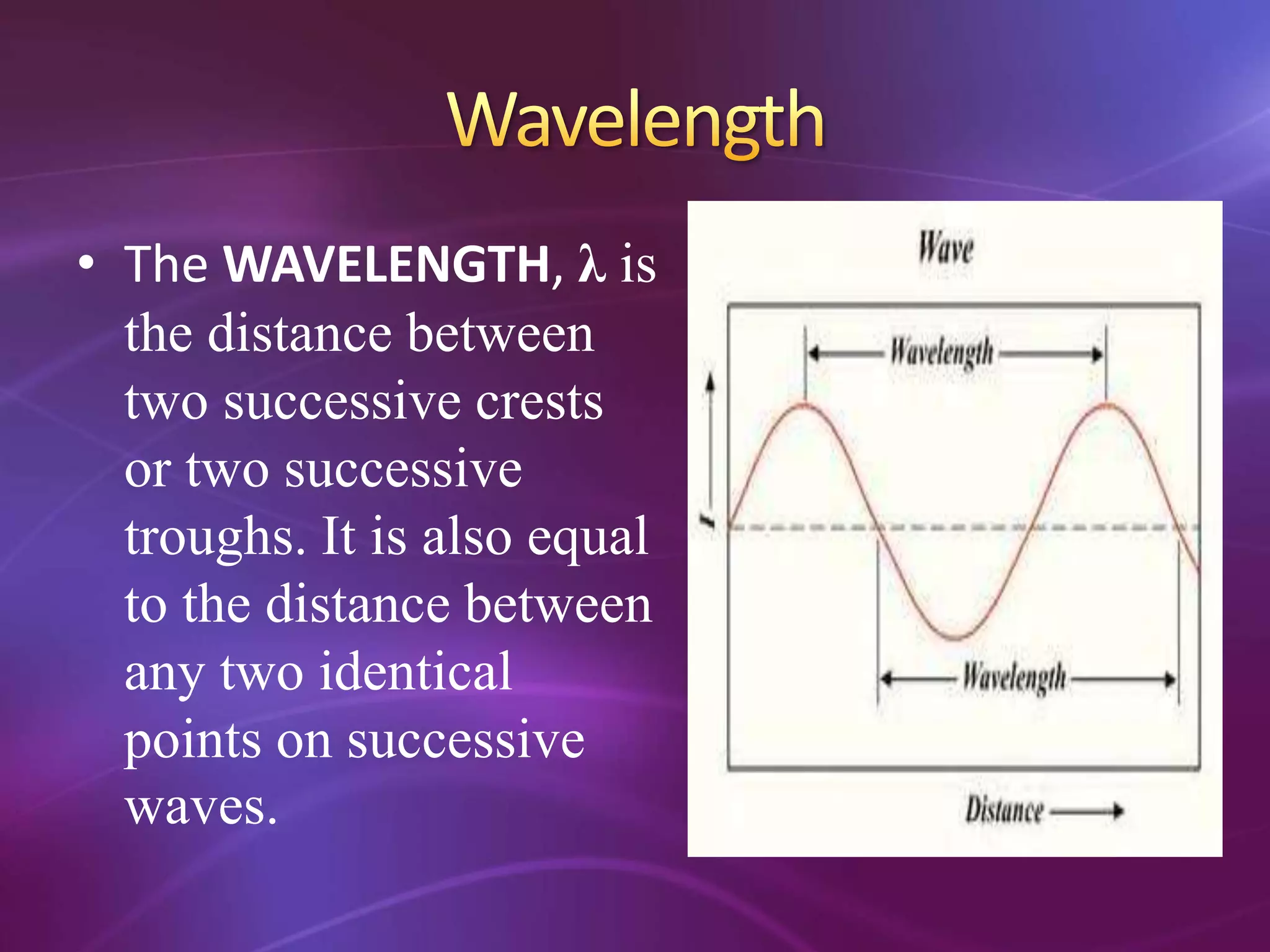
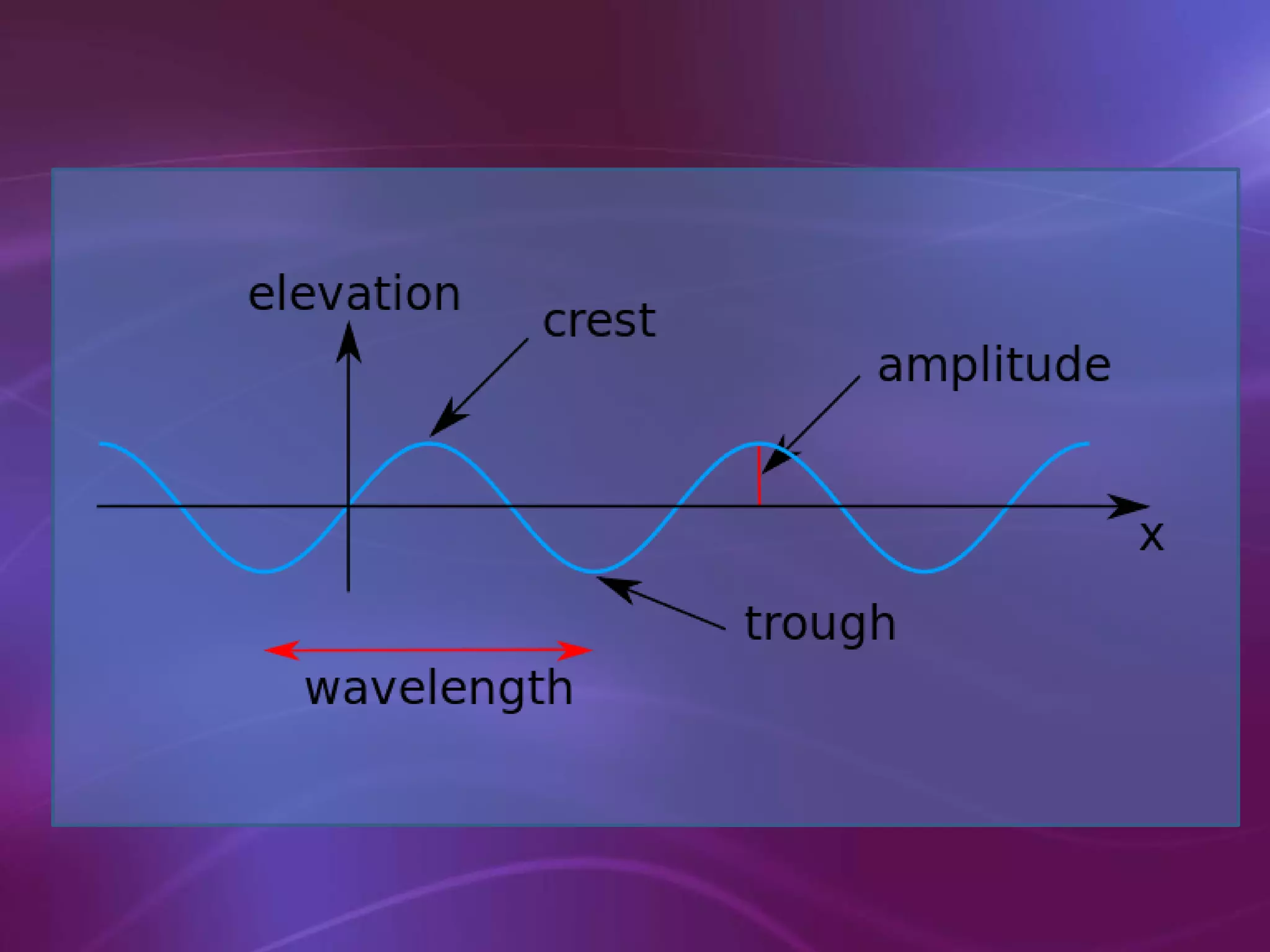
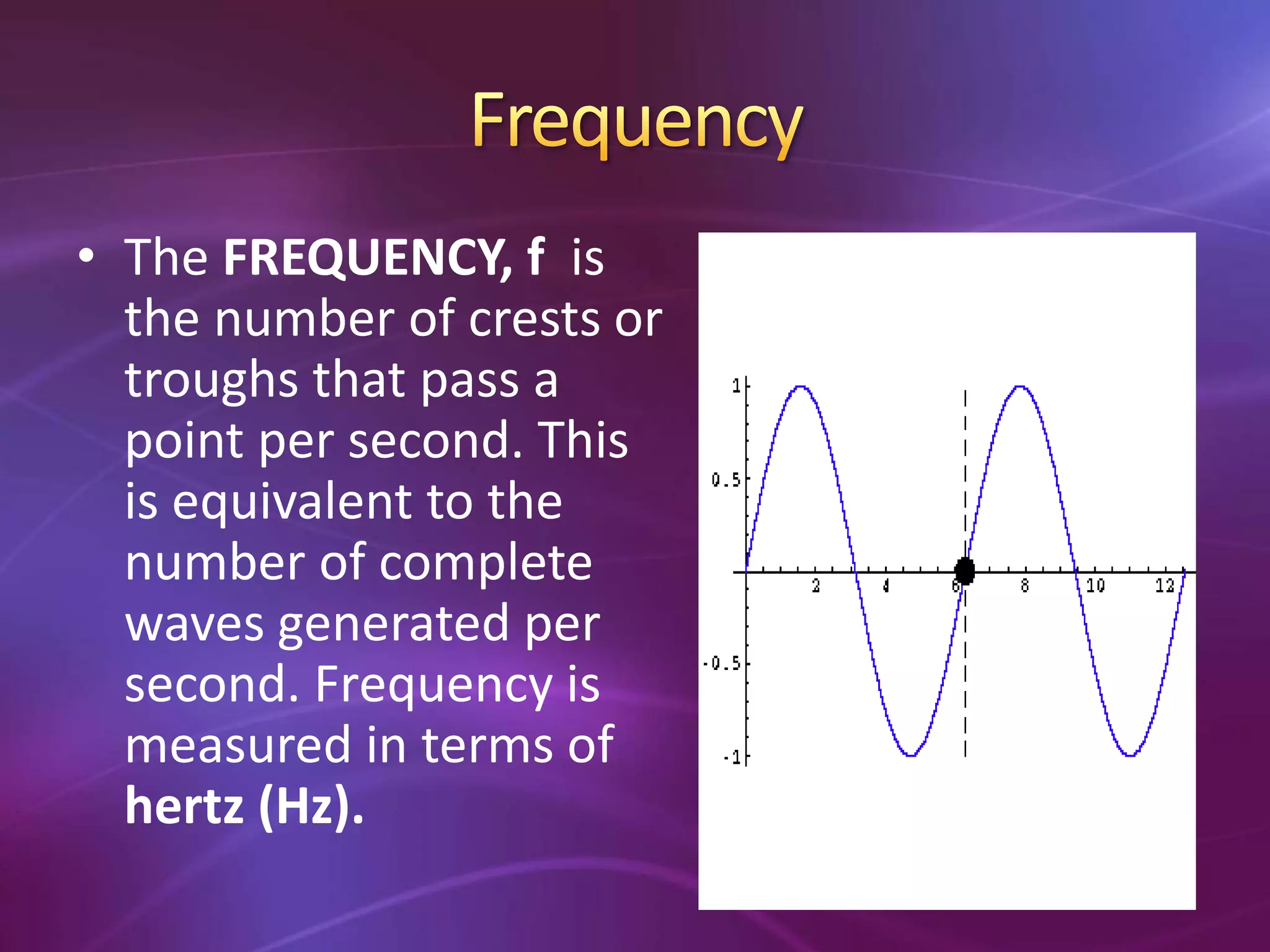
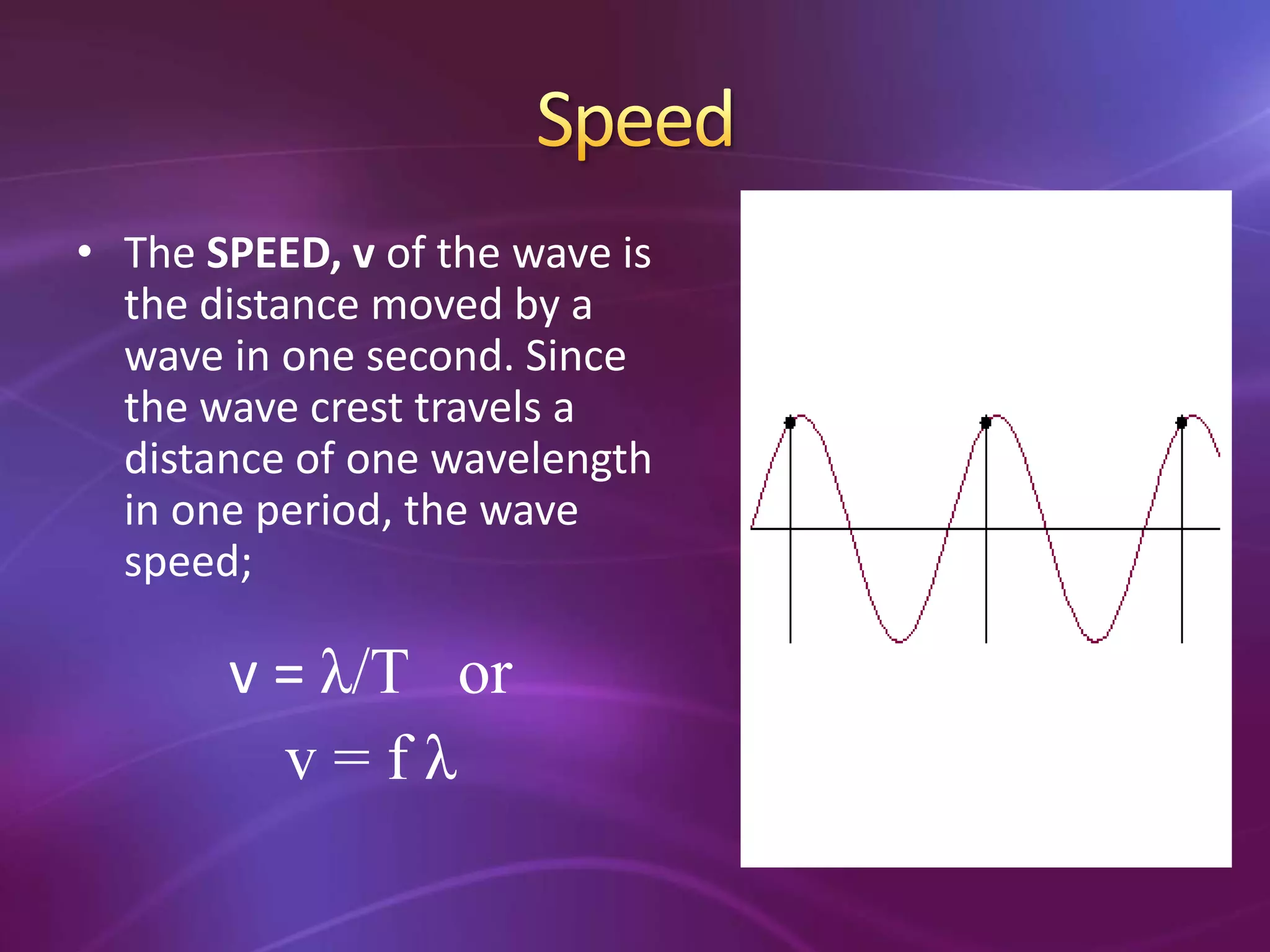
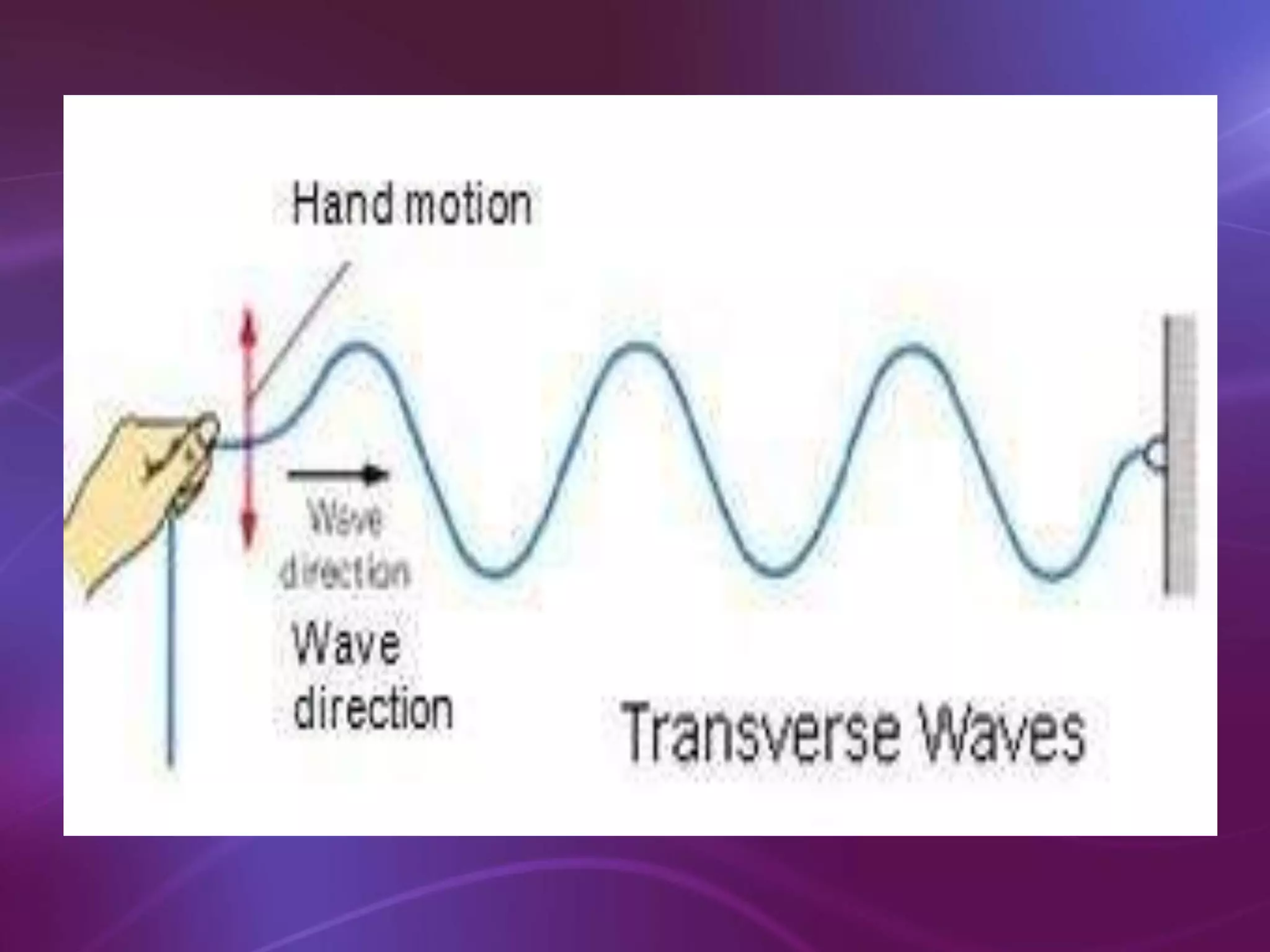
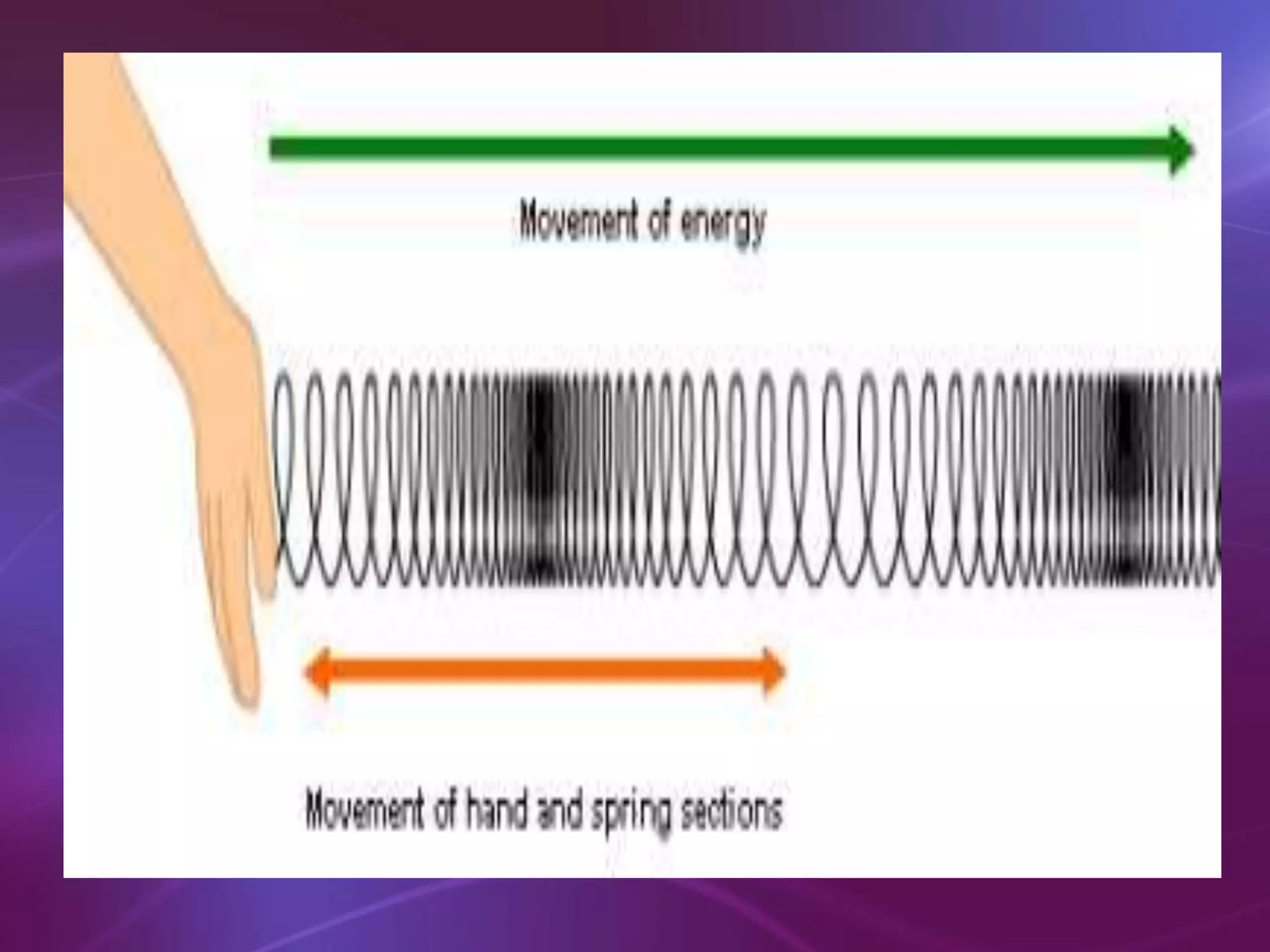
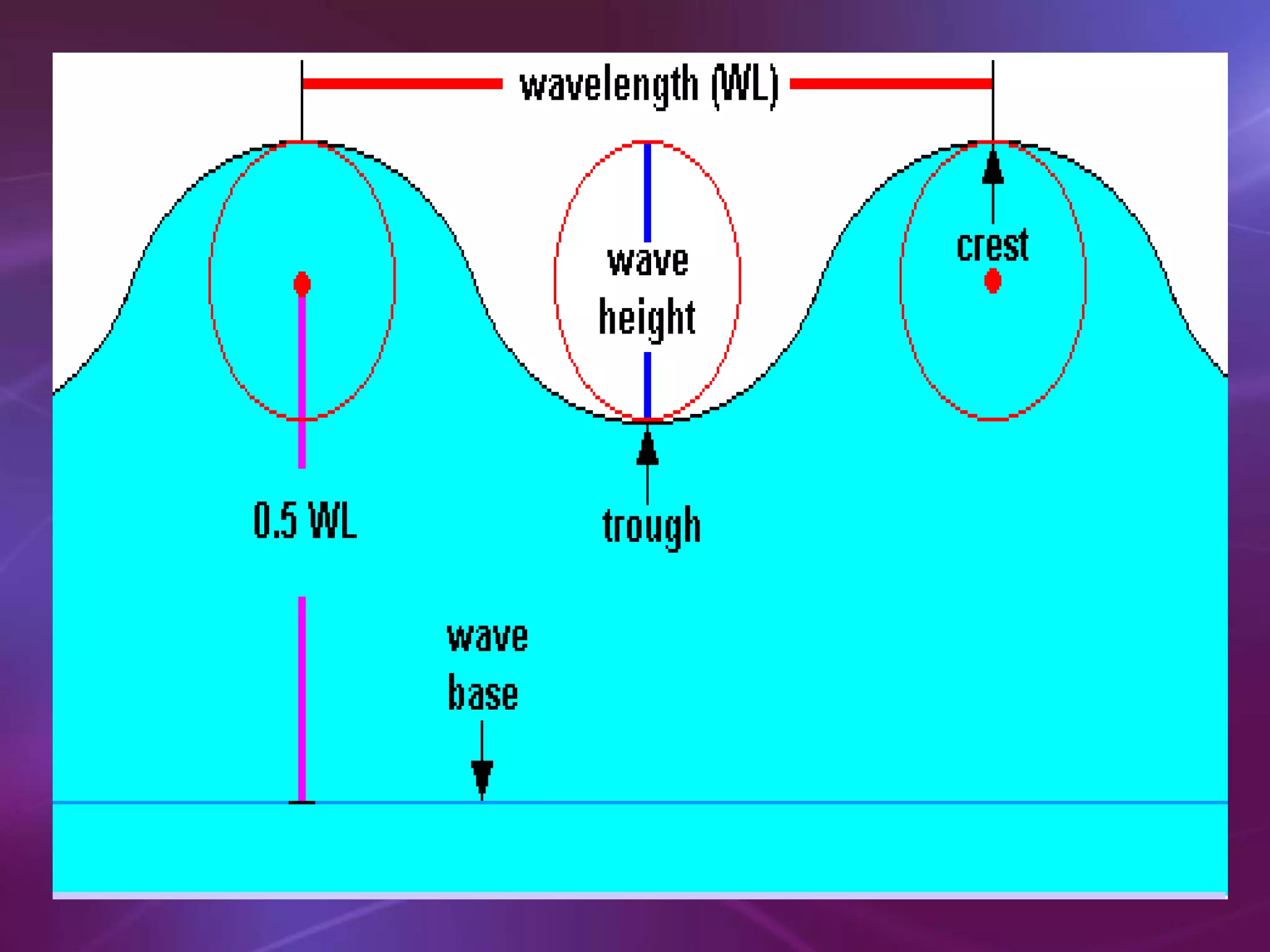
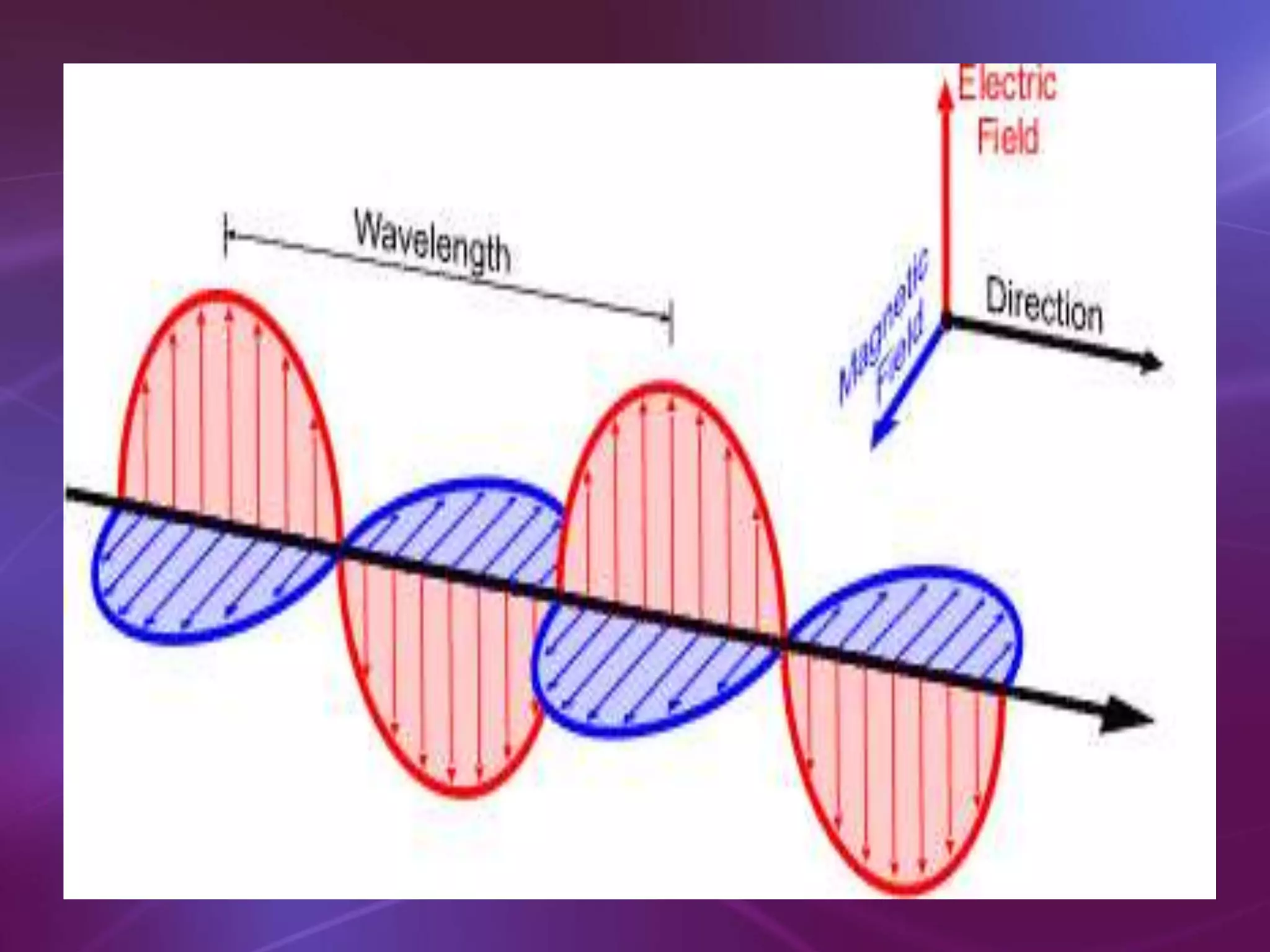
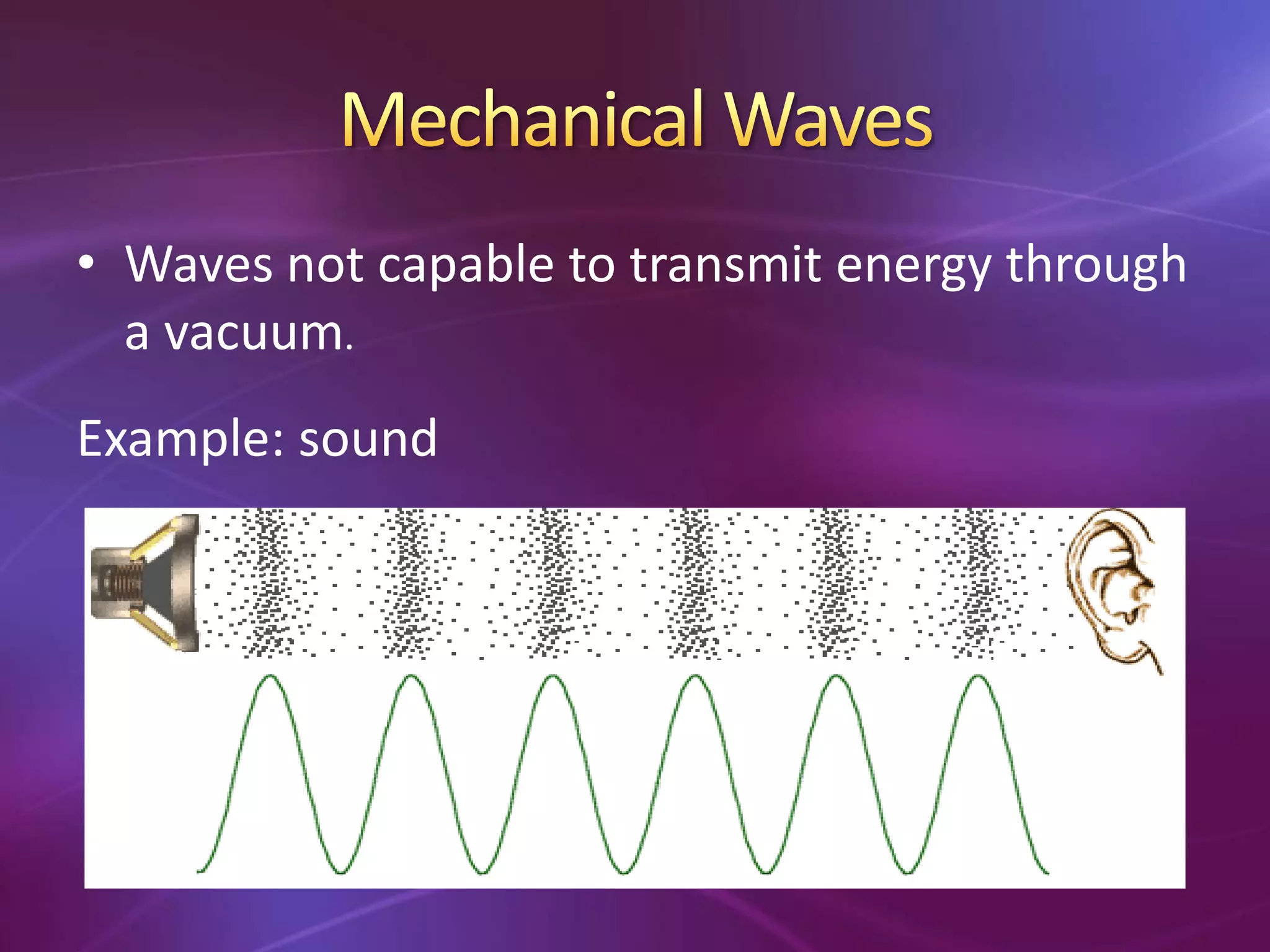
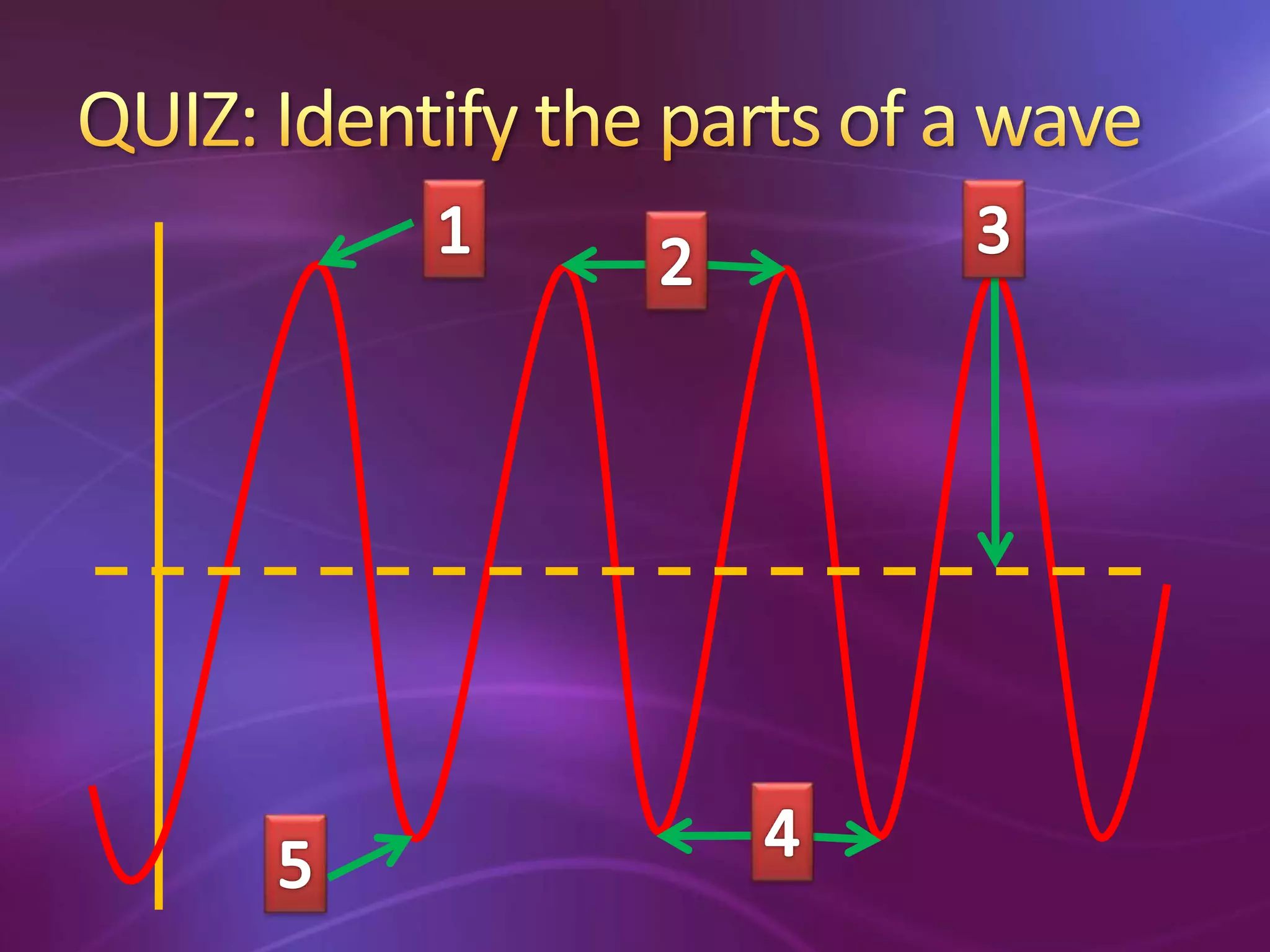
The document is a teacher's guide discussing various properties of waves, including definitions of wave motion, amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed. It explains different types of waves such as transverse, longitudinal, and surface waves, and their particle movement relative to wave motion. Additionally, it includes true or false statements and identification exercises related to wave concepts.