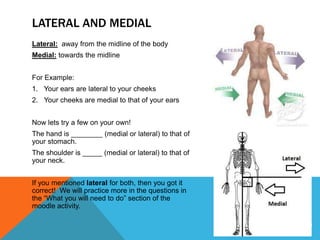
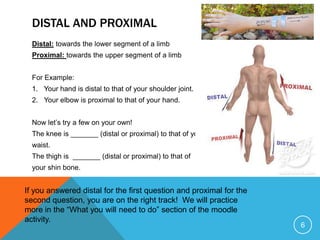
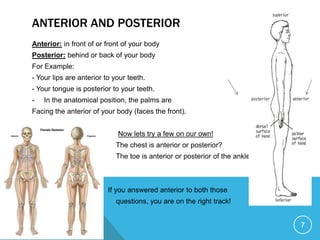
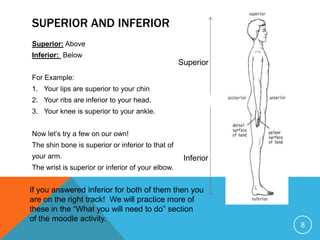
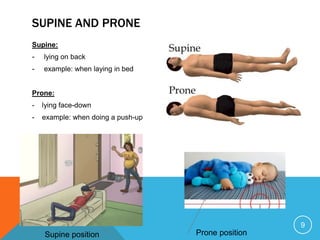
The document discusses establishing a common anatomical language to facilitate communication between doctors worldwide. It defines the anatomical position as standing erect with palms, feet, and head facing forward. Key directional terms are also introduced, including lateral/medial, distal/proximal, anterior/posterior, and superior/inferior. Understanding these universally accepted directional references is fundamental to anatomical descriptions.