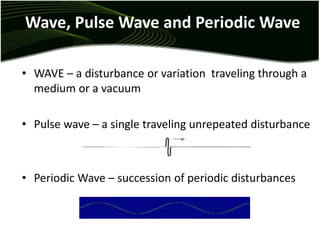
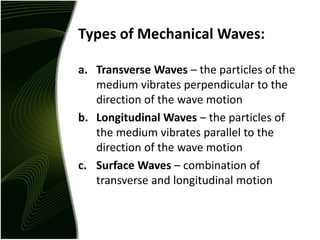
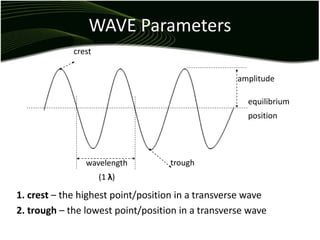
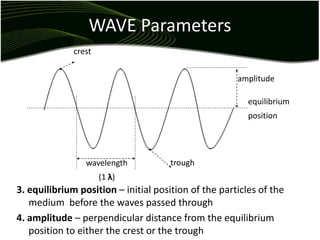
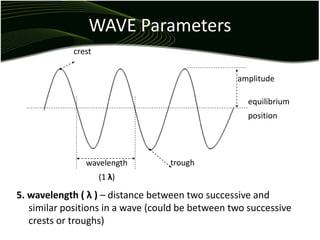
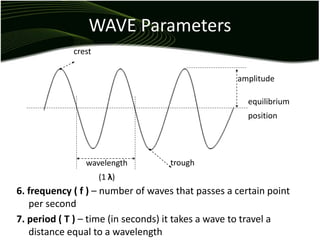
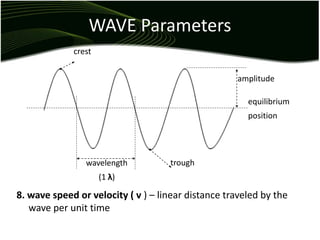
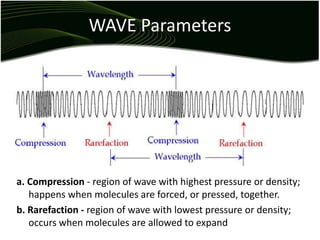
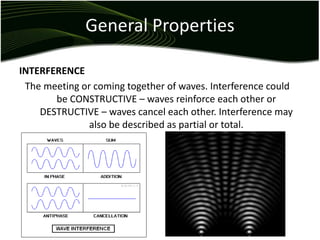
Waves are disturbances that transfer energy through a medium without transferring matter. There are two main types of waves: mechanical waves, which require a medium, and electromagnetic waves, which can travel through vacuum. Key wave parameters include amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed. Mechanical waves can be transverse, with oscillations perpendicular to the direction of travel, or longitudinal, with oscillations parallel to travel.