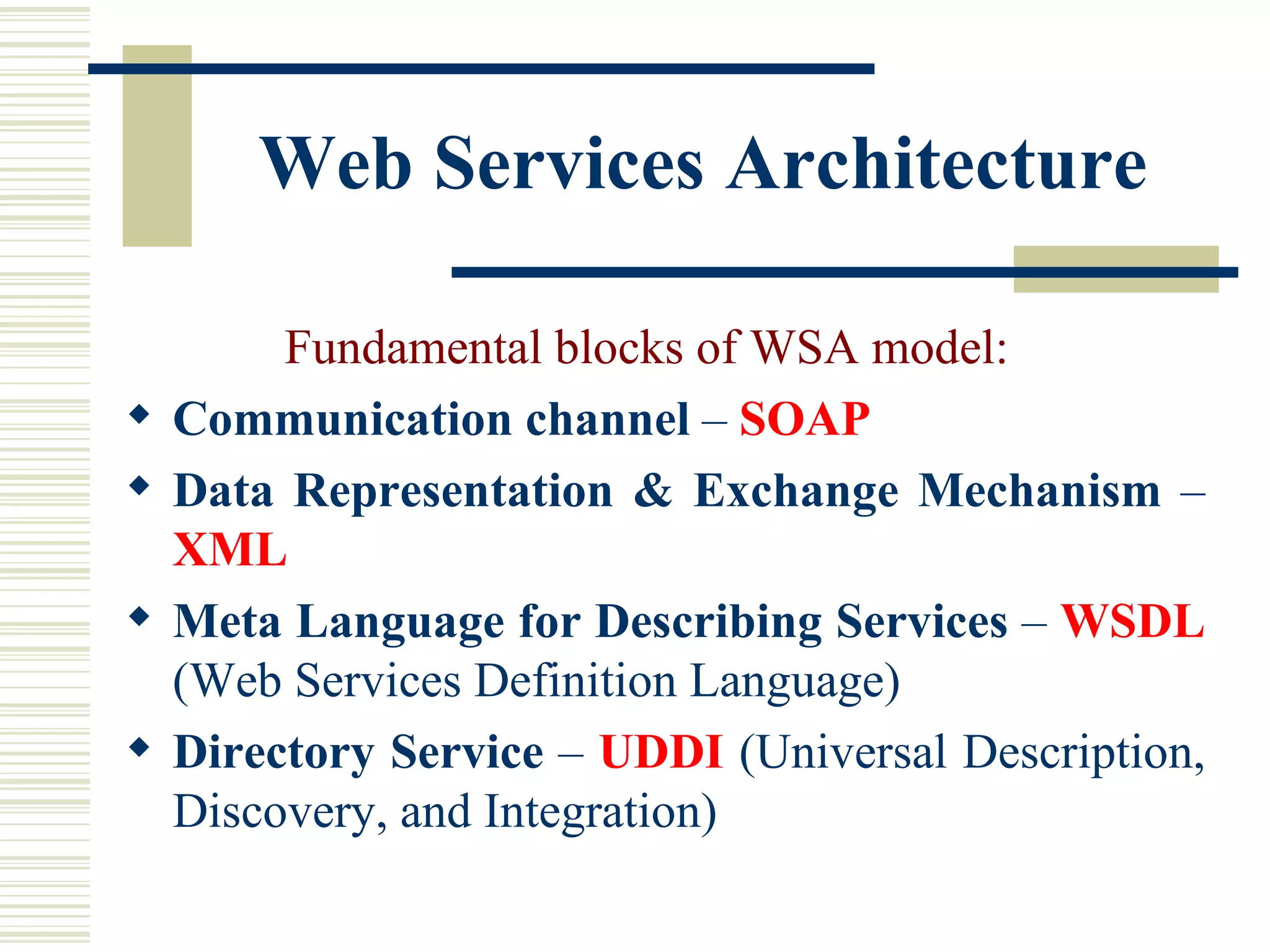
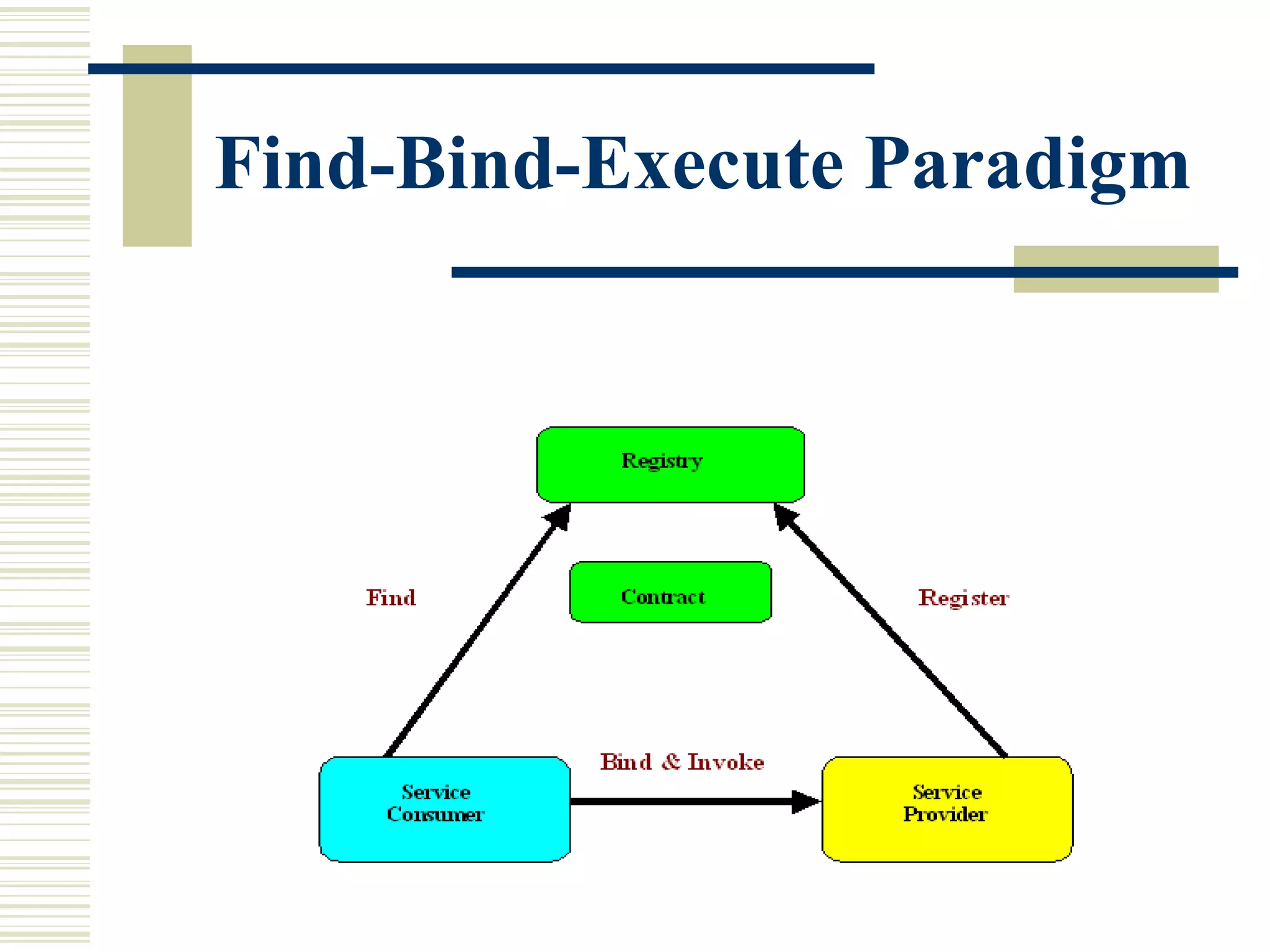
Web services allow applications to share data and capabilities across various operating systems, platforms, and devices using standard web technologies like HTTP, XML, and SOAP. A web service is a programmable application accessible via standard web protocols that is self-contained, self-describing, and loosely coupled. The web services architecture includes communication channels, XML for data representation and exchange, WSDL for describing services, and UDDI for service discovery. Web services offer advantages like platform independence, use of open standards, and easy incorporation into existing XML messaging solutions.