This document discusses measurement systems and units. It provides details on:
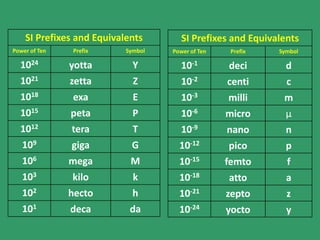
- The English and International (SI) systems of measurement, including their base units and prefixes. The English system uses arbitrary objects while SI uses multiples of ten.
- Conversions within and between the two systems. SI is easier for conversions while English uses arbitrary units like inches and pounds.
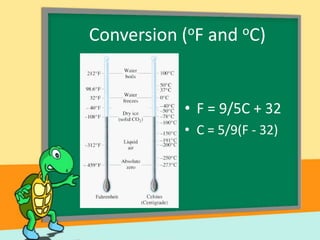
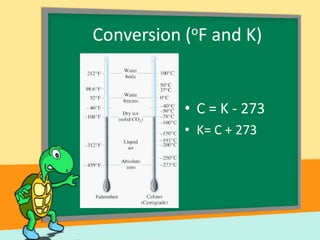
- Temperature scales including Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin. It provides the definitions and formulas for converting between the scales.
- Proper reporting of measurements, which requires providing both the measured quantity and the correct unit with the appropriate number of significant figures.