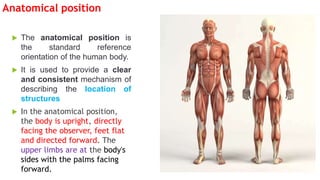
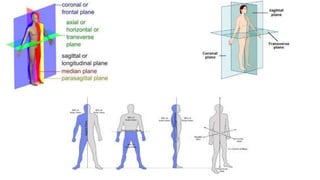
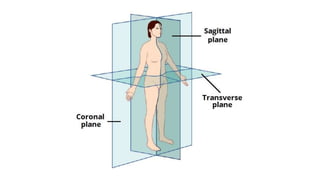
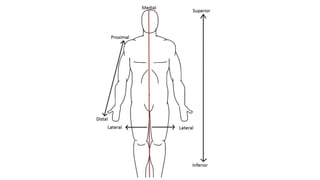
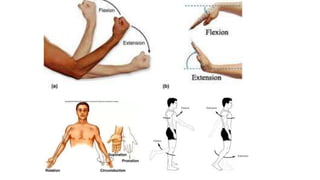
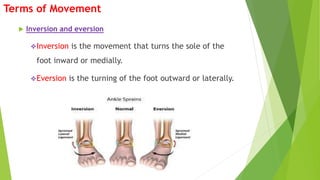
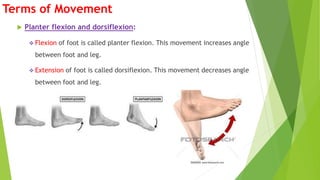
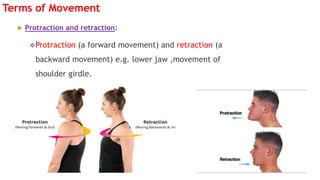
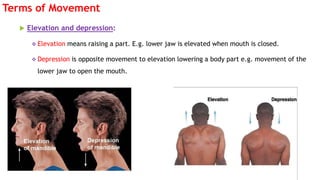
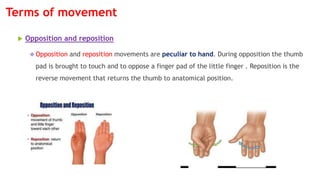
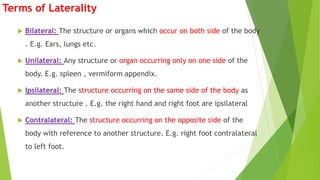
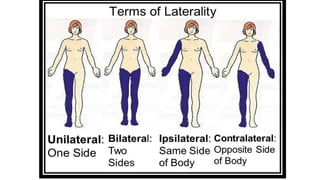
The document outlines the anatomical position, which serves as a standard reference for describing human body structures. It details various anatomical planes, terms of position, terms of movement, and concepts of laterality that are essential for understanding human anatomy. These elements provide a framework for accurately analyzing and communicating about the human body and its movements.