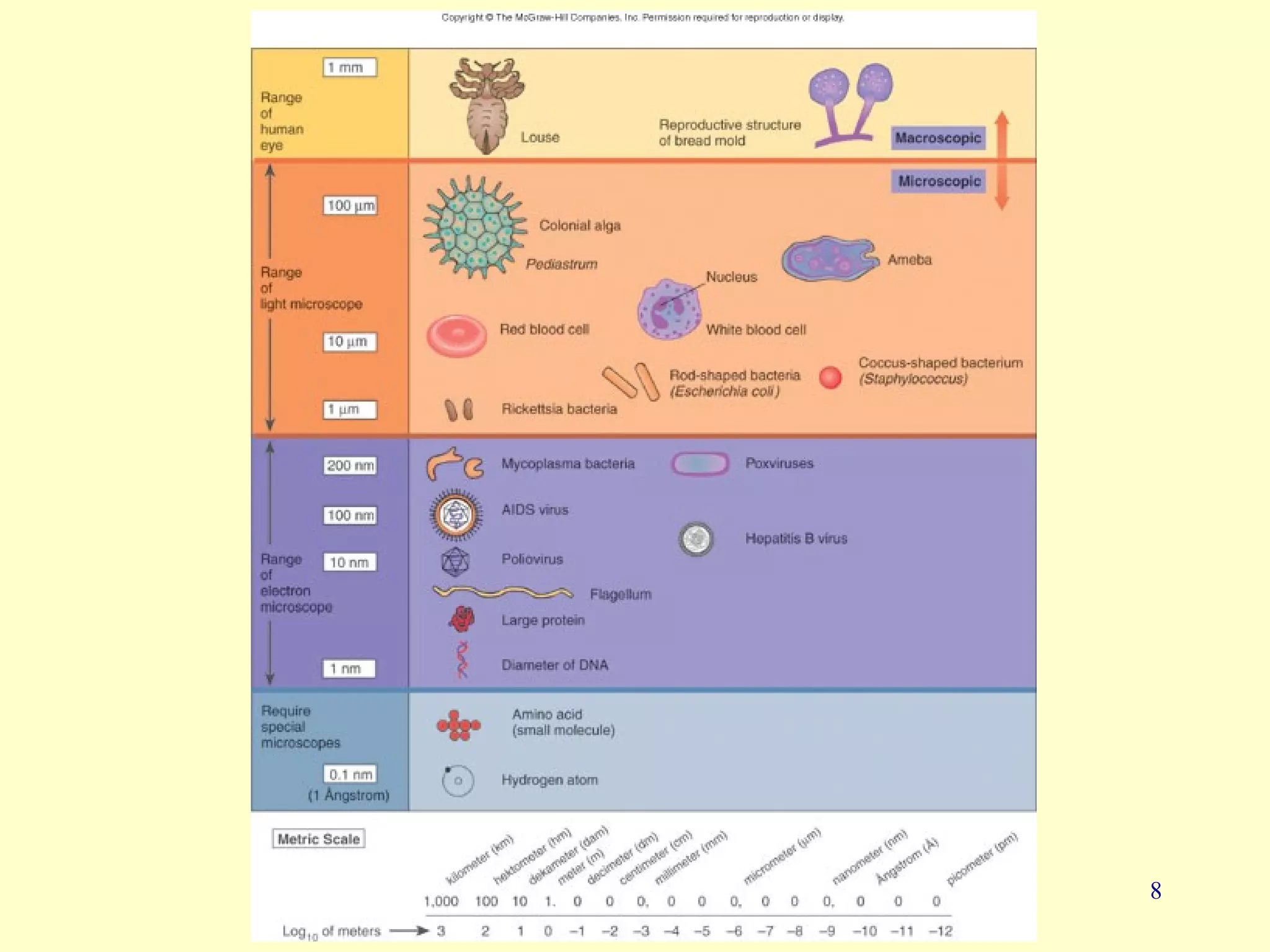
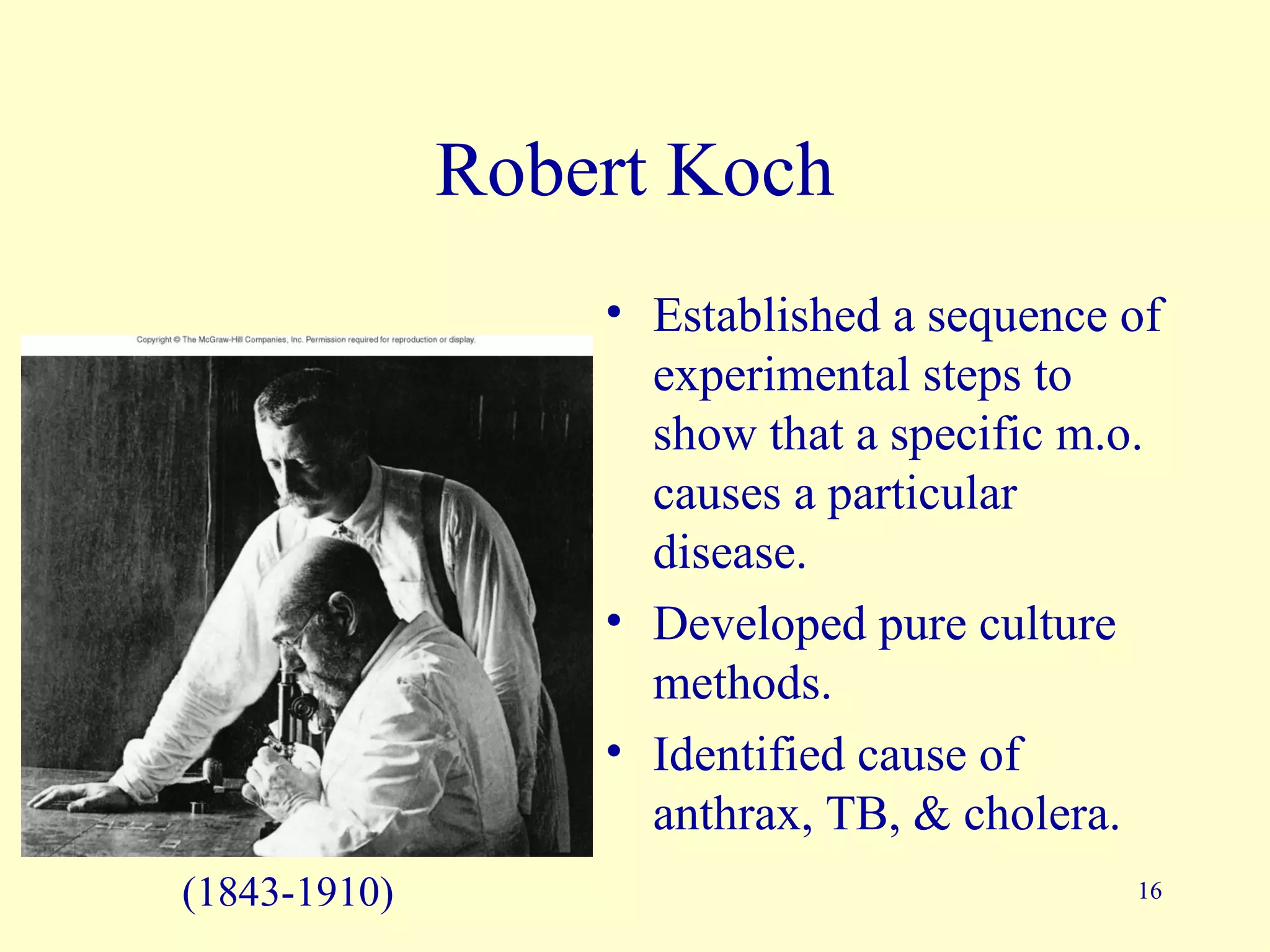
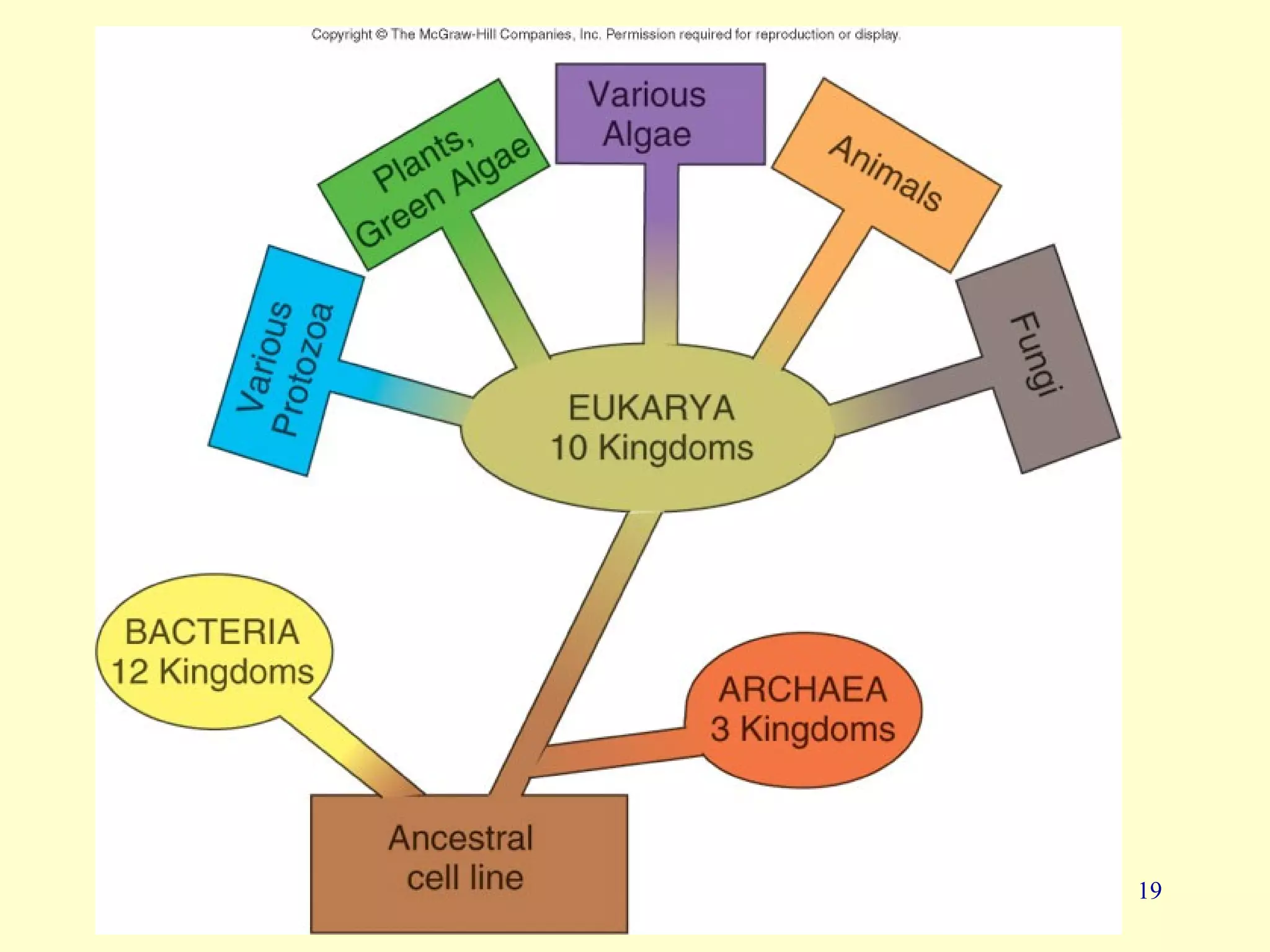
This document provides an overview of key concepts in microbiology. It discusses [1] the study of microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa, [2] the branches of microbiology including immunology and food/water microbiology, [3] the impact of microbes including their role in nutrient production and disease, and [4] pioneers like Antonie van Leeuwenhoek who first observed microbes under a microscope and Louis Pasteur who disproved spontaneous generation.