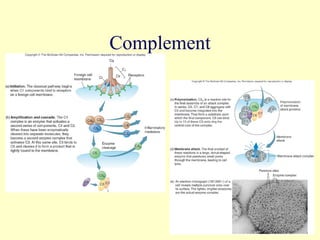
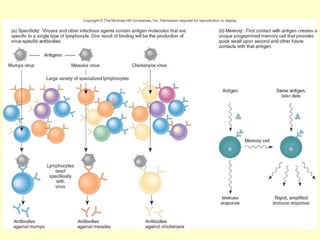
The document summarizes the host defenses against microbial pathogens. It describes the three lines of defense as: 1) physical and chemical barriers like skin and mucus, 2) innate immune responses involving phagocytes and inflammation, and 3) adaptive immune responses mediated by B and T lymphocytes and antibodies. Key aspects covered include the roles of leukocytes, lymph nodes, interferon, complement, and the specificity of adaptive immunity.