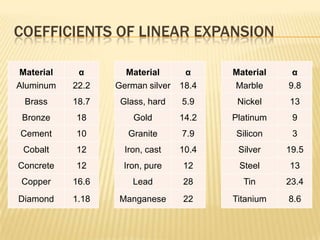
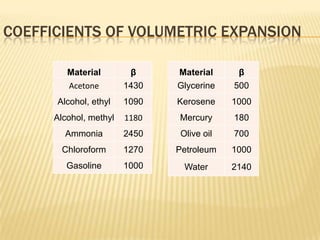
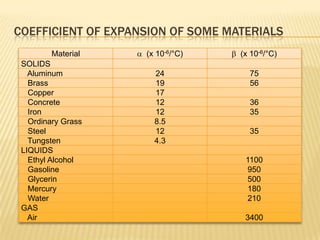
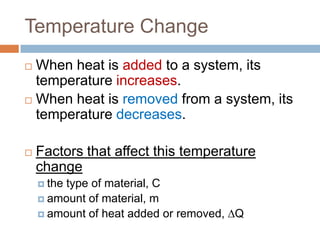
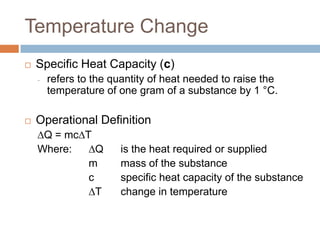
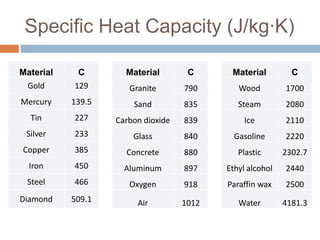
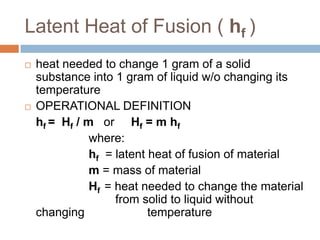
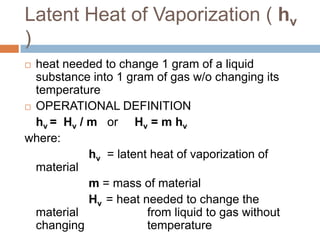
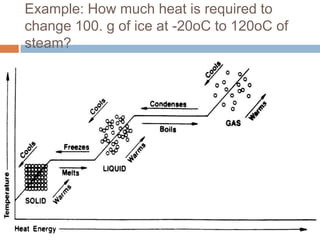
Thermal expansion, temperature change, and phase change are the three main effects of heat. Thermal expansion causes materials to expand when heated and contract when cooled. The amount of expansion depends on the original length, temperature change, and material's coefficient of linear or volumetric expansion. Temperature change occurs when heat is added or removed from an object, increasing or decreasing its temperature. This temperature change depends on the specific heat capacity of the material, its mass, and the amount of heat added or removed. Phase change involves heat being absorbed or released during changes between solid, liquid, and gas states without a change in temperature. This heat of fusion or vaporization allows materials to change phases.