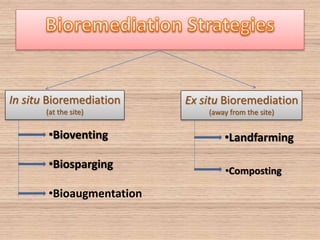
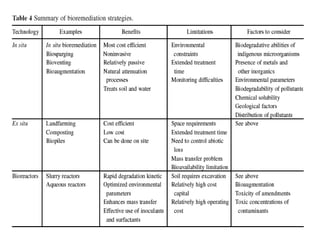
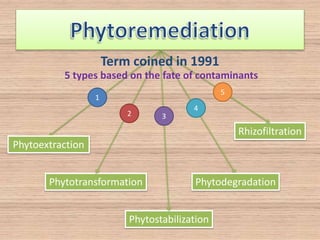
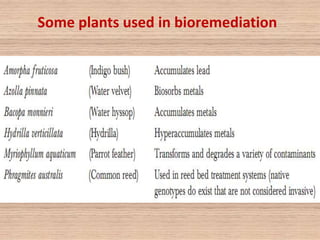
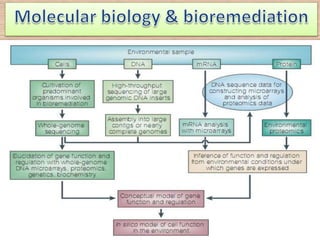
Bioremediation uses living organisms like bacteria and fungi to break down pollutants. There are two types - in situ remediation which treats pollutants on site, and ex situ which treats them off site. Phytoextraction uses plants to absorb contaminants from soil or water. Essential factors for effective microbial bioremediation include microbial populations, oxygen, water, nutrients, temperature, and pH. A case study describes using oil-eating bacteria to clean an oil spill in Mumbai. Bioremediation was also used to clean Railadevi Lake in Thane, India. Limitations include the long time needed and potential food chain contamination.